Na Zhang
Paying Less Generalization Tax: A Cross-Domain Generalization Study of RL Training for LLM Agents
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Generalist LLM agents are often post-trained on a narrow set of environments but deployed across far broader, unseen domains. In this work, we investigate the challenge of agentic post-training when the eventual test domains are unknown. Specifically, we analyze which properties of reinforcement learning (RL) environments and modeling choices have the greatest influence on out-of-domain performance. First, we identify two environment axes that strongly correlate with cross-domain generalization: (i) state information richness, i.e., the amount of information for the agent to process from the state, and (ii) planning complexity, estimated via goal reachability and trajectory length under a base policy. Notably, domain realism and text-level similarity are not the primary factors; for instance, the simple grid-world domain Sokoban leads to even stronger generalization in SciWorld than the more realistic ALFWorld. Motivated by these findings, we further show that increasing state information richness alone can already effectively improve cross-domain robustness. We propose a randomization technique, which is low-overhead and broadly applicable: add small amounts of distractive goal-irrelevant features to the state to make it richer without altering the task. Beyond environment-side properties, we also examine several modeling choices: (a) SFT warmup or mid-training helps prevent catastrophic forgetting during RL but undermines generalization to domains that are not included in the mid-training datamix; and (b) turning on step-by-step thinking during RL, while not always improving in-domain performance, plays a crucial role in preserving generalization.
Rotate Your Character: Revisiting Video Diffusion Models for High-Quality 3D Character Generation
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Generating high-quality 3D characters from single images remains a significant challenge in digital content creation, particularly due to complex body poses and self-occlusion. In this paper, we present RCM (Rotate your Character Model), an advanced image-to-video diffusion framework tailored for high-quality novel view synthesis (NVS) and 3D character generation. Compared to existing diffusion-based approaches, RCM offers several key advantages: (1) transferring characters with any complex poses into a canonical pose, enabling consistent novel view synthesis across the entire viewing orbit, (2) high-resolution orbital video generation at 1024x1024 resolution, (3) controllable observation positions given different initial camera poses, and (4) multi-view conditioning supporting up to 4 input images, accommodating diverse user scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RCM outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both novel view synthesis and 3D generation quality.
Underwater target 6D State Estimation via UUV Attitude Enhance Observability
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Accurate relative state observation of Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) for tracking uncooperative targets remains a significant challenge due to the absence of GPS, complex underwater dynamics, and sensor limitations. Existing localization approaches rely on either global positioning infrastructure or multi-UUV collaboration, both of which are impractical for a single UUV operating in large or unknown environments. To address this, we propose a novel persistent relative 6D state estimation framework that enables a single UUV to estimate its relative motion to a non-cooperative target using only successive noisy range measurements from two monostatic sonar sensors. Our key contribution is an observability-enhanced attitude control strategy, which optimally adjusts the UUV's orientation to improve the observability of relative state estimation using a Kalman filter, effectively mitigating the impact of sensor noise and drift accumulation. Additionally, we introduce a rigorously proven Lyapunov-based tracking control strategy that guarantees long-term stability by ensuring that the UUV maintains an optimal measurement range, preventing localization errors from diverging over time. Through theoretical analysis and simulations, we demonstrate that our method significantly improves 6D relative state estimation accuracy and robustness compared to conventional approaches. This work provides a scalable, infrastructure-free solution for UUVs tracking uncooperative targets underwater.
Consistency-aware Fake Videos Detection on Short Video Platforms
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:This paper focuses to detect the fake news on the short video platforms. While significant research efforts have been devoted to this task with notable progress in recent years, current detection accuracy remains suboptimal due to the rapid evolution of content manipulation and generation technologies. Existing approaches typically employ a cross-modal fusion strategy that directly combines raw video data with metadata inputs before applying a classification layer. However, our empirical observations reveal a critical oversight: manipulated content frequently exhibits inter-modal inconsistencies that could serve as valuable discriminative features, yet remain underutilized in contemporary detection frameworks. Motivated by this insight, we propose a novel detection paradigm that explicitly identifies and leverages cross-modal contradictions as discriminative cues. Our approach consists of two core modules: Cross-modal Consistency Learning (CMCL) and Multi-modal Collaborative Diagnosis (MMCD). CMCL includes Pseudo-label Generation (PLG) and Cross-modal Consistency Diagnosis (CMCD). In PLG, a Multimodal Large Language Model is used to generate pseudo-labels for evaluating cross-modal semantic consistency. Then, CMCD extracts [CLS] tokens and computes cosine loss to quantify cross-modal inconsistencies. MMCD further integrates multimodal features through Multimodal Feature Fusion (MFF) and Probability Scores Fusion (PSF). MFF employs a co-attention mechanism to enhance semantic interactions across different modalities, while a Transformer is utilized for comprehensive feature fusion. Meanwhile, PSF further integrates the fake news probability scores obtained in the previous step. Extensive experiments on established benchmarks (FakeSV and FakeTT) demonstrate our model exhibits outstanding performance in Fake videos detection.
Stably unactivated neurons in ReLU neural networks
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:The choice of architecture of a neural network influences which functions will be realizable by that neural network and, as a result, studying the expressiveness of a chosen architecture has received much attention. In ReLU neural networks, the presence of stably unactivated neurons can reduce the network's expressiveness. In this work, we investigate the probability of a neuron in the second hidden layer of such neural networks being stably unactivated when the weights and biases are initialized from symmetric probability distributions. For networks with input dimension $n_0$, we prove that if the first hidden layer has $n_0+1$ neurons then this probability is exactly $\frac{2^{n_0}+1}{4^{n_0+1}}$, and if the first hidden layer has $n_1$ neurons, $n_1 \le n_0$, then the probability is $\frac{1}{2^{n_1+1}}$. Finally, for the case when the first hidden layer has more neurons than $n_0+1$, a conjecture is proposed along with the rationale. Computational evidence is presented to support the conjecture.
IPMix: Label-Preserving Data Augmentation Method for Training Robust Classifiers
Oct 17, 2023
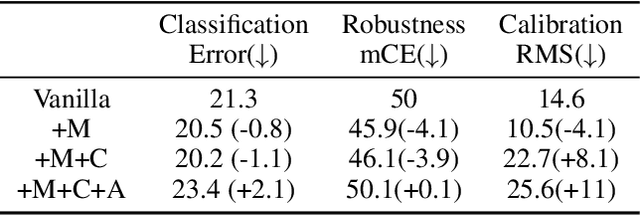

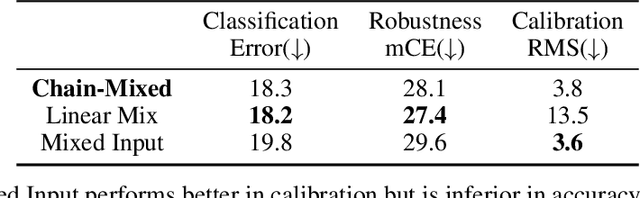
Abstract:Data augmentation has been proven effective for training high-accuracy convolutional neural network classifiers by preventing overfitting. However, building deep neural networks in real-world scenarios requires not only high accuracy on clean data but also robustness when data distributions shift. While prior methods have proposed that there is a trade-off between accuracy and robustness, we propose IPMix, a simple data augmentation approach to improve robustness without hurting clean accuracy. IPMix integrates three levels of data augmentation (image-level, patch-level, and pixel-level) into a coherent and label-preserving technique to increase the diversity of training data with limited computational overhead. To further improve the robustness, IPMix introduces structural complexity at different levels to generate more diverse images and adopts the random mixing method for multi-scale information fusion. Experiments demonstrate that IPMix outperforms state-of-the-art corruption robustness on CIFAR-C and ImageNet-C. In addition, we show that IPMix also significantly improves the other safety measures, including robustness to adversarial perturbations, calibration, prediction consistency, and anomaly detection, achieving state-of-the-art or comparable results on several benchmarks, including ImageNet-R, ImageNet-A, and ImageNet-O.
Evaluating the Generation Capabilities of Large Chinese Language Models
Aug 11, 2023

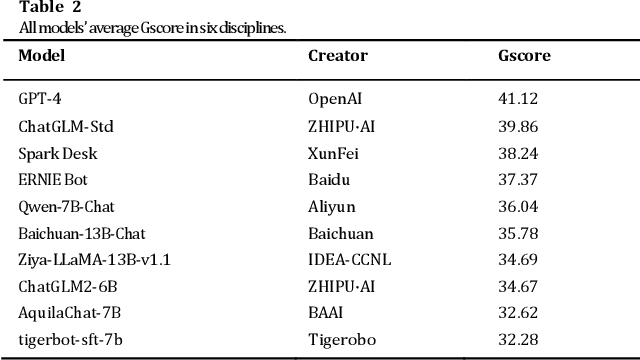
Abstract:This paper presents CG-Eval, the first comprehensive evaluation of the generation capabilities of large Chinese language models across a wide range of academic disciplines. The models' performance was assessed based on their ability to generate accurate and relevant responses to different types of questions in six disciplines, namely, Science and Engineering, Humanities and Social Sciences, Mathematical Calculations, Medical Practitioner Qualification Examination, Judicial Examination, and Certified Public Accountant Examination. This paper also presents Gscore, a composite index derived from the weighted sum of multiple metrics to measure the quality of model's generation against a reference. The test data and test results can be found at http://cgeval.besteasy.com/.
Face Image Quality Enhancement Study for Face Recognition
Jul 08, 2023Abstract:Unconstrained face recognition is an active research area among computer vision and biometric researchers for many years now. Still the problem of face recognition in low quality photos has not been well-studied so far. In this paper, we explore the face recognition performance on low quality photos, and we try to improve the accuracy in dealing with low quality face images. We assemble a large database with low quality photos, and examine the performance of face recognition algorithms for three different quality sets. Using state-of-the-art facial image enhancement approaches, we explore the face recognition performance for the enhanced face images. To perform this without experimental bias, we have developed a new protocol for recognition with low quality face photos and validate the performance experimentally. Our designed protocol for face recognition with low quality face images can be useful to other researchers. Moreover, experiment results show some of the challenging aspects of this problem.
Facial Landmark Detection Evaluation on MOBIO Database
Jul 06, 2023



Abstract:MOBIO is a bi-modal database that was captured almost exclusively on mobile phones. It aims to improve research into deploying biometric techniques to mobile devices. Research has been shown that face and speaker recognition can be performed in a mobile environment. Facial landmark localization aims at finding the coordinates of a set of pre-defined key points for 2D face images. A facial landmark usually has specific semantic meaning, e.g. nose tip or eye centre, which provides rich geometric information for other face analysis tasks such as face recognition, emotion estimation and 3D face reconstruction. Pretty much facial landmark detection methods adopt still face databases, such as 300W, AFW, AFLW, or COFW, for evaluation, but seldomly use mobile data. Our work is first to perform facial landmark detection evaluation on the mobile still data, i.e., face images from MOBIO database. About 20,600 face images have been extracted from this audio-visual database and manually labeled with 22 landmarks as the groundtruth. Several state-of-the-art facial landmark detection methods are adopted to evaluate their performance on these data. The result shows that the data from MOBIO database is pretty challenging. This database can be a new challenging one for facial landmark detection evaluation.
A Study on the Impact of Face Image Quality on Face Recognition in the Wild
Jul 05, 2023Abstract:Deep learning has received increasing interests in face recognition recently. Large quantities of deep learning methods have been proposed to handle various problems appeared in face recognition. Quite a lot deep methods claimed that they have gained or even surpassed human-level face verification performance in certain databases. As we know, face image quality poses a great challenge to traditional face recognition methods, e.g. model-driven methods with hand-crafted features. However, a little research focus on the impact of face image quality on deep learning methods, and even human performance. Therefore, we raise a question: Is face image quality still one of the challenges for deep learning based face recognition, especially in unconstrained condition. Based on this, we further investigate this problem on human level. In this paper, we partition face images into three different quality sets to evaluate the performance of deep learning methods on cross-quality face images in the wild, and then design a human face verification experiment on these cross-quality data. The result indicates that quality issue still needs to be studied thoroughly in deep learning, human own better capability in building the relations between different face images with large quality gaps, and saying deep learning method surpasses human-level is too optimistic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge