Tse-Tin Chan
Diffusion Model-based Reinforcement Learning for Version Age of Information Scheduling: Average and Tail-Risk-Sensitive Control
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Ensuring timely and semantically accurate information delivery is critical in real-time wireless systems. While Age of Information (AoI) quantifies temporal freshness, Version Age of Information (VAoI) captures semantic staleness by accounting for version evolution between transmitters and receivers. Existing VAoI scheduling approaches primarily focus on minimizing average VAoI, overlooking rare but severe staleness events that can compromise reliability under stochastic packet arrivals and unreliable channels. This paper investigates both average-oriented and tail-risk-sensitive VAoI scheduling in a multi-user status update system with long-term transmission cost constraints. We first formulate the average VAoI minimization problem as a constrained Markov decision process and introduce a deep diffusion-based Soft Actor-Critic (D2SAC) algorithm. By generating actions through a diffusion-based denoising process, D2SAC enhances policy expressiveness and establishes a strong baseline for mean performance. Building on this foundation, we put forth RS-D3SAC, a risk-sensitive deep distributional diffusion-based Soft Actor-Critic algorithm. RS-D3SAC integrates a diffusion-based actor with a quantile-based distributional critic, explicitly modeling the full VAoI return distribution. This enables principled tail-risk optimization via Conditional Value-at-Risk (CVaR) while satisfying long-term transmission cost constraints. Extensive simulations show that, while D2SAC reduces average VAoI, RS-D3SAC consistently achieves substantial reductions in CVaR without sacrificing mean performance. The dominant gain in tail-risk reduction stems from the distributional critic, with the diffusion-based actor providing complementary refinement to stabilize and enrich policy decisions, highlighting their effectiveness for robust and risk-aware VAoI scheduling in multi-user wireless systems.
MetaTrading: An Immersion-Aware Model Trading Framework for Vehicular Metaverse Services
Oct 25, 2024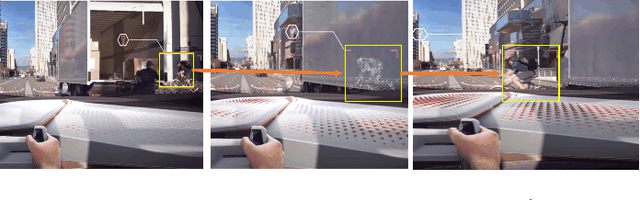
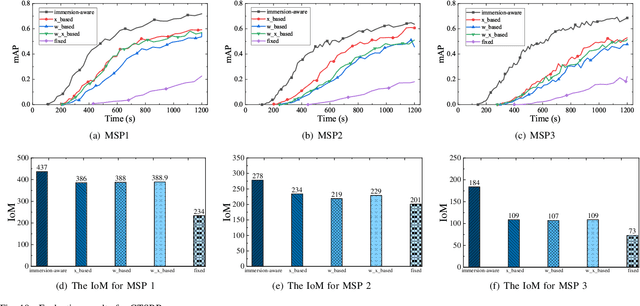
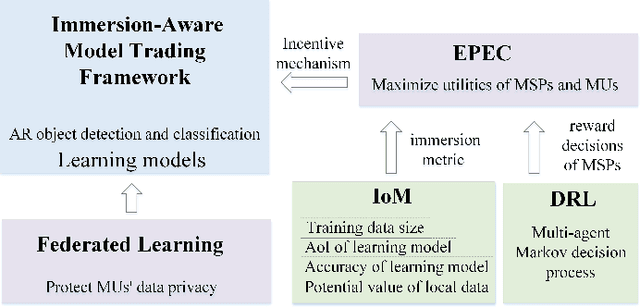
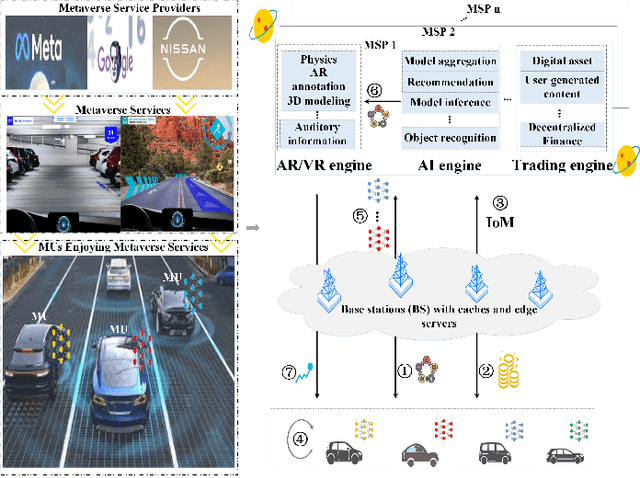
Abstract:Updates of extensive Internet of Things (IoT) data are critical to the immersion of vehicular metaverse services. However, providing high-quality and sustainable data in unstable and resource-constrained vehicular networks remains a significant challenge. To address this problem, we put forth a novel immersion-aware model trading framework that incentivizes metaverse users (MUs) to contribute learning models trained by their latest local data for augmented reality (AR) services in the vehicular metaverse, while preserving their privacy through federated learning. To comprehensively evaluate the contribution of locally trained learning models provided by MUs to AR services, we design a new immersion metric that captures service immersion by considering the freshness and accuracy of learning models, as well as the amount and potential value of raw data used for training. We model the trading interactions between metaverse service providers (MSPs) and MUs as an equilibrium problem with equilibrium constraints (EPEC) to analyze and balance their costs and gains. Moreover, considering dynamic network conditions and privacy concerns, we formulate the reward decisions of MSPs as a multi-agent Markov decision process. Then, a fully distributed dynamic reward method based on deep reinforcement learning is presented, which operates without any private information about MUs and other MSPs. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework can effectively provide higher-value models for object detection and classification in AR services on real AR-related vehicle datasets compared to benchmark schemes.
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Assisted Semantic Communication Systems
Jun 29, 2023



Abstract:Semantic communication, which focuses on conveying the meaning of information rather than exact bit reconstruction, has gained considerable attention in recent years. Meanwhile, reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is a promising technology that can achieve high spectral and energy efficiency by dynamically reflecting incident signals through programmable passive components. In this paper, we put forth a semantic communication scheme aided by RIS. Using text transmission as an example, experimental results demonstrate that the RIS-assisted semantic communication system outperforms the point-to-point semantic communication system in terms of bilingual evaluation understudy (BLEU) scores in Rayleigh fading channels, especially at low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regimes. In addition, the RIS-assisted semantic communication system exhibits superior robustness against channel estimation errors compared to its point-to-point counterpart. RIS can improve performance as it provides extra line-of-sight (LoS) paths and enhances signal propagation conditions compared to point-to-point systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge