Jiuxin Cao
DyTopo: Dynamic Topology Routing for Multi-Agent Reasoning via Semantic Matching
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Multi-agent systems built from prompted large language models can improve multi-round reasoning, yet most existing pipelines rely on fixed, trajectory-wide communication patterns that are poorly matched to the stage-dependent needs of iterative problem solving. We introduce DyTopo, a manager-guided multi-agent framework that reconstructs a sparse directed communication graph at each round. Conditioned on the manager's round goal, each agent outputs lightweight natural-language query (need) and \key (offer) descriptors; DyTopo embeds these descriptors and performs semantic matching, routing private messages only along the induced edges. Across code generation and mathematical reasoning benchmarks and four LLM backbones, DyTopo consistently outperforms over the strongest baseline (avg. +6.2). Beyond accuracy, DyTopo yields an interpretable coordination trace via the evolving graphs, enabling qualitative inspection of how communication pathways reconfigure across rounds.
Evidence-Augmented Policy Optimization with Reward Co-Evolution for Long-Context Reasoning
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:While Reinforcement Learning (RL) has advanced LLM reasoning, applying it to long-context scenarios is hindered by sparsity of outcome rewards. This limitation fails to penalize ungrounded "lucky guesses," leaving the critical process of needle-in-a-haystack evidence retrieval largely unsupervised. To address this, we propose EAPO (Evidence-Augmented Policy Optimization). We first establish the Evidence-Augmented Reasoning paradigm, validating via Tree-Structured Evidence Sampling that precise evidence extraction is the decisive bottleneck for long-context reasoning. Guided by this insight, EAPO introduces a specialized RL algorithm where a reward model computes a Group-Relative Evidence Reward, providing dense process supervision to explicitly improve evidence quality. To sustain accurate supervision throughout training, we further incorporate an Adaptive Reward-Policy Co-Evolution mechanism. This mechanism iteratively refines the reward model using outcome-consistent rollouts, sharpening its discriminative capability to ensure precise process guidance. Comprehensive evaluations across eight benchmarks demonstrate that EAPO significantly enhances long-context reasoning performance compared to SOTA baselines.
D^3ETOR: Debate-Enhanced Pseudo Labeling and Frequency-Aware Progressive Debiasing for Weakly-Supervised Camouflaged Object Detection with Scribble Annotations
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Weakly-Supervised Camouflaged Object Detection (WSCOD) aims to locate and segment objects that are visually concealed within their surrounding scenes, relying solely on sparse supervision such as scribble annotations. Despite recent progress, existing WSCOD methods still lag far behind fully supervised ones due to two major limitations: (1) the pseudo masks generated by general-purpose segmentation models (e.g., SAM) and filtered via rules are often unreliable, as these models lack the task-specific semantic understanding required for effective pseudo labeling in COD; and (2) the neglect of inherent annotation bias in scribbles, which hinders the model from capturing the global structure of camouflaged objects. To overcome these challenges, we propose ${D}^{3}$ETOR, a two-stage WSCOD framework consisting of Debate-Enhanced Pseudo Labeling and Frequency-Aware Progressive Debiasing. In the first stage, we introduce an adaptive entropy-driven point sampling method and a multi-agent debate mechanism to enhance the capability of SAM for COD, improving the interpretability and precision of pseudo masks. In the second stage, we design FADeNet, which progressively fuses multi-level frequency-aware features to balance global semantic understanding with local detail modeling, while dynamically reweighting supervision strength across regions to alleviate scribble bias. By jointly exploiting the supervision signals from both the pseudo masks and scribble semantics, ${D}^{3}$ETOR significantly narrows the gap between weakly and fully supervised COD, achieving state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks.
${D}^{3}${ETOR}: ${D}$ebate-Enhanced Pseudo Labeling and Frequency-Aware Progressive ${D}$ebiasing for Weakly-Supervised Camouflaged Object ${D}$etection with Scribble Annotations
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Weakly-Supervised Camouflaged Object Detection (WSCOD) aims to locate and segment objects that are visually concealed within their surrounding scenes, relying solely on sparse supervision such as scribble annotations. Despite recent progress, existing WSCOD methods still lag far behind fully supervised ones due to two major limitations: (1) the pseudo masks generated by general-purpose segmentation models (e.g., SAM) and filtered via rules are often unreliable, as these models lack the task-specific semantic understanding required for effective pseudo labeling in COD; and (2) the neglect of inherent annotation bias in scribbles, which hinders the model from capturing the global structure of camouflaged objects. To overcome these challenges, we propose ${D}^{3}$ETOR, a two-stage WSCOD framework consisting of Debate-Enhanced Pseudo Labeling and Frequency-Aware Progressive Debiasing. In the first stage, we introduce an adaptive entropy-driven point sampling method and a multi-agent debate mechanism to enhance the capability of SAM for COD, improving the interpretability and precision of pseudo masks. In the second stage, we design FADeNet, which progressively fuses multi-level frequency-aware features to balance global semantic understanding with local detail modeling, while dynamically reweighting supervision strength across regions to alleviate scribble bias. By jointly exploiting the supervision signals from both the pseudo masks and scribble semantics, ${D}^{3}$ETOR significantly narrows the gap between weakly and fully supervised COD, achieving state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks.
MaskSearch: A Universal Pre-Training Framework to Enhance Agentic Search Capability
May 27, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Language Models (RALMs) represent a classic paradigm where models enhance generative capabilities using external knowledge retrieved via a specialized module. Recent advancements in Agent techniques enable Large Language Models (LLMs) to autonomously utilize tools for retrieval, planning, and reasoning. While existing training-based methods show promise, their agentic abilities are limited by inherent characteristics of the task-specific data used during training. To further enhance the universal search capability of agents, we propose a novel pre-training framework, MaskSearch. In the pre-training stage, we introduce the Retrieval Augmented Mask Prediction (RAMP) task, where the model learns to leverage search tools to fill masked spans on a large number of pre-training data, thus acquiring universal retrieval and reasoning capabilities for LLMs. After that, the model is trained on downstream tasks to achieve further improvement. We apply both Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) for training. For SFT, we combine agent-based and distillation-based methods to generate training data, starting with a multi-agent system consisting of a planner, rewriter, observer, and followed by a self-evolving teacher model. While for RL, we employ DAPO as the training framework and adopt a hybrid reward system consisting of answer rewards and format rewards. Additionally, we introduce a curriculum learning approach that allows the model to learn progressively from easier to more challenging instances based on the number of masked spans. We evaluate the effectiveness of our framework in the scenario of open-domain multi-hop question answering. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that MaskSearch significantly enhances the performance of LLM-based search agents on both in-domain and out-of-domain downstream tasks.
External Reliable Information-enhanced Multimodal Contrastive Learning for Fake News Detection
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:With the rapid development of the Internet, the information dissemination paradigm has changed and the efficiency has been improved greatly. While this also brings the quick spread of fake news and leads to negative impacts on cyberspace. Currently, the information presentation formats have evolved gradually, with the news formats shifting from texts to multimodal contents. As a result, detecting multimodal fake news has become one of the research hotspots. However, multimodal fake news detection research field still faces two main challenges: the inability to fully and effectively utilize multimodal information for detection, and the low credibility or static nature of the introduced external information, which limits dynamic updates. To bridge the gaps, we propose ERIC-FND, an external reliable information-enhanced multimodal contrastive learning framework for fake news detection. ERIC-FND strengthens the representation of news contents by entity-enriched external information enhancement method. It also enriches the multimodal news information via multimodal semantic interaction method where the multimodal constrative learning is employed to make different modality representations learn from each other. Moreover, an adaptive fusion method is taken to integrate the news representations from different dimensions for the eventual classification. Experiments are done on two commonly used datasets in different languages, X (Twitter) and Weibo. Experiment results demonstrate that our proposed model ERIC-FND outperforms existing state-of-the-art fake news detection methods under the same settings.
Positive Text Reframing under Multi-strategy Optimization
Jul 27, 2024Abstract:Differing from sentiment transfer, positive reframing seeks to substitute negative perspectives with positive expressions while preserving the original meaning. With the emergence of pre-trained language models (PLMs), it is possible to achieve acceptable results by fine-tuning PLMs. Nevertheless, generating fluent, diverse and task-constrained reframing text remains a significant challenge. To tackle this issue, a \textbf{m}ulti-\textbf{s}trategy \textbf{o}ptimization \textbf{f}ramework (MSOF) is proposed in this paper. Starting from the objective of positive reframing, we first design positive sentiment reward and content preservation reward to encourage the model to transform the negative expressions of the original text while ensuring the integrity and consistency of the semantics. Then, different decoding optimization approaches are introduced to improve the quality of text generation. Finally, based on the modeling formula of positive reframing, we propose a multi-dimensional re-ranking method that further selects candidate sentences from three dimensions: strategy consistency, text similarity and fluency. Extensive experiments on two Seq2Seq PLMs, BART and T5, demonstrate our framework achieves significant improvements on unconstrained and controlled positive reframing tasks.
Overview of AI-Debater 2023: The Challenges of Argument Generation Tasks
Jul 24, 2024



Abstract:In this paper we present the results of the AI-Debater 2023 Challenge held by the Chinese Conference on Affect Computing (CCAC 2023), and introduce the related datasets. We organize two tracks to handle the argumentative generation tasks in different scenarios, namely, Counter-Argument Generation (Track 1) and Claim-based Argument Generation (Track 2). Each track is equipped with its distinct dataset and baseline model respectively. In total, 32 competing teams register for the challenge, from which we received 11 successful submissions. In this paper, we will present the results of the challenge and a summary of the systems, highlighting commonalities and innovations among participating systems. Datasets and baseline models of the AI-Debater 2023 Challenge have been already released and can be accessed through the official website of the challenge.
Context-Enhanced Video Moment Retrieval with Large Language Models
May 21, 2024Abstract:Current methods for Video Moment Retrieval (VMR) struggle to align complex situations involving specific environmental details, character descriptions, and action narratives. To tackle this issue, we propose a Large Language Model-guided Moment Retrieval (LMR) approach that employs the extensive knowledge of Large Language Models (LLMs) to improve video context representation as well as cross-modal alignment, facilitating accurate localization of target moments. Specifically, LMR introduces a context enhancement technique with LLMs to generate crucial target-related context semantics. These semantics are integrated with visual features for producing discriminative video representations. Finally, a language-conditioned transformer is designed to decode free-form language queries, on the fly, using aligned video representations for moment retrieval. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LMR achieves state-of-the-art results, outperforming the nearest competitor by up to 3.28\% and 4.06\% on the challenging QVHighlights and Charades-STA benchmarks, respectively. More importantly, the performance gains are significantly higher for localization of complex queries.
Community Detection for Heterogeneous Multiple Social Networks
May 07, 2024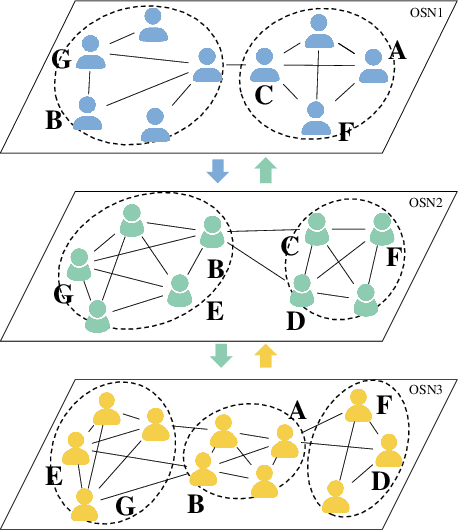
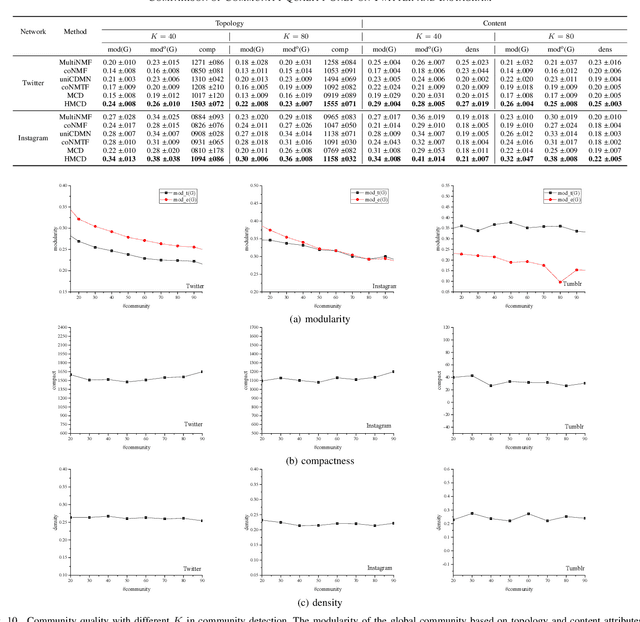
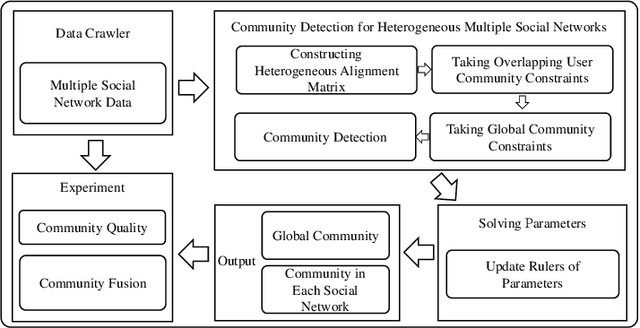
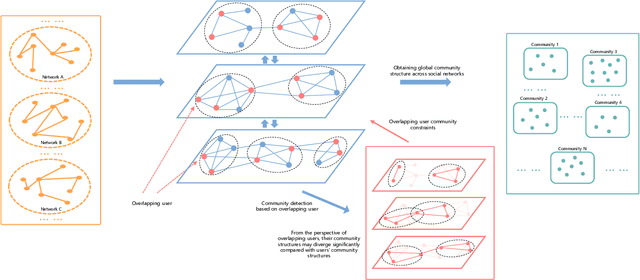
Abstract:The community plays a crucial role in understanding user behavior and network characteristics in social networks. Some users can use multiple social networks at once for a variety of objectives. These users are called overlapping users who bridge different social networks. Detecting communities across multiple social networks is vital for interaction mining, information diffusion, and behavior migration analysis among networks. This paper presents a community detection method based on nonnegative matrix tri-factorization for multiple heterogeneous social networks, which formulates a common consensus matrix to represent the global fused community. Specifically, the proposed method involves creating adjacency matrices based on network structure and content similarity, followed by alignment matrices which distinguish overlapping users in different social networks. With the generated alignment matrices, the method could enhance the fusion degree of the global community by detecting overlapping user communities across networks. The effectiveness of the proposed method is evaluated with new metrics on Twitter, Instagram, and Tumblr datasets. The results of the experiments demonstrate its superior performance in terms of community quality and community fusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge