Hoda Heidari
ETH Zurich
Moral Change or Noise? On Problems of Aligning AI With Temporally Unstable Human Feedback
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Alignment methods in moral domains seek to elicit moral preferences of human stakeholders and incorporate them into AI. This presupposes moral preferences as static targets, but such preferences often evolve over time. Proper alignment of AI to dynamic human preferences should ideally account for "legitimate" changes to moral reasoning, while ignoring changes related to attention deficits, cognitive biases, or other arbitrary factors. However, common AI alignment approaches largely neglect temporal changes in preferences, posing serious challenges to proper alignment, especially in high-stakes applications of AI, e.g., in healthcare domains, where misalignment can jeopardize the trustworthiness of the system and yield serious individual and societal harms. This work investigates the extent to which people's moral preferences change over time, and the impact of such changes on AI alignment. Our study is grounded in the kidney allocation domain, where we elicit responses to pairwise comparisons of hypothetical kidney transplant patients from over 400 participants across 3-5 sessions. We find that, on average, participants change their response to the same scenario presented at different times around 6-20% of the time (exhibiting "response instability"). Additionally, we observe significant shifts in several participants' retrofitted decision-making models over time (capturing "model instability"). The predictive performance of simple AI models decreases as a function of both response and model instability. Moreover, predictive performance diminishes over time, highlighting the importance of accounting for temporal changes in preferences during training. These findings raise fundamental normative and technical challenges relevant to AI alignment, highlighting the need to better understand the object of alignment (what to align to) when user preferences change significantly over time.
Towards Cognitively-Faithful Decision-Making Models to Improve AI Alignment
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Recent AI work trends towards incorporating human-centric objectives, with the explicit goal of aligning AI models to personal preferences and societal values. Using standard preference elicitation methods, researchers and practitioners build models of human decisions and judgments, which are then used to align AI behavior with that of humans. However, models commonly used in such elicitation processes often do not capture the true cognitive processes of human decision making, such as when people use heuristics to simplify information associated with a decision problem. As a result, models learned from people's decisions often do not align with their cognitive processes, and can not be used to validate the learning framework for generalization to other decision-making tasks. To address this limitation, we take an axiomatic approach to learning cognitively faithful decision processes from pairwise comparisons. Building on the vast literature characterizing the cognitive processes that contribute to human decision-making, and recent work characterizing such processes in pairwise comparison tasks, we define a class of models in which individual features are first processed and compared across alternatives, and then the processed features are then aggregated via a fixed rule, such as the Bradley-Terry rule. This structured processing of information ensures such models are realistic and feasible candidates to represent underlying human decision-making processes. We demonstrate the efficacy of this modeling approach in learning interpretable models of human decision making in a kidney allocation task, and show that our proposed models match or surpass the accuracy of prior models of human pairwise decision-making.
Persona-Augmented Benchmarking: Evaluating LLMs Across Diverse Writing Styles
Jul 29, 2025Abstract:Current benchmarks for evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) often do not exhibit enough writing style diversity, with many adhering primarily to standardized conventions. Such benchmarks do not fully capture the rich variety of communication patterns exhibited by humans. Thus, it is possible that LLMs, which are optimized on these benchmarks, may demonstrate brittle performance when faced with "non-standard" input. In this work, we test this hypothesis by rewriting evaluation prompts using persona-based LLM prompting, a low-cost method to emulate diverse writing styles. Our results show that, even with identical semantic content, variations in writing style and prompt formatting significantly impact the estimated performance of the LLM under evaluation. Notably, we identify distinct writing styles that consistently trigger either low or high performance across a range of models and tasks, irrespective of model family, size, and recency. Our work offers a scalable approach to augment existing benchmarks, improving the external validity of the assessments they provide for measuring LLM performance across linguistic variations.
The Backfiring Effect of Weak AI Safety Regulation
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Recent policy proposals aim to improve the safety of general-purpose AI, but there is little understanding of the efficacy of different regulatory approaches to AI safety. We present a strategic model that explores the interactions between the regulator, the general-purpose AI technology creators, and domain specialists--those who adapt the AI for specific applications. Our analysis examines how different regulatory measures, targeting different parts of the development chain, affect the outcome of the development process. In particular, we assume AI technology is described by two key attributes: safety and performance. The regulator first sets a minimum safety standard that applies to one or both players, with strict penalties for non-compliance. The general-purpose creator then develops the technology, establishing its initial safety and performance levels. Next, domain specialists refine the AI for their specific use cases, and the resulting revenue is distributed between the specialist and generalist through an ex-ante bargaining process. Our analysis of this game reveals two key insights: First, weak safety regulation imposed only on the domain specialists can backfire. While it might seem logical to regulate use cases (as opposed to the general-purpose technology), our analysis shows that weak regulations targeting domain specialists alone can unintentionally reduce safety. This effect persists across a wide range of settings. Second, in sharp contrast to the previous finding, we observe that stronger, well-placed regulation can in fact benefit all players subjected to it. When regulators impose appropriate safety standards on both AI creators and domain specialists, the regulation functions as a commitment mechanism, leading to safety and performance gains, surpassing what is achieved under no regulation or regulating one player only.
Can AI Model the Complexities of Human Moral Decision-Making? A Qualitative Study of Kidney Allocation Decisions
Mar 02, 2025Abstract:A growing body of work in Ethical AI attempts to capture human moral judgments through simple computational models. The key question we address in this work is whether such simple AI models capture {the critical} nuances of moral decision-making by focusing on the use case of kidney allocation. We conducted twenty interviews where participants explained their rationale for their judgments about who should receive a kidney. We observe participants: (a) value patients' morally-relevant attributes to different degrees; (b) use diverse decision-making processes, citing heuristics to reduce decision complexity; (c) can change their opinions; (d) sometimes lack confidence in their decisions (e.g., due to incomplete information); and (e) express enthusiasm and concern regarding AI assisting humans in kidney allocation decisions. Based on these findings, we discuss challenges of computationally modeling moral judgments {as a stand-in for human input}, highlight drawbacks of current approaches, and suggest future directions to address these issues.
International AI Safety Report
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:The first International AI Safety Report comprehensively synthesizes the current evidence on the capabilities, risks, and safety of advanced AI systems. The report was mandated by the nations attending the AI Safety Summit in Bletchley, UK. Thirty nations, the UN, the OECD, and the EU each nominated a representative to the report's Expert Advisory Panel. A total of 100 AI experts contributed, representing diverse perspectives and disciplines. Led by the report's Chair, these independent experts collectively had full discretion over the report's content.
Public Procurement for Responsible AI? Understanding U.S. Cities' Practices, Challenges, and Needs
Nov 07, 2024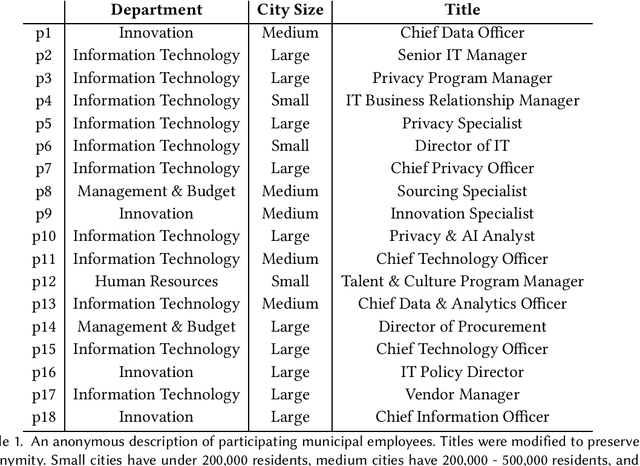
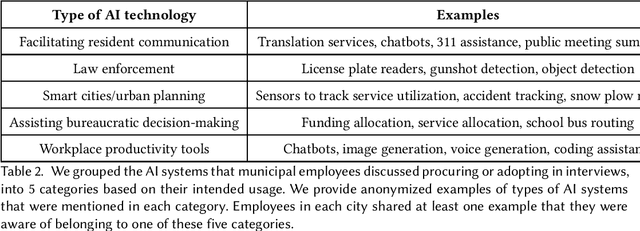
Abstract:Most AI tools adopted by governments are not developed internally, but instead are acquired from third-party vendors in a process called public procurement. While scholars and regulatory proposals have recently turned towards procurement as a site of intervention to encourage responsible AI governance practices, little is known about the practices and needs of city employees in charge of AI procurement. In this paper, we present findings from semi-structured interviews with 18 city employees across 7 US cities. We find that AI acquired by cities often does not go through a conventional public procurement process, posing challenges to oversight and governance. We identify five key types of challenges to leveraging procurement for responsible AI that city employees face when interacting with colleagues, AI vendors, and members of the public. We conclude by discussing recommendations and implications for governments, researchers, and policymakers.
Rethinking Distance Metrics for Counterfactual Explainability
Oct 18, 2024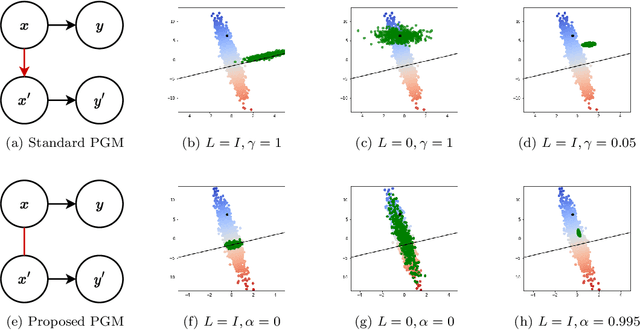
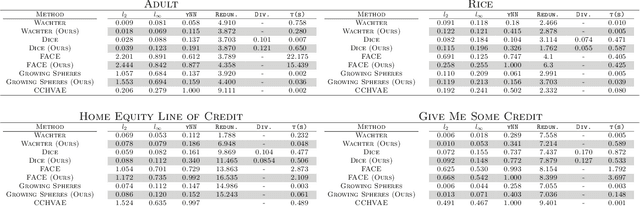
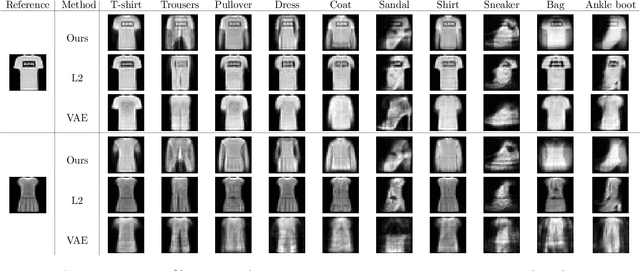
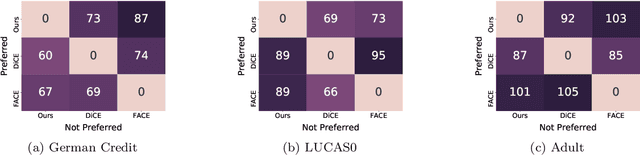
Abstract:Counterfactual explanations have been a popular method of post-hoc explainability for a variety of settings in Machine Learning. Such methods focus on explaining classifiers by generating new data points that are similar to a given reference, while receiving a more desirable prediction. In this work, we investigate a framing for counterfactual generation methods that considers counterfactuals not as independent draws from a region around the reference, but as jointly sampled with the reference from the underlying data distribution. Through this framing, we derive a distance metric, tailored for counterfactual similarity that can be applied to a broad range of settings. Through both quantitative and qualitative analyses of counterfactual generation methods, we show that this framing allows us to express more nuanced dependencies among the covariates.
'Simulacrum of Stories': Examining Large Language Models as Qualitative Research Participants
Sep 28, 2024Abstract:The recent excitement around generative models has sparked a wave of proposals suggesting the replacement of human participation and labor in research and development--e.g., through surveys, experiments, and interviews--with synthetic research data generated by large language models (LLMs). We conducted interviews with 19 qualitative researchers to understand their perspectives on this paradigm shift. Initially skeptical, researchers were surprised to see similar narratives emerge in the LLM-generated data when using the interview probe. However, over several conversational turns, they went on to identify fundamental limitations, such as how LLMs foreclose participants' consent and agency, produce responses lacking in palpability and contextual depth, and risk delegitimizing qualitative research methods. We argue that the use of LLMs as proxies for participants enacts the surrogate effect, raising ethical and epistemological concerns that extend beyond the technical limitations of current models to the core of whether LLMs fit within qualitative ways of knowing.
On The Stability of Moral Preferences: A Problem with Computational Elicitation Methods
Aug 05, 2024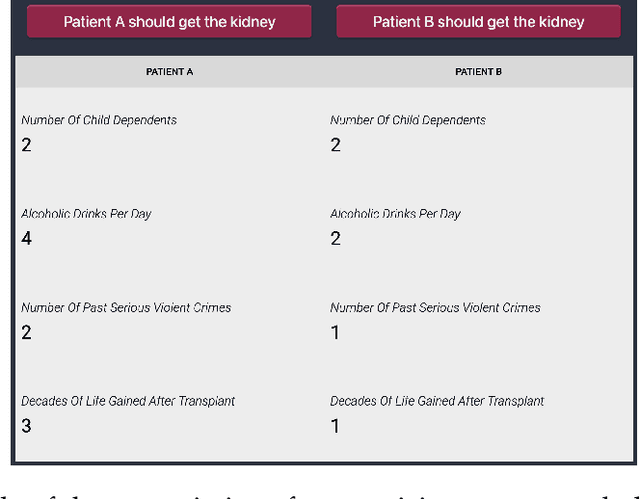
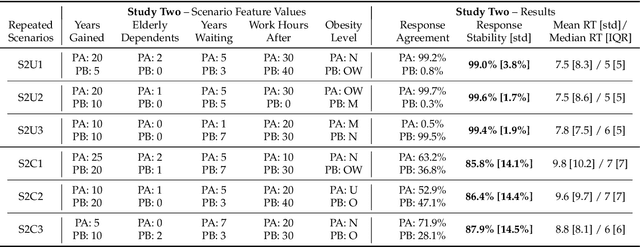
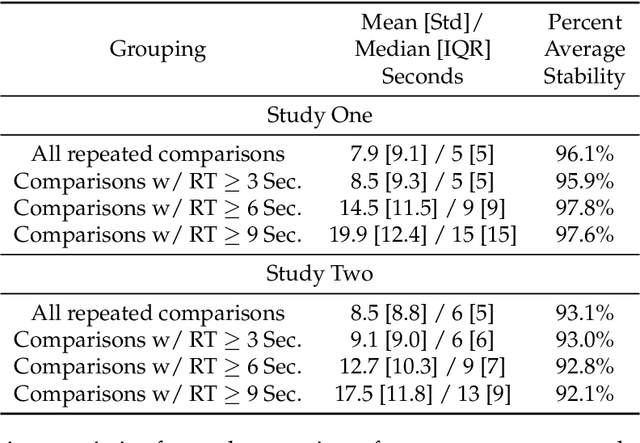
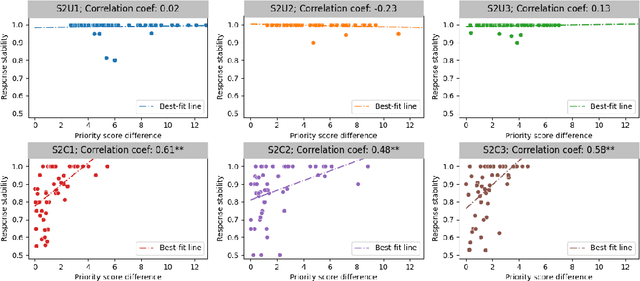
Abstract:Preference elicitation frameworks feature heavily in the research on participatory ethical AI tools and provide a viable mechanism to enquire and incorporate the moral values of various stakeholders. As part of the elicitation process, surveys about moral preferences, opinions, and judgments are typically administered only once to each participant. This methodological practice is reasonable if participants' responses are stable over time such that, all other relevant factors being held constant, their responses today will be the same as their responses to the same questions at a later time. However, we do not know how often that is the case. It is possible that participants' true moral preferences change, are subject to temporary moods or whims, or are influenced by environmental factors we don't track. If participants' moral responses are unstable in such ways, it would raise important methodological and theoretical issues for how participants' true moral preferences, opinions, and judgments can be ascertained. We address this possibility here by asking the same survey participants the same moral questions about which patient should receive a kidney when only one is available ten times in ten different sessions over two weeks, varying only presentation order across sessions. We measured how often participants gave different responses to simple (Study One) and more complicated (Study Two) repeated scenarios. On average, the fraction of times participants changed their responses to controversial scenarios was around 10-18% across studies, and this instability is observed to have positive associations with response time and decision-making difficulty. We discuss the implications of these results for the efficacy of moral preference elicitation, highlighting the role of response instability in causing value misalignment between stakeholders and AI tools trained on their moral judgments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge