Hongjia Wu
Doc2AHP: Inferring Structured Multi-Criteria Decision Models via Semantic Trees with LLMs
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable proficiency in semantic understanding, they often struggle to ensure structural consistency and reasoning reliability in complex decision-making tasks that demand rigorous logic. Although classical decision theories, such as the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), offer systematic rational frameworks, their construction relies heavily on labor-intensive domain expertise, creating an "expert bottleneck" that hinders scalability in general scenarios. To bridge the gap between the generalization capabilities of LLMs and the rigor of decision theory, we propose Doc2AHP, a novel structured inference framework guided by AHP principles. Eliminating the need for extensive annotated data or manual intervention, our approach leverages the structural principles of AHP as constraints to direct the LLM in a constrained search within the unstructured document space, thereby enforcing the logical entailment between parent and child nodes. Furthermore, we introduce a multi-agent weighting mechanism coupled with an adaptive consistency optimization strategy to ensure the numerical consistency of weight allocation. Empirical results demonstrate that Doc2AHP not only empowers non-expert users to construct high-quality decision models from scratch but also significantly outperforms direct generative baselines in both logical completeness and downstream task accuracy.
Retrieval Augmented Decision-Making: A Requirements-Driven, Multi-Criteria Framework for Structured Decision Support
May 24, 2025Abstract:Various industries have produced a large number of documents such as industrial plans, technical guidelines, and regulations that are structurally complex and content-wise fragmented. This poses significant challenges for experts and decision-makers in terms of retrieval and understanding. Although existing LLM-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation methods can provide context-related suggestions, they lack quantitative weighting and traceable reasoning paths, making it difficult to offer multi-level and transparent decision support. To address this issue, this paper proposes the RAD method, which integrates Multi-Criteria Decision Making with the semantic understanding capabilities of LLMs. The method automatically extracts key criteria from industry documents, builds a weighted hierarchical decision model, and generates structured reports under model guidance. The RAD framework introduces explicit weight assignment and reasoning chains in decision generation to ensure accuracy, completeness, and traceability. Experiments show that in various decision-making tasks, the decision reports generated by RAD significantly outperform existing methods in terms of detail, rationality, and structure, demonstrating its application value and potential in complex decision support scenarios.
MetaTrading: An Immersion-Aware Model Trading Framework for Vehicular Metaverse Services
Oct 25, 2024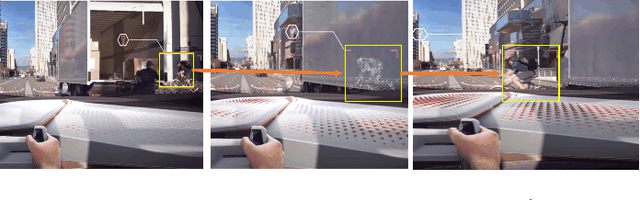
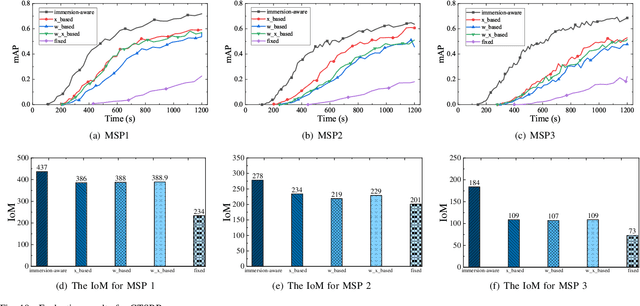
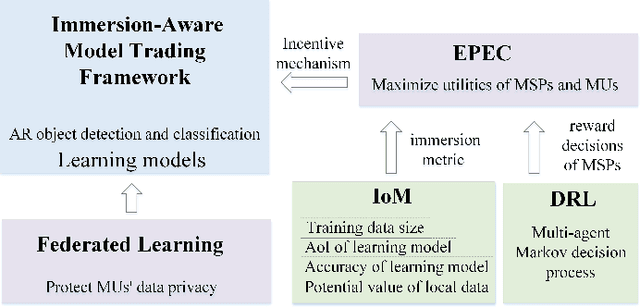
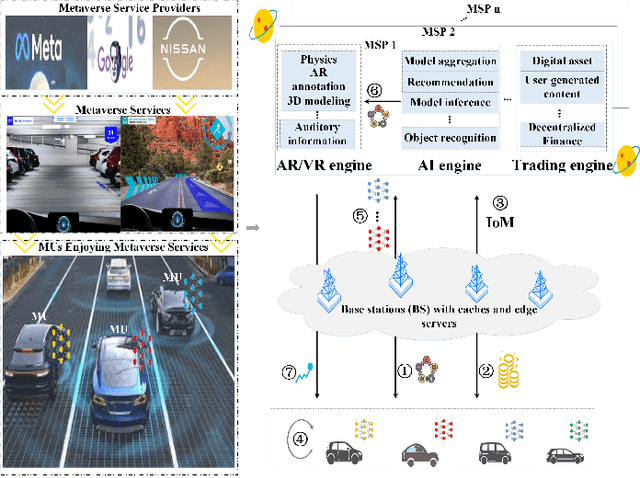
Abstract:Updates of extensive Internet of Things (IoT) data are critical to the immersion of vehicular metaverse services. However, providing high-quality and sustainable data in unstable and resource-constrained vehicular networks remains a significant challenge. To address this problem, we put forth a novel immersion-aware model trading framework that incentivizes metaverse users (MUs) to contribute learning models trained by their latest local data for augmented reality (AR) services in the vehicular metaverse, while preserving their privacy through federated learning. To comprehensively evaluate the contribution of locally trained learning models provided by MUs to AR services, we design a new immersion metric that captures service immersion by considering the freshness and accuracy of learning models, as well as the amount and potential value of raw data used for training. We model the trading interactions between metaverse service providers (MSPs) and MUs as an equilibrium problem with equilibrium constraints (EPEC) to analyze and balance their costs and gains. Moreover, considering dynamic network conditions and privacy concerns, we formulate the reward decisions of MSPs as a multi-agent Markov decision process. Then, a fully distributed dynamic reward method based on deep reinforcement learning is presented, which operates without any private information about MUs and other MSPs. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework can effectively provide higher-value models for object detection and classification in AR services on real AR-related vehicle datasets compared to benchmark schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge