Jayden Ooi
Towards Content Provider Aware Recommender Systems: A Simulation Study on the Interplay between User and Provider Utilities
May 06, 2021
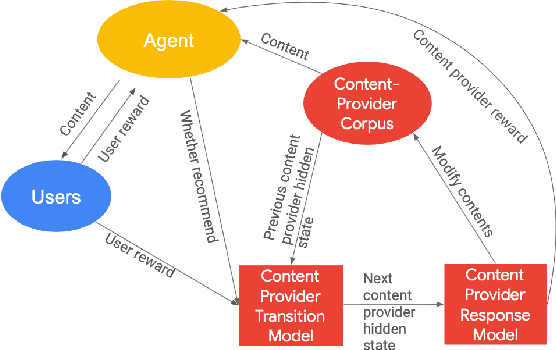
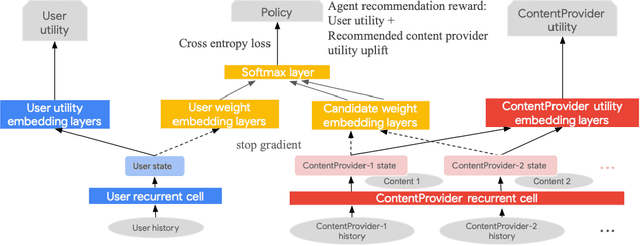
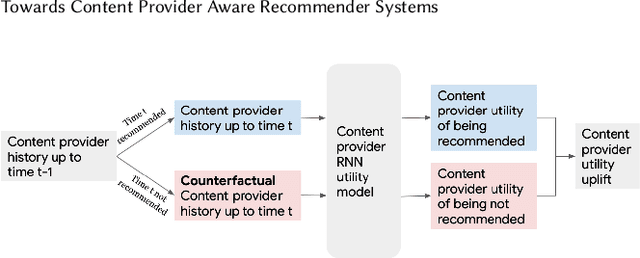
Abstract:Most existing recommender systems focus primarily on matching users to content which maximizes user satisfaction on the platform. It is increasingly obvious, however, that content providers have a critical influence on user satisfaction through content creation, largely determining the content pool available for recommendation. A natural question thus arises: can we design recommenders taking into account the long-term utility of both users and content providers? By doing so, we hope to sustain more providers and a more diverse content pool for long-term user satisfaction. Understanding the full impact of recommendations on both user and provider groups is challenging. This paper aims to serve as a research investigation of one approach toward building a provider-aware recommender, and evaluating its impact in a simulated setup. To characterize the user-recommender-provider interdependence, we complement user modeling by formalizing provider dynamics as well. The resulting joint dynamical system gives rise to a weakly-coupled partially observable Markov decision process driven by recommender actions and user feedback to providers. We then build a REINFORCE recommender agent, coined EcoAgent, to optimize a joint objective of user utility and the counterfactual utility lift of the provider associated with the recommended content, which we show to be equivalent to maximizing overall user utility and the utilities of all providers on the platform under some mild assumptions. To evaluate our approach, we introduce a simulation environment capturing the key interactions among users, providers, and the recommender. We offer a number of simulated experiments that shed light on both the benefits and the limitations of our approach. These results help understand how and when a provider-aware recommender agent is of benefit in building multi-stakeholder recommender systems.
Finding Fast Transformers: One-Shot Neural Architecture Search by Component Composition
Aug 15, 2020
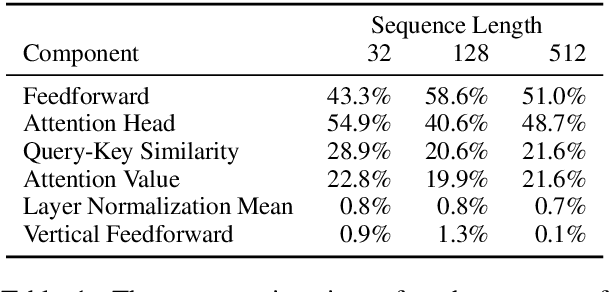
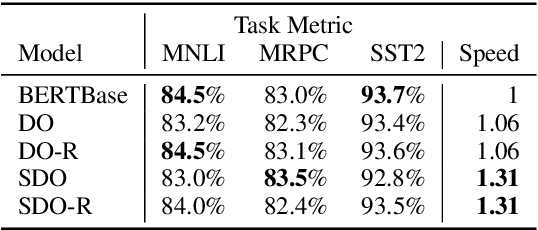
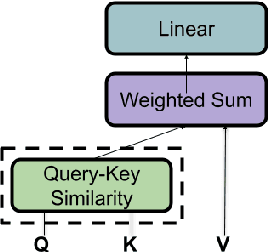
Abstract:Transformer-based models have achieved stateof-the-art results in many tasks in natural language processing. However, such models are usually slow at inference time, making deployment difficult. In this paper, we develop an efficient algorithm to search for fast models while maintaining model quality. We describe a novel approach to decompose the Transformer architecture into smaller components, and propose a sampling-based one-shot architecture search method to find an optimal model for inference. The model search process is more efficient than alternatives, adding only a small overhead to training time. By applying our methods to BERT-base architectures, we achieve 10% to 30% speedup for pre-trained BERT and 70% speedup on top of a previous state-of-the-art distilled BERT model on Cloud TPU-v2 with a generally acceptable drop in performance.
ConQUR: Mitigating Delusional Bias in Deep Q-learning
Feb 27, 2020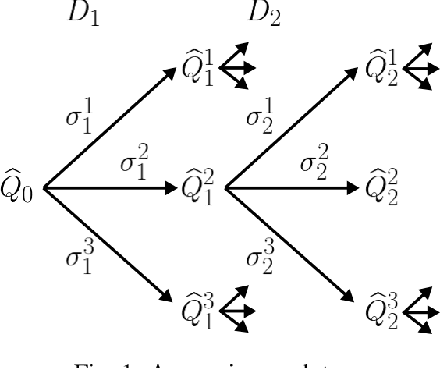


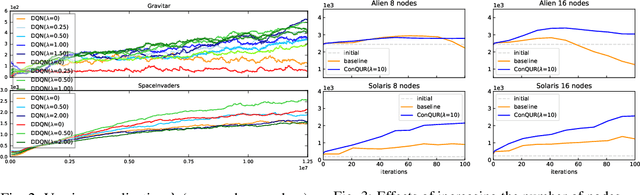
Abstract:Delusional bias is a fundamental source of error in approximate Q-learning. To date, the only techniques that explicitly address delusion require comprehensive search using tabular value estimates. In this paper, we develop efficient methods to mitigate delusional bias by training Q-approximators with labels that are "consistent" with the underlying greedy policy class. We introduce a simple penalization scheme that encourages Q-labels used across training batches to remain (jointly) consistent with the expressible policy class. We also propose a search framework that allows multiple Q-approximators to be generated and tracked, thus mitigating the effect of premature (implicit) policy commitments. Experimental results demonstrate that these methods can improve the performance of Q-learning in a variety of Atari games, sometimes dramatically.
Data Efficient Training for Reinforcement Learning with Adaptive Behavior Policy Sharing
Feb 12, 2020



Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning (RL) is proven powerful for decision making in simulated environments. However, training deep RL model is challenging in real world applications such as production-scale health-care or recommender systems because of the expensiveness of interaction and limitation of budget at deployment. One aspect of the data inefficiency comes from the expensive hyper-parameter tuning when optimizing deep neural networks. We propose Adaptive Behavior Policy Sharing (ABPS), a data-efficient training algorithm that allows sharing of experience collected by behavior policy that is adaptively selected from a pool of agents trained with an ensemble of hyper-parameters. We further extend ABPS to evolve hyper-parameters during training by hybridizing ABPS with an adapted version of Population Based Training (ABPS-PBT). We conduct experiments with multiple Atari games with up to 16 hyper-parameter/architecture setups. ABPS achieves superior overall performance, reduced variance on top 25% agents, and equivalent performance on the best agent compared to conventional hyper-parameter tuning with independent training, even though ABPS only requires the same number of environmental interactions as training a single agent. We also show that ABPS-PBT further improves the convergence speed and reduces the variance.
BRPO: Batch Residual Policy Optimization
Feb 08, 2020



Abstract:In batch reinforcement learning (RL), one often constrains a learned policy to be close to the behavior (data-generating) policy, e.g., by constraining the learned action distribution to differ from the behavior policy by some maximum degree that is the same at each state. This can cause batch RL to be overly conservative, unable to exploit large policy changes at frequently-visited, high-confidence states without risking poor performance at sparsely-visited states. To remedy this, we propose residual policies, where the allowable deviation of the learned policy is state-action-dependent. We derive a new for RL method, BRPO, which learns both the policy and allowable deviation that jointly maximize a lower bound on policy performance. We show that BRPO achieves the state-of-the-art performance in a number of tasks.
Advantage Amplification in Slowly Evolving Latent-State Environments
May 29, 2019


Abstract:Latent-state environments with long horizons, such as those faced by recommender systems, pose significant challenges for reinforcement learning (RL). In this work, we identify and analyze several key hurdles for RL in such environments, including belief state error and small action advantage. We develop a general principle of advantage amplification that can overcome these hurdles through the use of temporal abstraction. We propose several aggregation methods and prove they induce amplification in certain settings. We also bound the loss in optimality incurred by our methods in environments where latent state evolves slowly and demonstrate their performance empirically in a stylized user-modeling task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge