Hui Zeng
Noise-Aware Quantum Architecture Search Based on NSGA-II Algorithm
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Quantum architecture search (QAS) has emerged to automate the design of high-performance quantum circuits under specific tasks and hardware constraints. We propose a noise-aware quantum architecture search (NA-QAS) framework based on variational quantum circuit design. By incorporating a noise model into the training of parameterized quantum circuits (PQCs) , the proposed framework identifies the noise-robust architectures. We introduce a hybrid Hamiltonian $\varepsilon$ -greedy strategy to optimize evaluation costs and circumvent local optima. Furthermore, an enhanced variable-depth NSGA-II algorithm is employed to navigate the vast search space, enabling an automated trade-off between architectural expressibility and quantum hardware overhead. The effectiveness of the framework is validated through binary classification and iris multi-classification tasks under a noisy condition. Compared to existing approaches, our framework can search for quantum architectures with superior performance and greater resource efficiency under a noisy condition.
Lethe: Layer- and Time-Adaptive KV Cache Pruning for Reasoning-Intensive LLM Serving
Nov 12, 2025



Abstract:Generative reasoning with large language models (LLMs) often involves long decoding sequences, leading to substantial memory and latency overheads from accumulating key-value (KV) caches. While existing KV compression methods primarily focus on reducing prefill memory from long input sequences, they fall short in addressing the dynamic and layer-sensitive nature of long-form generation, which is central to reasoning tasks. We propose Lethe, a dynamic KV cache management framework that introduces adaptivity along both the spatial and temporal dimensions of decoding. Along the spatial dimension, Lethe performs layerwise sparsity-aware allocation, assigning token pruning budgets to each transformer layer based on estimated attention redundancy. Along the temporal dimension, Lethe conducts multi-round token pruning during generation, driven by a Recency-Aware Selective Retention} (RASR) mechanism. RASR extends traditional recency-based heuristics by also considering token relevance derived from evolving attention patterns, enabling informed decisions about which tokens to retain or evict. Empirical results demonstrate that Lethe achieves a favorable balance between efficiency and generation quality across diverse models and tasks, increases throughput by up to 2.56x.
Everywhere Attack: Attacking Locally and Globally to Boost Targeted Transferability
Jan 01, 2025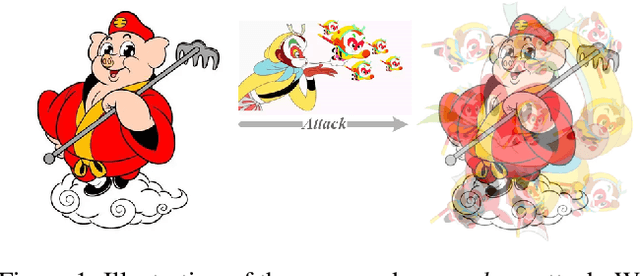
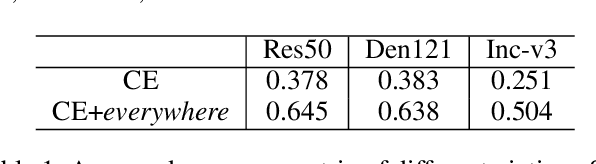
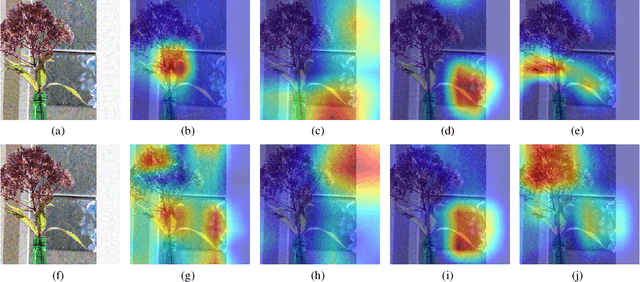
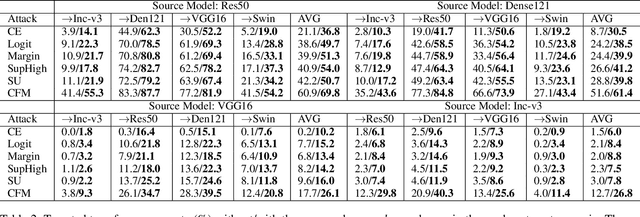
Abstract:Adversarial examples' (AE) transferability refers to the phenomenon that AEs crafted with one surrogate model can also fool other models. Notwithstanding remarkable progress in untargeted transferability, its targeted counterpart remains challenging. This paper proposes an everywhere scheme to boost targeted transferability. Our idea is to attack a victim image both globally and locally. We aim to optimize 'an army of targets' in every local image region instead of the previous works that optimize a high-confidence target in the image. Specifically, we split a victim image into non-overlap blocks and jointly mount a targeted attack on each block. Such a strategy mitigates transfer failures caused by attention inconsistency between surrogate and victim models and thus results in stronger transferability. Our approach is method-agnostic, which means it can be easily combined with existing transferable attacks for even higher transferability. Extensive experiments on ImageNet demonstrate that the proposed approach universally improves the state-of-the-art targeted attacks by a clear margin, e.g., the transferability of the widely adopted Logit attack can be improved by 28.8%-300%.We also evaluate the crafted AEs on a real-world platform: Google Cloud Vision. Results further support the superiority of the proposed method.
Two Heads Are Better Than One: Averaging along Fine-Tuning to Improve Targeted Transferability
Dec 30, 2024



Abstract:With much longer optimization time than that of untargeted attacks notwithstanding, the transferability of targeted attacks is still far from satisfactory. Recent studies reveal that fine-tuning an existing adversarial example (AE) in feature space can efficiently boost its targeted transferability. However, existing fine-tuning schemes only utilize the endpoint and ignore the valuable information in the fine-tuning trajectory. Noting that the vanilla fine-tuning trajectory tends to oscillate around the periphery of a flat region of the loss surface, we propose averaging over the fine-tuning trajectory to pull the crafted AE towards a more centered region. We compare the proposed method with existing fine-tuning schemes by integrating them with state-of-the-art targeted attacks in various attacking scenarios. Experimental results uphold the superiority of the proposed method in boosting targeted transferability. The code is available at github.com/zengh5/Avg_FT.
MetaTrading: An Immersion-Aware Model Trading Framework for Vehicular Metaverse Services
Oct 25, 2024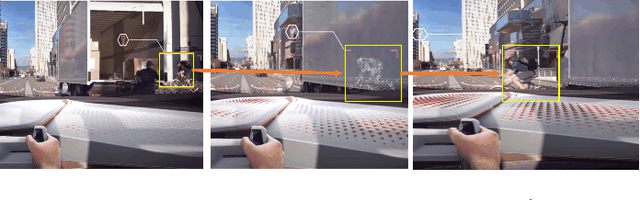
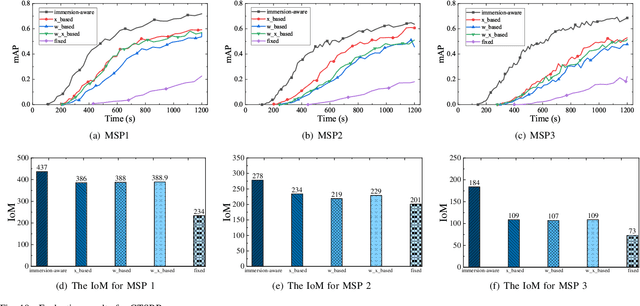
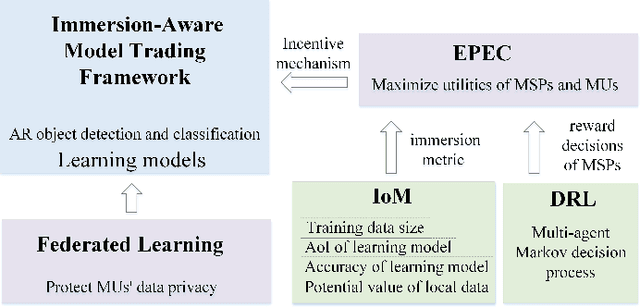
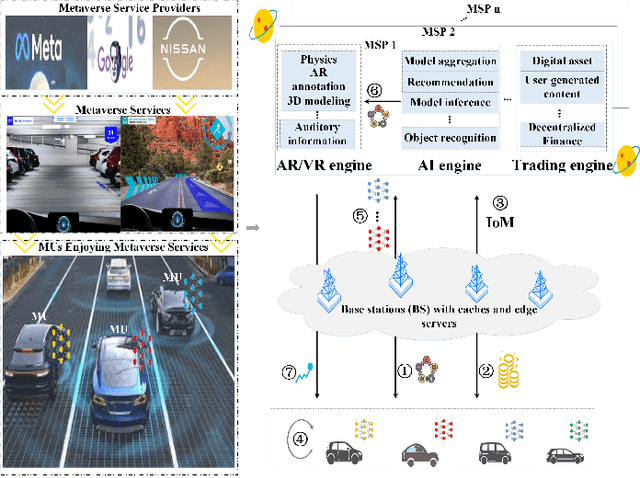
Abstract:Updates of extensive Internet of Things (IoT) data are critical to the immersion of vehicular metaverse services. However, providing high-quality and sustainable data in unstable and resource-constrained vehicular networks remains a significant challenge. To address this problem, we put forth a novel immersion-aware model trading framework that incentivizes metaverse users (MUs) to contribute learning models trained by their latest local data for augmented reality (AR) services in the vehicular metaverse, while preserving their privacy through federated learning. To comprehensively evaluate the contribution of locally trained learning models provided by MUs to AR services, we design a new immersion metric that captures service immersion by considering the freshness and accuracy of learning models, as well as the amount and potential value of raw data used for training. We model the trading interactions between metaverse service providers (MSPs) and MUs as an equilibrium problem with equilibrium constraints (EPEC) to analyze and balance their costs and gains. Moreover, considering dynamic network conditions and privacy concerns, we formulate the reward decisions of MSPs as a multi-agent Markov decision process. Then, a fully distributed dynamic reward method based on deep reinforcement learning is presented, which operates without any private information about MUs and other MSPs. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework can effectively provide higher-value models for object detection and classification in AR services on real AR-related vehicle datasets compared to benchmark schemes.
NTIRE 2024 Restore Any Image Model in the Wild Challenge
May 16, 2024
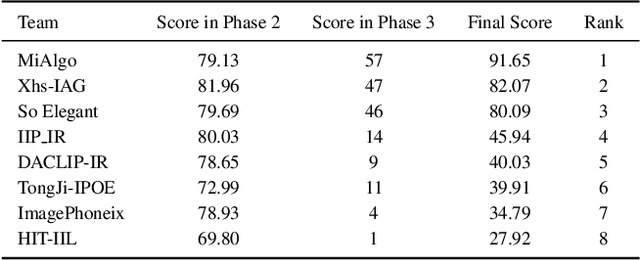

Abstract:In this paper, we review the NTIRE 2024 challenge on Restore Any Image Model (RAIM) in the Wild. The RAIM challenge constructed a benchmark for image restoration in the wild, including real-world images with/without reference ground truth in various scenarios from real applications. The participants were required to restore the real-captured images from complex and unknown degradation, where generative perceptual quality and fidelity are desired in the restoration result. The challenge consisted of two tasks. Task one employed real referenced data pairs, where quantitative evaluation is available. Task two used unpaired images, and a comprehensive user study was conducted. The challenge attracted more than 200 registrations, where 39 of them submitted results with more than 400 submissions. Top-ranked methods improved the state-of-the-art restoration performance and obtained unanimous recognition from all 18 judges. The proposed datasets are available at https://drive.google.com/file/d/1DqbxUoiUqkAIkExu3jZAqoElr_nu1IXb/view?usp=sharing and the homepage of this challenge is at https://codalab.lisn.upsaclay.fr/competitions/17632.
Enhancing targeted transferability via feature space fine-tuning
Jan 13, 2024



Abstract:Adversarial examples (AEs) have been extensively studied due to their potential for privacy protection and inspiring robust neural networks. Yet, making a targeted AE transferable across unknown models remains challenging. In this paper, to alleviate the overfitting dilemma common in an AE crafted by existing simple iterative attacks, we propose fine-tuning it in the feature space. Specifically, starting with an AE generated by a baseline attack, we encourage the features conducive to the target class and discourage the features to the original class in a middle layer of the source model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that only a few iterations of fine-tuning can boost existing attacks' targeted transferability nontrivially and universally. Our results also verify that the simple iterative attacks can yield comparable or even better transferability than the resource-intensive methods, which rest on training target-specific classifiers or generators with additional data. The code is available at: github.com/zengh5/TA_feature_FT.
Guided Image Restoration via Simultaneous Feature and Image Guided Fusion
Dec 14, 2023



Abstract:Guided image restoration (GIR), such as guided depth map super-resolution and pan-sharpening, aims to enhance a target image using guidance information from another image of the same scene. Currently, joint image filtering-inspired deep learning-based methods represent the state-of-the-art for GIR tasks. Those methods either deal with GIR in an end-to-end way by elaborately designing filtering-oriented deep neural network (DNN) modules, focusing on the feature-level fusion of inputs; or explicitly making use of the traditional joint filtering mechanism by parameterizing filtering coefficients with DNNs, working on image-level fusion. The former ones are good at recovering contextual information but tend to lose fine-grained details, while the latter ones can better retain textual information but might lead to content distortions. In this work, to inherit the advantages of both methodologies while mitigating their limitations, we proposed a Simultaneous Feature and Image Guided Fusion (SFIGF) network, that simultaneously considers feature and image-level guided fusion following the guided filter (GF) mechanism. In the feature domain, we connect the cross-attention (CA) with GF, and propose a GF-inspired CA module for better feature-level fusion; in the image domain, we fully explore the GF mechanism and design GF-like structure for better image-level fusion. Since guided fusion is implemented in both feature and image domains, the proposed SFIGF is expected to faithfully reconstruct both contextual and textual information from sources and thus lead to better GIR results. We apply SFIGF to 4 typical GIR tasks, and experimental results on these tasks demonstrate its effectiveness and general availability.
Evaluating the Generation Capabilities of Large Chinese Language Models
Aug 11, 2023

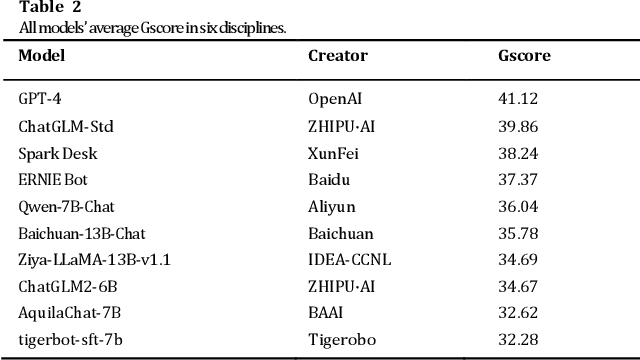
Abstract:This paper presents CG-Eval, the first comprehensive evaluation of the generation capabilities of large Chinese language models across a wide range of academic disciplines. The models' performance was assessed based on their ability to generate accurate and relevant responses to different types of questions in six disciplines, namely, Science and Engineering, Humanities and Social Sciences, Mathematical Calculations, Medical Practitioner Qualification Examination, Judicial Examination, and Certified Public Accountant Examination. This paper also presents Gscore, a composite index derived from the weighted sum of multiple metrics to measure the quality of model's generation against a reference. The test data and test results can be found at http://cgeval.besteasy.com/.
Measuring Massive Multitask Chinese Understanding
May 15, 2023



Abstract:The development of large-scale Chinese language models is flourishing, yet there is a lack of corresponding capability assessments. Therefore, we propose a test to measure the multitask accuracy of large Chinese language models. This test encompasses four major domains, including medicine, law, psychology, and education, with 15 subtasks in medicine and 8 subtasks in education. We found that the best-performing models in the zero-shot setting outperformed the worst-performing models by nearly 18.6 percentage points on average. Across the four major domains, the highest average zero-shot accuracy of all models is 0.512. In the subdomains, only the GPT-3.5-turbo model achieved a zero-shot accuracy of 0.693 in clinical medicine, which was the highest accuracy among all models across all subtasks. All models performed poorly in the legal domain, with the highest zero-shot accuracy reaching only 0.239. By comprehensively evaluating the breadth and depth of knowledge across multiple disciplines, this test can more accurately identify the shortcomings of the models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge