Jinjing Zhou
DGI: Easy and Efficient Inference for GNNs
Nov 28, 2022Abstract:While many systems have been developed to train Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), efficient model inference and evaluation remain to be addressed. For instance, using the widely adopted node-wise approach, model evaluation can account for up to 94% of the time in the end-to-end training process due to neighbor explosion, which means that a node accesses its multi-hop neighbors. On the other hand, layer-wise inference avoids the neighbor explosion problem by conducting inference layer by layer such that the nodes only need their one-hop neighbors in each layer. However, implementing layer-wise inference requires substantial engineering efforts because users need to manually decompose a GNN model into layers for computation and split workload into batches to fit into device memory. In this paper, we develop Deep Graph Inference (DGI) -- a system for easy and efficient GNN model inference, which automatically translates the training code of a GNN model for layer-wise execution. DGI is general for various GNN models and different kinds of inference requests, and supports out-of-core execution on large graphs that cannot fit in CPU memory. Experimental results show that DGI consistently outperforms layer-wise inference across different datasets and hardware settings, and the speedup can be over 1,000x.
DGL-LifeSci: An Open-Source Toolkit for Deep Learning on Graphs in Life Science
Jun 27, 2021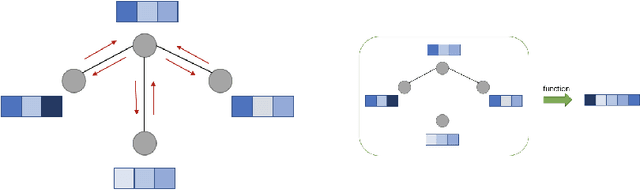
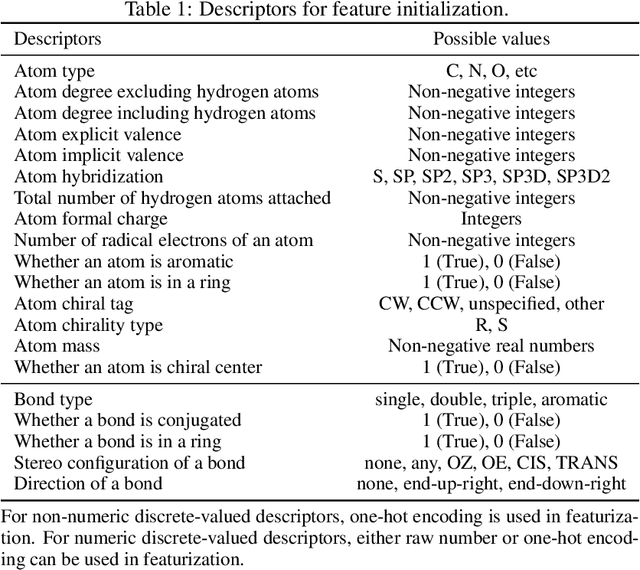
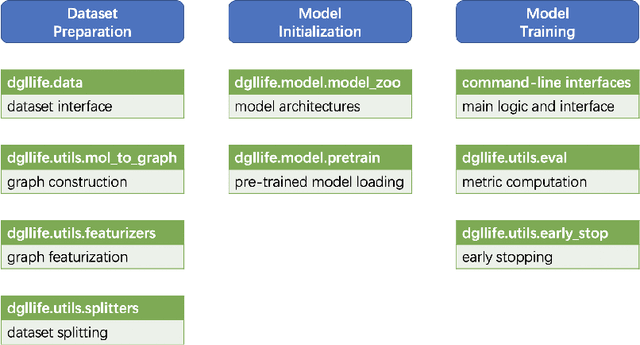

Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) constitute a class of deep learning methods for graph data. They have wide applications in chemistry and biology, such as molecular property prediction, reaction prediction and drug-target interaction prediction. Despite the interest, GNN-based modeling is challenging as it requires graph data pre-processing and modeling in addition to programming and deep learning. Here we present DGL-LifeSci, an open-source package for deep learning on graphs in life science. DGL-LifeSci is a python toolkit based on RDKit, PyTorch and Deep Graph Library (DGL). DGL-LifeSci allows GNN-based modeling on custom datasets for molecular property prediction, reaction prediction and molecule generation. With its command-line interfaces, users can perform modeling without any background in programming and deep learning. We test the command-line interfaces using standard benchmarks MoleculeNet, USPTO, and ZINC. Compared with previous implementations, DGL-LifeSci achieves a speed up by up to 6x. For modeling flexibility, DGL-LifeSci provides well-optimized modules for various stages of the modeling pipeline. In addition, DGL-LifeSci provides pre-trained models for reproducing the test experiment results and applying models without training. The code is distributed under an Apache-2.0 License and is freely accessible at https://github.com/awslabs/dgl-lifesci.
Graph Neural Networks Inspired by Classical Iterative Algorithms
Mar 10, 2021



Abstract:Despite the recent success of graph neural networks (GNN), common architectures often exhibit significant limitations, including sensitivity to oversmoothing, long-range dependencies, and spurious edges, e.g., as can occur as a result of graph heterophily or adversarial attacks. To at least partially address these issues within a simple transparent framework, we consider a new family of GNN layers designed to mimic and integrate the update rules of two classical iterative algorithms, namely, proximal gradient descent and iterative reweighted least squares (IRLS). The former defines an extensible base GNN architecture that is immune to oversmoothing while nonetheless capturing long-range dependencies by allowing arbitrary propagation steps. In contrast, the latter produces a novel attention mechanism that is explicitly anchored to an underlying end-toend energy function, contributing stability with respect to edge uncertainty. When combined we obtain an extremely simple yet robust model that we evaluate across disparate scenarios including standardized benchmarks, adversarially-perturbated graphs, graphs with heterophily, and graphs involving long-range dependencies. In doing so, we compare against SOTA GNN approaches that have been explicitly designed for the respective task, achieving competitive or superior node classification accuracy.
DistDGL: Distributed Graph Neural Network Training for Billion-Scale Graphs
Oct 16, 2020



Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNN) have shown great success in learning from graph-structured data. They are widely used in various applications, such as recommendation, fraud detection, and search. In these domains, the graphs are typically large, containing hundreds of millions of nodes and several billions of edges. To tackle this challenge, we develop DistDGL, a system for training GNNs in a mini-batch fashion on a cluster of machines. DistDGL is based on the Deep Graph Library (DGL), a popular GNN development framework. DistDGL distributes the graph and its associated data (initial features and embeddings) across the machines and uses this distribution to derive a computational decomposition by following an owner-compute rule. DistDGL follows a synchronous training approach and allows ego-networks forming the mini-batches to include non-local nodes. To minimize the overheads associated with distributed computations, DistDGL uses a high-quality and light-weight min-cut graph partitioning algorithm along with multiple balancing constraints. This allows it to reduce communication overheads and statically balance the computations. It further reduces the communication by replicating halo nodes and by using sparse embedding updates. The combination of these design choices allows DistDGL to train high-quality models while achieving high parallel efficiency and memory scalability. We demonstrate our optimizations on both inductive and transductive GNN models. Our results show that DistDGL achieves linear speedup without compromising model accuracy and requires only 13 seconds to complete a training epoch for a graph with 100 million nodes and 3 billion edges on a cluster with 16 machines.
Deep Graph Library: Towards Efficient and Scalable Deep Learning on Graphs
Sep 03, 2019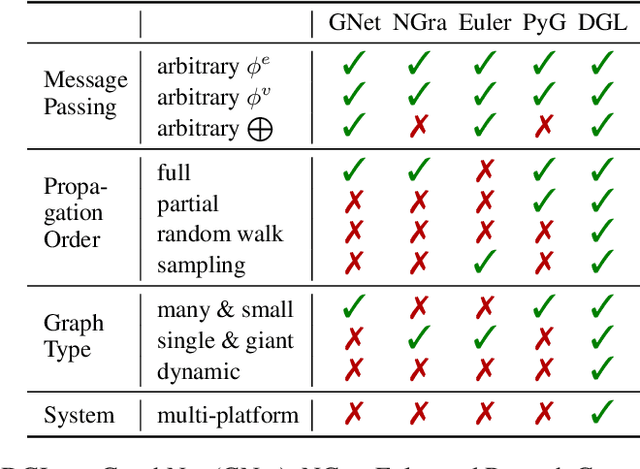
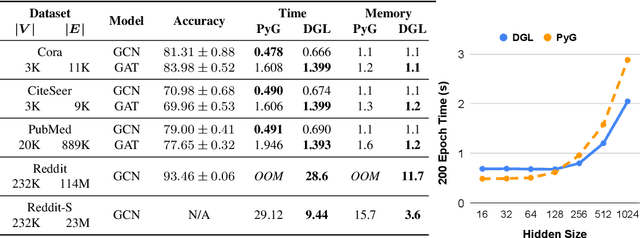
Abstract:Accelerating research in the emerging field of deep graph learning requires new tools. Such systems should support graph as the core abstraction and take care to maintain both forward (i.e. supporting new research ideas) and backward (i.e. integration with existing components) compatibility. In this paper, we present Deep Graph Library (DGL). DGL enables arbitrary message handling and mutation operators, flexible propagation rules, and is framework agnostic so as to leverage high-performance tensor, autograd operations, and other feature extraction modules already available in existing frameworks. DGL carefully handles the sparse and irregular graph structure, deals with graphs big and small which may change dynamically, fuses operations, and performs auto-batching, all to take advantages of modern hardware. DGL has been tested on a variety of models, including but not limited to the popular Graph Neural Networks (GNN) and its variants, with promising speed, memory footprint and scalability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge