Jianan Cui
Deep unrolled primal dual network for TOF-PET list-mode image reconstruction
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Time-of-flight (TOF) information provides more accurate location data for annihilation photons, thereby enhancing the quality of PET reconstruction images and reducing noise. List-mode reconstruction has a significant advantage in handling TOF information. However, current advanced TOF PET list-mode reconstruction algorithms still require improvements when dealing with low-count data. Deep learning algorithms have shown promising results in PET image reconstruction. Nevertheless, the incorporation of TOF information poses significant challenges related to the storage space required by deep learning methods, particularly for the advanced deep unrolled methods. In this study, we propose a deep unrolled primal dual network for TOF-PET list-mode reconstruction. The network is unrolled into multiple phases, with each phase comprising a dual network for list-mode domain updates and a primal network for image domain updates. We utilize CUDA for parallel acceleration and computation of the system matrix for TOF list-mode data, and we adopt a dynamic access strategy to mitigate memory consumption. Reconstructed images of different TOF resolutions and different count levels show that the proposed method outperforms the LM-OSEM, LM-EMTV, LM-SPDHG,LM-SPDHG-TV and FastPET method in both visually and quantitative analysis. These results demonstrate the potential application of deep unrolled methods for TOF-PET list-mode data and show better performance than current mainstream TOF-PET list-mode reconstruction algorithms, providing new insights for the application of deep learning methods in TOF list-mode data. The codes for this work are available at https://github.com/RickHH/LMPDnet
Anatomy-guided fiber trajectory distribution estimation for cranial nerves tractography
Feb 29, 2024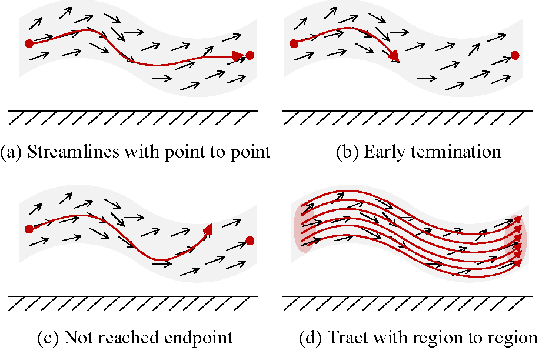
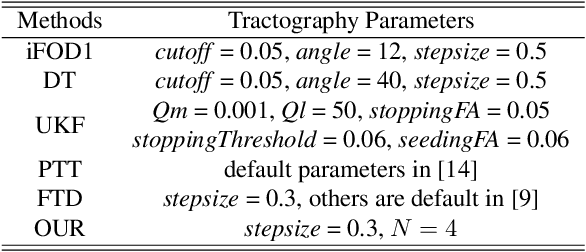
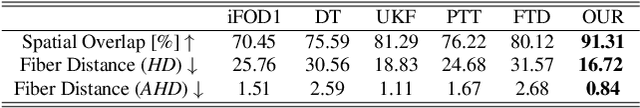
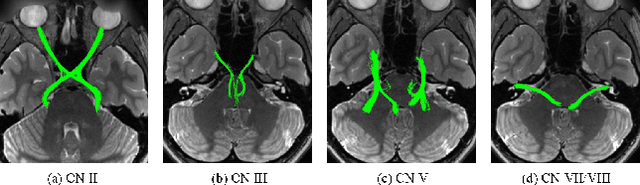
Abstract:Diffusion MRI tractography is an important tool for identifying and analyzing the intracranial course of cranial nerves (CNs). However, the complex environment of the skull base leads to ambiguous spatial correspondence between diffusion directions and fiber geometry, and existing diffusion tractography methods of CNs identification are prone to producing erroneous trajectories and missing true positive connections. To overcome the above challenge, we propose a novel CNs identification framework with anatomy-guided fiber trajectory distribution, which incorporates anatomical shape prior knowledge during the process of CNs tracing to build diffusion tensor vector fields. We introduce higher-order streamline differential equations for continuous flow field representations to directly characterize the fiber trajectory distribution of CNs from the tract-based level. The experimental results on the vivo HCP dataset and the clinical MDM dataset demonstrate that the proposed method reduces false-positive fiber production compared to competing methods and produces reconstructed CNs (i.e. CN II, CN III, CN V, and CN VII/VIII) that are judged to better correspond to the known anatomy.
STPDnet: Spatial-temporal convolutional primal dual network for dynamic PET image reconstruction
Mar 08, 2023



Abstract:Dynamic positron emission tomography (dPET) image reconstruction is extremely challenging due to the limited counts received in individual frame. In this paper, we propose a spatial-temporal convolutional primal dual network (STPDnet) for dynamic PET image reconstruction. Both spatial and temporal correlations are encoded by 3D convolution operators. The physical projection of PET is embedded in the iterative learning process of the network, which provides the physical constraints and enhances interpretability. The experiments of real rat scan data have shown that the proposed method can achieve substantial noise reduction in both temporal and spatial domains and outperform the maximum likelihood expectation maximization (MLEM), spatial-temporal kernel method (KEM-ST), DeepPET and Learned Primal Dual (LPD).
LMPDNet: TOF-PET list-mode image reconstruction using model-based deep learning method
Feb 21, 2023



Abstract:The integration of Time-of-Flight (TOF) information in the reconstruction process of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) yields improved image properties. However, implementing the cutting-edge model-based deep learning methods for TOF-PET reconstruction is challenging due to the substantial memory requirements. In this study, we present a novel model-based deep learning approach, LMPDNet, for TOF-PET reconstruction from list-mode data. We address the issue of real-time parallel computation of the projection matrix for list-mode data, and propose an iterative model-based module that utilizes a dedicated network model for list-mode data. Our experimental results indicate that the proposed LMPDNet outperforms traditional iteration-based TOF-PET list-mode reconstruction algorithms. Additionally, we compare the spatial and temporal consumption of list-mode data and sinogram data in model-based deep learning methods, demonstrating the superiority of list-mode data in model-based TOF-PET reconstruction.
A Noise-level-aware Framework for PET Image Denoising
Mar 15, 2022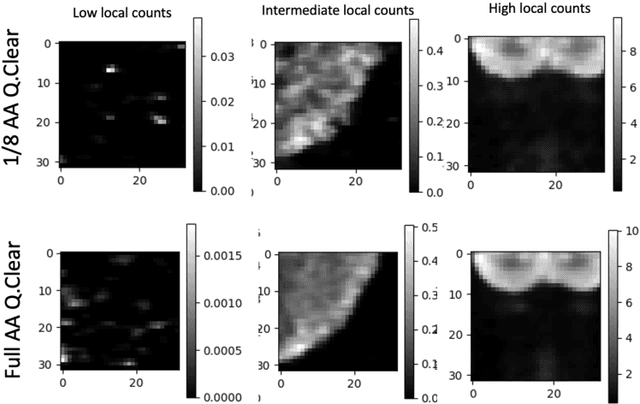
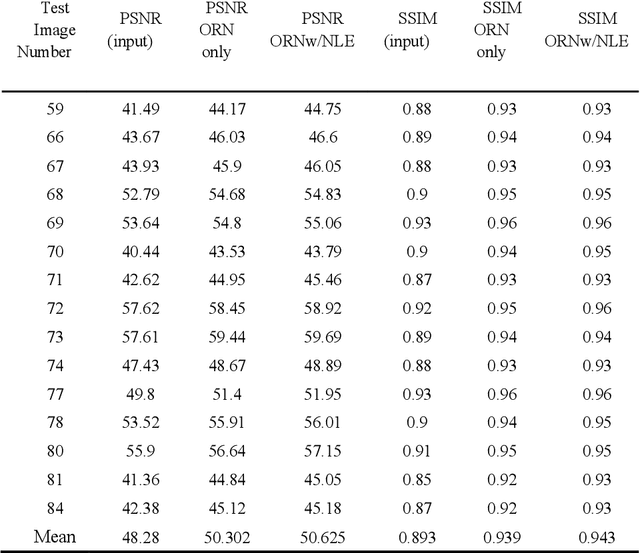
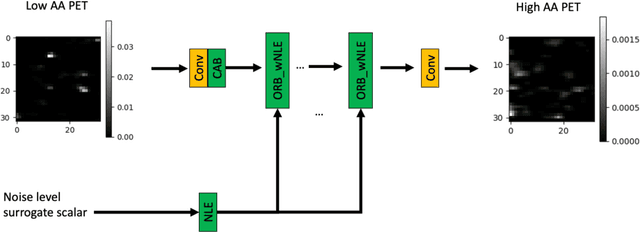
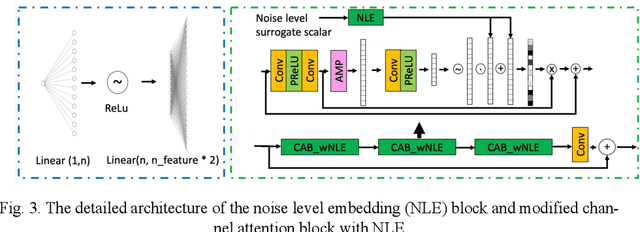
Abstract:In PET, the amount of relative (signal-dependent) noise present in different body regions can be significantly different and is inherently related to the number of counts present in that region. The number of counts in a region depends, in principle and among other factors, on the total administered activity, scanner sensitivity, image acquisition duration, radiopharmaceutical tracer uptake in the region, and patient local body morphometry surrounding the region. In theory, less amount of denoising operations is needed to denoise a high-count (low relative noise) image than images a low-count (high relative noise) image, and vice versa. The current deep-learning-based methods for PET image denoising are predominantly trained on image appearance only and have no special treatment for images of different noise levels. Our hypothesis is that by explicitly providing the local relative noise level of the input image to a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN), the DCNN can outperform itself trained on image appearance only. To this end, we propose a noise-level-aware framework denoising framework that allows embedding of local noise level into a DCNN. The proposed is trained and tested on 30 and 15 patient PET images acquired on a GE Discovery MI PET/CT system. Our experiments showed that the increases in both PSNR and SSIM from our backbone network with relative noise level embedding (NLE) versus the same network without NLE were statistically significant with p<0.001, and the proposed method significantly outperformed a strong baseline method by a large margin.
Super Resolution of Arterial Spin Labeling MR Imaging Using Unsupervised Multi-Scale Generative Adversarial Network
Sep 14, 2020



Abstract:Arterial spin labeling (ASL) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a powerful imaging technology that can measure cerebral blood flow (CBF) quantitatively. However, since only a small portion of blood is labeled compared to the whole tissue volume, conventional ASL suffers from low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), poor spatial resolution, and long acquisition time. In this paper, we proposed a super-resolution method based on a multi-scale generative adversarial network (GAN) through unsupervised training. The network only needs the low-resolution (LR) ASL image itself for training and the T1-weighted image as the anatomical prior. No training pairs or pre-training are needed. A low-pass filter guided item was added as an additional loss to suppress the noise interference from the LR ASL image. After the network was trained, the super-resolution (SR) image was generated by supplying the upsampled LR ASL image and corresponding T1-weighted image to the generator of the last layer. Performance of the proposed method was evaluated by comparing the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index (SSIM) using normal-resolution (NR) ASL image (5.5 min acquisition) and high-resolution (HR) ASL image (44 min acquisition) as the ground truth. Compared to the nearest, linear, and spline interpolation methods, the proposed method recovers more detailed structure information, reduces the image noise visually, and achieves the highest PSNR and SSIM when using HR ASL image as the ground-truth.
Clinically Translatable Direct Patlak Reconstruction from Dynamic PET with Motion Correction Using Convolutional Neural Network
Sep 13, 2020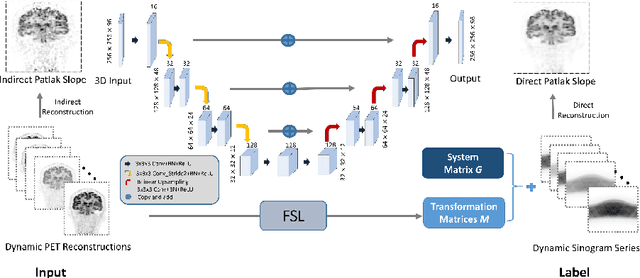
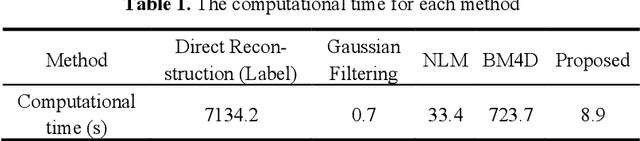
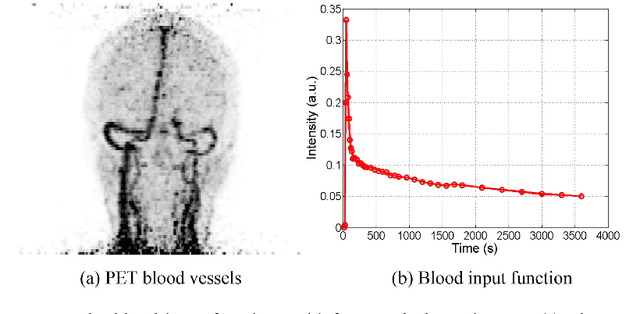
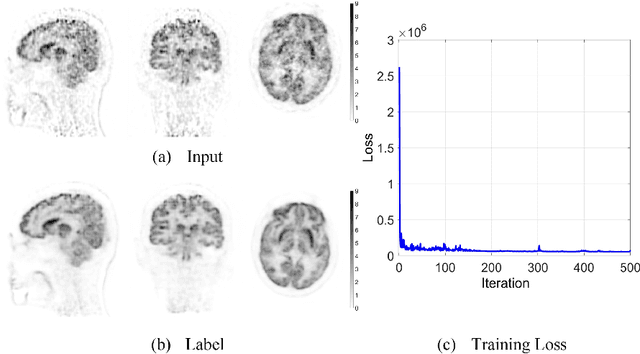
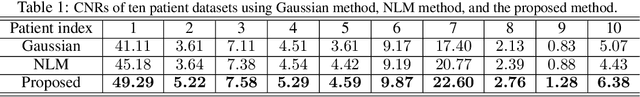
Abstract:Patlak model is widely used in 18F-FDG dynamic positron emission tomography (PET) imaging, where the estimated parametric images reveal important biochemical and physiology information. Because of better noise modeling and more information extracted from raw sinogram, direct Patlak reconstruction gains its popularity over the indirect approach which utilizes reconstructed dynamic PET images alone. As the prerequisite of direct Patlak methods, raw data from dynamic PET are rarely stored in clinics and difficult to obtain. In addition, the direct reconstruction is time-consuming due to the bottleneck of multiple-frame reconstruction. All of these impede the clinical adoption of direct Patlak reconstruction.In this work, we proposed a data-driven framework which maps the dynamic PET images to the high-quality motion-corrected direct Patlak images through a convolutional neural network. For the patient motion during the long period of dynamic PET scan, we combined the correction with the backward/forward projection in direct reconstruction to better fit the statistical model. Results based on fifteen clinical 18F-FDG dynamic brain PET datasets demonstrates the superiority of the proposed framework over Gaussian, nonlocal mean and BM4D denoising, regarding the image bias and contrast-to-noise ratio.
Learning Personalized Representation for Inverse Problems in Medical Imaging Using Deep Neural Network
Jul 04, 2018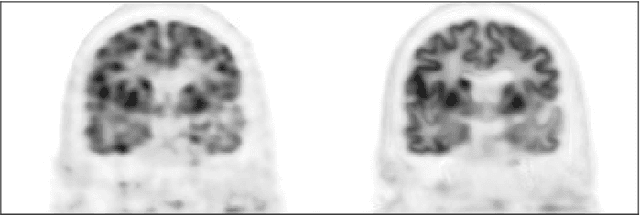
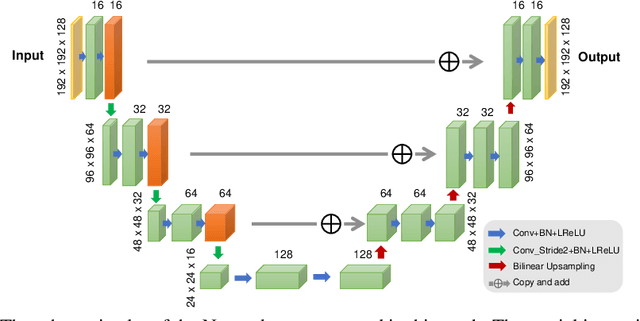
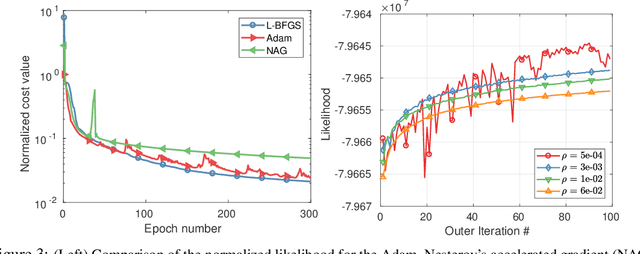
Abstract:Recently deep neural networks have been widely and successfully applied in computer vision tasks and attracted growing interests in medical imaging. One barrier for the application of deep neural networks to medical imaging is the need of large amounts of prior training pairs, which is not always feasible in clinical practice. In this work we propose a personalized representation learning framework where no prior training pairs are needed, but only the patient's own prior images. The representation is expressed using a deep neural network with the patient's prior images as network input. We then applied this novel image representation to inverse problems in medical imaging in which the original inverse problem was formulated as a constraint optimization problem and solved using the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm. Anatomically guided brain positron emission tomography (PET) image reconstruction and image denoising were employed as examples to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework. Quantification results based on simulation and real datasets show that the proposed personalized representation framework outperform other widely adopted methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge