Honggang Qi
MEMTS: Internalizing Domain Knowledge via Parameterized Memory for Retrieval-Free Domain Adaptation of Time Series Foundation Models
Feb 14, 2026Abstract:While Time Series Foundation Models (TSFMs) have demonstrated exceptional performance in generalized forecasting, their performance often degrades significantly when deployed in real-world vertical domains characterized by temporal distribution shifts and domain-specific periodic structures. Current solutions are primarily constrained by two paradigms: Domain-Adaptive Pretraining (DAPT), which improves short-term domain fitting but frequently disrupts previously learned global temporal patterns due to catastrophic forgetting; and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which incorporates external knowledge but introduces substantial retrieval overhead. This creates a severe scalability bottleneck that fails to meet the high-efficiency requirements of real-time stream processing. To break this impasse, we propose Memory for Time Series (MEMTS), a lightweight and plug-and-play method for retrieval-free domain adaptation in time series forecasting. The key component of MEMTS is a Knowledge Persistence Module (KPM), which internalizes domain-specific temporal dynamics, such as recurring seasonal patterns and trends into a compact set of learnable latent prototypes. In doing so, it transforms fragmented historical observations into continuous, parameterized knowledge representations. This paradigm shift enables MEMTS to achieve accurate domain adaptation with constant-time inference and near-zero latency, while effectively mitigating catastrophic forgetting of general temporal patterns, all without requiring any architectural modifications to the frozen TSFM backbone. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate the SOTA performance of MEMTS.
STG: Spatiotemporal Graph Neural Network with Fusion and Spatiotemporal Decoupling Learning for Prognostic Prediction of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis
May 06, 2025Abstract:We propose a multimodal spatiotemporal graph neural network (STG) framework to predict colorectal cancer liver metastasis (CRLM) progression. Current clinical models do not effectively integrate the tumor's spatial heterogeneity, dynamic evolution, and complex multimodal data relationships, limiting their predictive accuracy. Our STG framework combines preoperative CT imaging and clinical data into a heterogeneous graph structure, enabling joint modeling of tumor distribution and temporal evolution through spatial topology and cross-modal edges. The framework uses GraphSAGE to aggregate spatiotemporal neighborhood information and leverages supervised and contrastive learning strategies to enhance the model's ability to capture temporal features and improve robustness. A lightweight version of the model reduces parameter count by 78.55%, maintaining near-state-of-the-art performance. The model jointly optimizes recurrence risk regression and survival analysis tasks, with contrastive loss improving feature representational discriminability and cross-modal consistency. Experimental results on the MSKCC CRLM dataset show a time-adjacent accuracy of 85% and a mean absolute error of 1.1005, significantly outperforming existing methods. The innovative heterogeneous graph construction and spatiotemporal decoupling mechanism effectively uncover the associations between dynamic tumor microenvironment changes and prognosis, providing reliable quantitative support for personalized treatment decisions.
PupiNet: Seamless OCT-OCTA Interconversion Through Wavelet-Driven and Multi-Scale Attention Mechanisms
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) are key diagnostic tools for clinical evaluation and management of retinal diseases. Compared to traditional OCT, OCTA provides richer microvascular information, but its acquisition requires specialized sensors and high-cost equipment, creating significant challenges for the clinical deployment of hardware-dependent OCTA imaging methods. Given the technical complexity of OCTA image acquisition and potential mechanical artifacts, this study proposes a bidirectional image conversion framework called PupiNet, which accurately achieves bidirectional transformation between 3D OCT and 3D OCTA. The generator module of this framework innovatively integrates wavelet transformation and multi-scale attention mechanisms, significantly enhancing image conversion quality. Meanwhile, an Adaptive Discriminator Augmentation (ADA) module has been incorporated into the discriminator to optimize model training stability and convergence efficiency. To ensure clinical accuracy of vascular structures in the converted images, we designed a Vessel Structure Matcher (VSM) supervision module, achieving precise matching of vascular morphology between generated images and target images. Additionally, the Hierarchical Feature Calibration (HFC) module further guarantees high consistency of texture details between generated images and target images across different depth levels. To rigorously validate the clinical effectiveness of the proposed method, we conducted a comprehensive evaluation on a paired OCT-OCTA image dataset containing 300 eyes with various retinal pathologies. Experimental results demonstrate that PupiNet not only reliably achieves high-quality bidirectional transformation between the two modalities but also shows significant advantages in image fidelity, vessel structure preservation, and clinical usability.
4D-ACFNet: A 4D Attention Mechanism-Based Prognostic Framework for Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Integrating Multimodal Spatiotemporal Features
Mar 12, 2025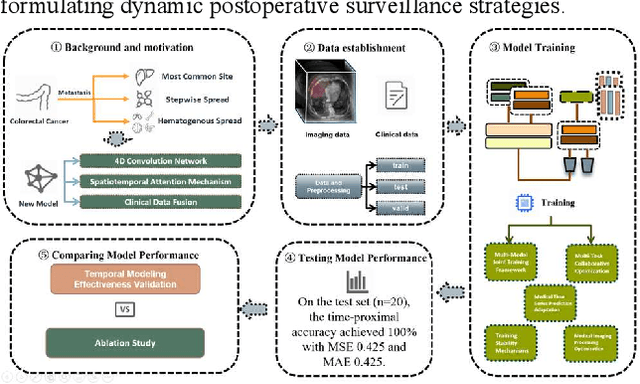

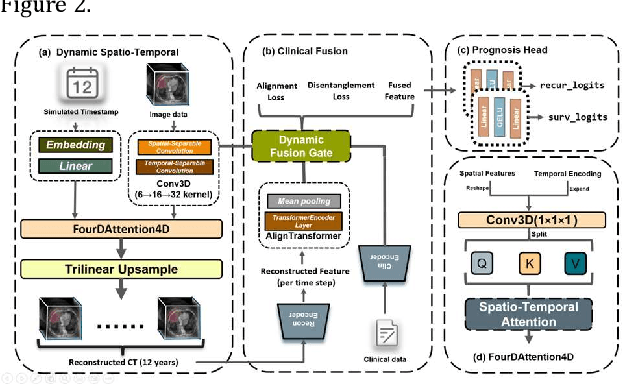

Abstract:Postoperative prognostic prediction for colorectal cancer liver metastasis (CRLM) remains challenging due to tumor heterogeneity, dynamic evolution of the hepatic microenvironment, and insufficient multimodal data fusion. To address these issues, we propose 4D-ACFNet, the first framework that synergistically integrates lightweight spatiotemporal modeling, cross-modal dynamic calibration, and personalized temporal prediction within a unified architecture. Specifically, it incorporates a novel 4D spatiotemporal attention mechanism, which employs spatiotemporal separable convolution (reducing parameter count by 41%) and virtual timestamp encoding to model the interannual evolution patterns of postoperative dynamic processes, such as liver regeneration and steatosis. For cross-modal feature alignment, Transformer layers are integrated to jointly optimize modality alignment loss and disentanglement loss, effectively suppressing scale mismatch and redundant interference in clinical-imaging data. Additionally, we design a dynamic prognostic decision module that generates personalized interannual recurrence risk heatmaps through temporal upsampling and a gated classification head, overcoming the limitations of traditional methods in temporal dynamic modeling and cross-modal alignment. Experiments on 197 CRLM patients demonstrate that the model achieves 100% temporal adjacency accuracy (TAA), with performance significantly surpassing existing approaches. This study establishes the first spatiotemporal modeling paradigm for postoperative dynamic monitoring of CRLM. The proposed framework can be extended to prognostic analysis of multi-cancer metastases, advancing precision surgery from "spatial resection" to "spatiotemporal cure."
A Residual Multi-task Network for Joint Classification and Regression in Medical Imaging
Feb 27, 2025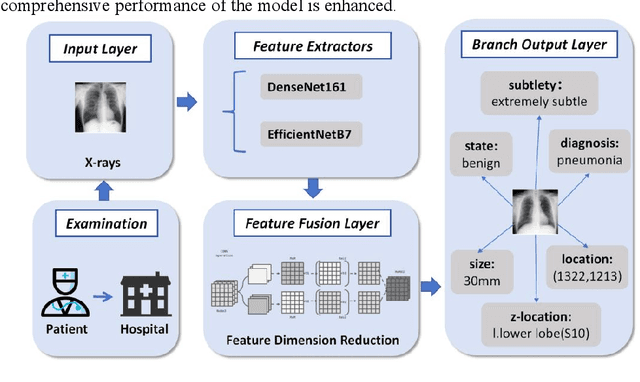
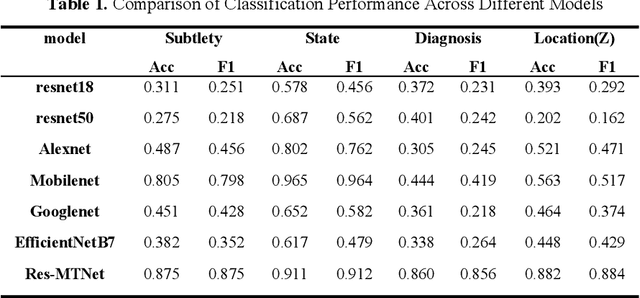
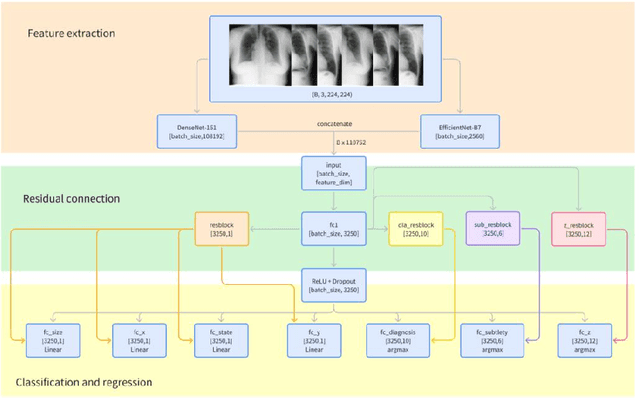
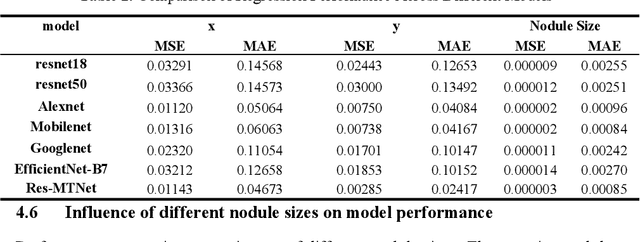
Abstract:Detection and classification of pulmonary nodules is a challenge in medical image analysis due to the variety of shapes and sizes of nodules and their high concealment. Despite the success of traditional deep learning methods in image classification, deep networks still struggle to perfectly capture subtle changes in lung nodule detection. Therefore, we propose a residual multi-task network (Res-MTNet) model, which combines multi-task learning and residual learning, and improves feature representation ability by sharing feature extraction layer and introducing residual connections. Multi-task learning enables the model to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, while the residual module solves the problem of disappearing gradients, ensuring stable training of deeper networks and facilitating information sharing between tasks. Res-MTNet enhances the robustness and accuracy of the model, providing a more reliable lung nodule analysis tool for clinical medicine and telemedicine.
RURANET++: An Unsupervised Learning Method for Diabetic Macular Edema Based on SCSE Attention Mechanisms and Dynamic Multi-Projection Head Clustering
Feb 27, 2025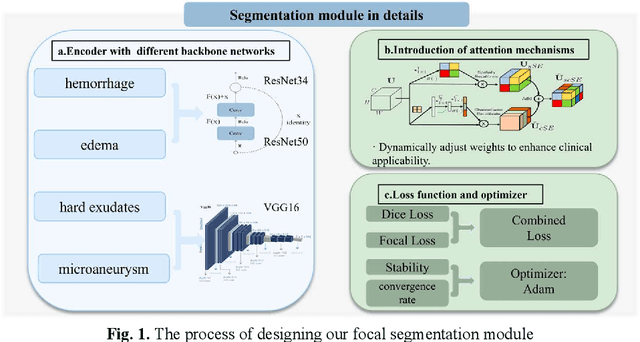
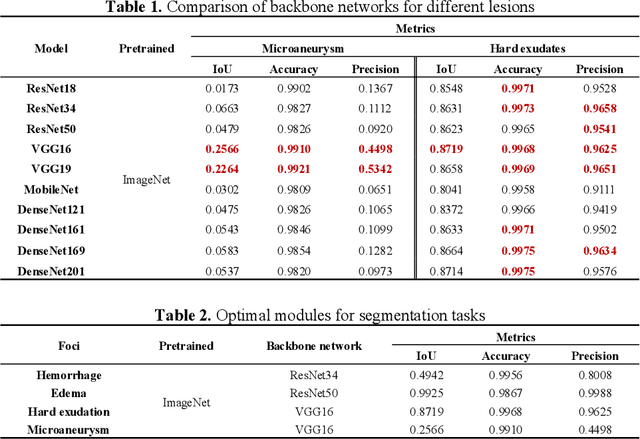
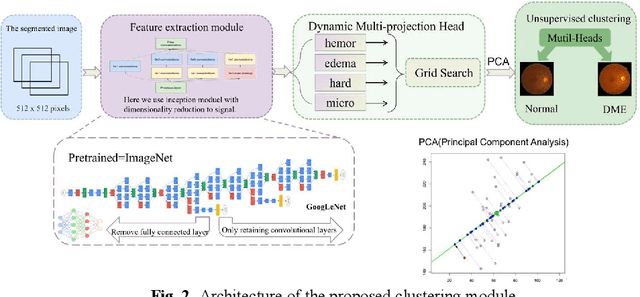
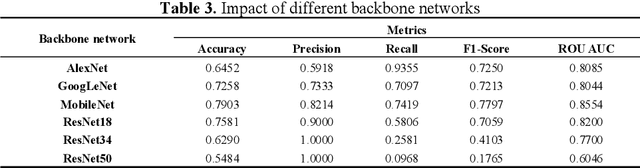
Abstract:Diabetic Macular Edema (DME), a prevalent complication among diabetic patients, constitutes a major cause of visual impairment and blindness. Although deep learning has achieved remarkable progress in medical image analysis, traditional DME diagnosis still relies on extensive annotated data and subjective ophthalmologist assessments, limiting practical applications. To address this, we present RURANET++, an unsupervised learning-based automated DME diagnostic system. This framework incorporates an optimized U-Net architecture with embedded Spatial and Channel Squeeze & Excitation (SCSE) attention mechanisms to enhance lesion feature extraction. During feature processing, a pre-trained GoogLeNet model extracts deep features from retinal images, followed by PCA-based dimensionality reduction to 50 dimensions for computational efficiency. Notably, we introduce a novel clustering algorithm employing multi-projection heads to explicitly control cluster diversity while dynamically adjusting similarity thresholds, thereby optimizing intra-class consistency and inter-class discrimination. Experimental results demonstrate superior performance across multiple metrics, achieving maximum accuracy (0.8411), precision (0.8593), recall (0.8411), and F1-score (0.8390), with exceptional clustering quality. This work provides an efficient unsupervised solution for DME diagnosis with significant clinical implications.
RetinaRegen: A Hybrid Model for Readability and Detail Restoration in Fundus Images
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Fundus image quality is crucial for diagnosing eye diseases, but real-world conditions often result in blurred or unreadable images, increasing diagnostic uncertainty. To address these challenges, this study proposes RetinaRegen, a hybrid model for retinal image restoration that integrates a readability classifi-cation model, a Diffusion Model, and a Variational Autoencoder (VAE). Ex-periments on the SynFundus-1M dataset show that the proposed method achieves a PSNR of 27.4521, an SSIM of 0.9556, and an LPIPS of 0.1911 for the readability labels of the optic disc (RO) region. These results demonstrate superior performance in restoring key regions, offering an effective solution to enhance fundus image quality and support clinical diagnosis.
DynSegNet:Dynamic Architecture Adjustment for Adversarial Learning in Segmenting Hemorrhagic Lesions from Fundus Images
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:The hemorrhagic lesion segmentation plays a critical role in ophthalmic diagnosis, directly influencing early disease detection, treatment planning, and therapeutic efficacy evaluation. However, the task faces significant challenges due to lesion morphological variability, indistinct boundaries, and low contrast with background tissues. To improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes, developing advanced segmentation techniques remains imperative. This paper proposes an adversarial learning-based dynamic architecture adjustment approach that integrates hierarchical U-shaped encoder-decoder, residual blocks, attention mechanisms, and ASPP modules. By dynamically optimizing feature fusion, our method enhances segmentation performance. Experimental results demonstrate a Dice coefficient of 0.6802, IoU of 0.5602, Recall of 0.766, Precision of 0.6525, and Accuracy of 0.9955, effectively addressing the challenges in fundus image hemorrhage segmentation.[* Corresponding author.]
Hints of Prompt: Enhancing Visual Representation for Multimodal LLMs in Autonomous Driving
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:In light of the dynamic nature of autonomous driving environments and stringent safety requirements, general MLLMs combined with CLIP alone often struggle to represent driving-specific scenarios accurately, particularly in complex interactions and long-tail cases. To address this, we propose the Hints of Prompt (HoP) framework, which introduces three key enhancements: Affinity hint to emphasize instance-level structure by strengthening token-wise connections, Semantic hint to incorporate high-level information relevant to driving-specific cases, such as complex interactions among vehicles and traffic signs, and Question hint to align visual features with the query context, focusing on question-relevant regions. These hints are fused through a Hint Fusion module, enriching visual representations and enhancing multimodal reasoning for autonomous driving VQA tasks. Extensive experiments confirm the effectiveness of the HoP framework, showing it significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods across all key metrics.
Active Fake: DeepFake Camouflage
Sep 05, 2024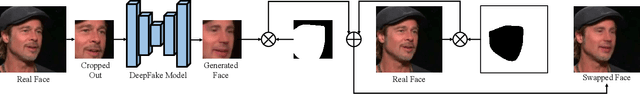
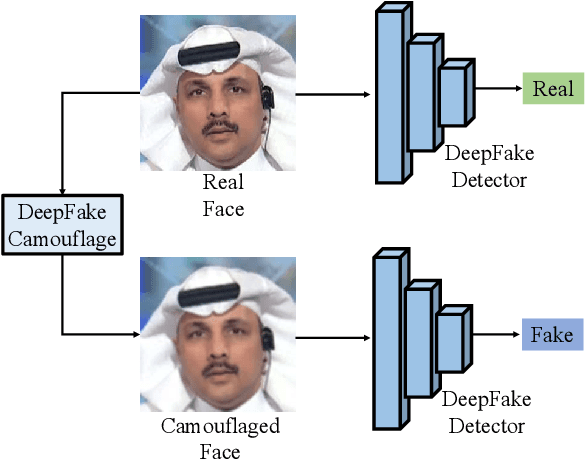
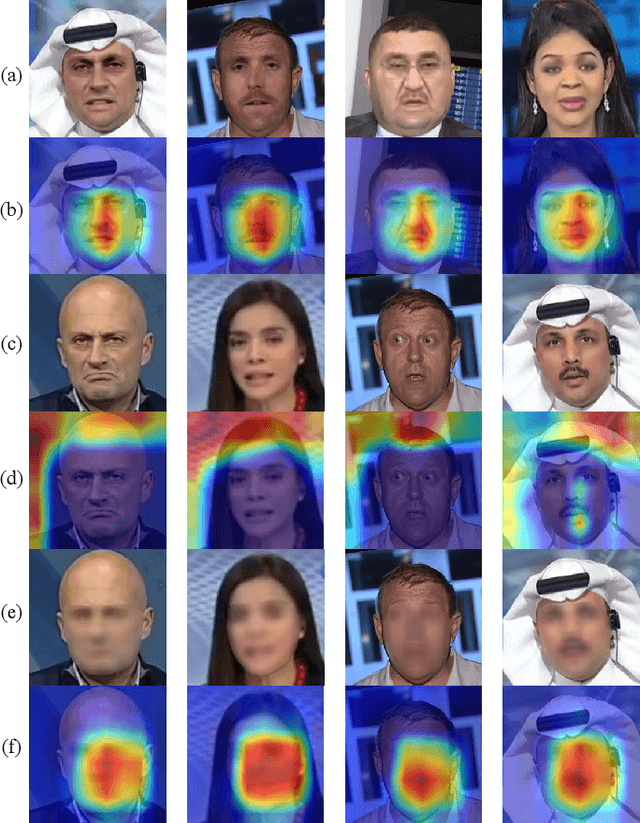
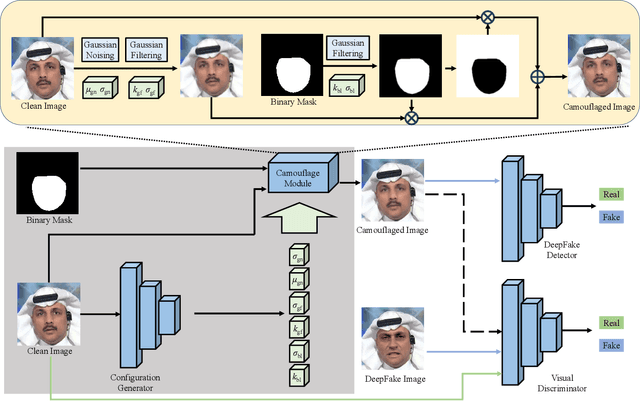
Abstract:DeepFake technology has gained significant attention due to its ability to manipulate facial attributes with high realism, raising serious societal concerns. Face-Swap DeepFake is the most harmful among these techniques, which fabricates behaviors by swapping original faces with synthesized ones. Existing forensic methods, primarily based on Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), effectively expose these manipulations and have become important authenticity indicators. However, these methods mainly concentrate on capturing the blending inconsistency in DeepFake faces, raising a new security issue, termed Active Fake, emerges when individuals intentionally create blending inconsistency in their authentic videos to evade responsibility. This tactic is called DeepFake Camouflage. To achieve this, we introduce a new framework for creating DeepFake camouflage that generates blending inconsistencies while ensuring imperceptibility, effectiveness, and transferability. This framework, optimized via an adversarial learning strategy, crafts imperceptible yet effective inconsistencies to mislead forensic detectors. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our method, highlighting the need for further research in active fake detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge