Anna Kawakami
Studying Up Public Sector AI: How Networks of Power Relations Shape Agency Decisions Around AI Design and Use
May 21, 2024Abstract:As public sector agencies rapidly introduce new AI tools in high-stakes domains like social services, it becomes critical to understand how decisions to adopt these tools are made in practice. We borrow from the anthropological practice to ``study up'' those in positions of power, and reorient our study of public sector AI around those who have the power and responsibility to make decisions about the role that AI tools will play in their agency. Through semi-structured interviews and design activities with 16 agency decision-makers, we examine how decisions about AI design and adoption are influenced by their interactions with and assumptions about other actors within these agencies (e.g., frontline workers and agency leaders), as well as those above (legal systems and contracted companies), and below (impacted communities). By centering these networks of power relations, our findings shed light on how infrastructural, legal, and social factors create barriers and disincentives to the involvement of a broader range of stakeholders in decisions about AI design and adoption. Agency decision-makers desired more practical support for stakeholder involvement around public sector AI to help overcome the knowledge and power differentials they perceived between them and other stakeholders (e.g., frontline workers and impacted community members). Building on these findings, we discuss implications for future research and policy around actualizing participatory AI approaches in public sector contexts.
Training Towards Critical Use: Learning to Situate AI Predictions Relative to Human Knowledge
Aug 30, 2023



Abstract:A growing body of research has explored how to support humans in making better use of AI-based decision support, including via training and onboarding. Existing research has focused on decision-making tasks where it is possible to evaluate "appropriate reliance" by comparing each decision against a ground truth label that cleanly maps to both the AI's predictive target and the human decision-maker's goals. However, this assumption does not hold in many real-world settings where AI tools are deployed today (e.g., social work, criminal justice, and healthcare). In this paper, we introduce a process-oriented notion of appropriate reliance called critical use that centers the human's ability to situate AI predictions against knowledge that is uniquely available to them but unavailable to the AI model. To explore how training can support critical use, we conduct a randomized online experiment in a complex social decision-making setting: child maltreatment screening. We find that, by providing participants with accelerated, low-stakes opportunities to practice AI-assisted decision-making in this setting, novices came to exhibit patterns of disagreement with AI that resemble those of experienced workers. A qualitative examination of participants' explanations for their AI-assisted decisions revealed that they drew upon qualitative case narratives, to which the AI model did not have access, to learn when (not) to rely on AI predictions. Our findings open new questions for the study and design of training for real-world AI-assisted decision-making.
Recentering Validity Considerations through Early-Stage Deliberations Around AI and Policy Design
Mar 26, 2023Abstract:AI-based decision-making tools are rapidly spreading across a range of real-world, complex domains like healthcare, criminal justice, and child welfare. A growing body of research has called for increased scrutiny around the validity of AI system designs. However, in real-world settings, it is often not possible to fully address questions around the validity of an AI tool without also considering the design of associated organizational and public policies. Yet, considerations around how an AI tool may interface with policy are often only discussed retrospectively, after the tool is designed or deployed. In this short position paper, we discuss opportunities to promote multi-stakeholder deliberations around the design of AI-based technologies and associated policies, at the earliest stages of a new project.
Can Workers Meaningfully Consent to Workplace Wellbeing Technologies?
Mar 13, 2023


Abstract:Sensing technologies deployed in the workplace can collect detailed data about individual activities and group interactions that are otherwise difficult to capture. A hopeful application of these technologies is that they can help businesses and workers optimize productivity and wellbeing. However, given the inherent and structural power dynamics in the workplace, the prevalent approach of accepting tacit compliance to monitor work activities rather than seeking workers' meaningful consent raises privacy and ethical concerns. This paper unpacks a range of challenges that workers face when consenting to workplace wellbeing technologies. Using a hypothetical case to prompt reflection among six multi-stakeholder focus groups involving 15 participants, we explored participants' expectations and capacity to consent to workplace sensing technologies. We sketched possible interventions that could better support more meaningful consent to workplace wellbeing technologies by drawing on critical computing and feminist scholarship -- which reframes consent from a purely individual choice to a structural condition experienced at the individual level that needs to be freely given, reversible, informed, enthusiastic, and specific (FRIES). The focus groups revealed that workers are vulnerable to meaningless consent -- dynamics that undo the value of data gathered in the name of "wellbeing," as well as an erosion of autonomy in the workplace. To meaningfully consent, participants wanted changes to how the technology works and is being used, as well as to the policies and practices surrounding the technology. Our mapping of what prevents workers from meaningfully consenting to workplace wellbeing technologies (challenges) and what they require to do so (interventions) underscores that the lack of meaningful consent is a structural problem requiring socio-technical solutions.
A Validity Perspective on Evaluating the Justified Use of Data-driven Decision-making Algorithms
Jun 30, 2022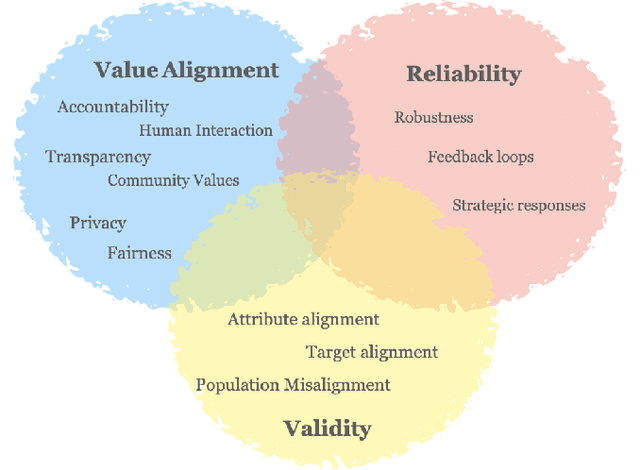
Abstract:This work seeks to center validity considerations in deliberations around whether and how to build data-driven algorithms in high-stakes domains. Toward this end, we translate key concepts from validity theory to predictive algorithms. We describe common challenges in problem formulation and data issues that jeopardize the validity of predictive algorithms. We distill these issues into a series of high-level questions intended to promote and document reflections on the legitimacy of the predictive task and the suitability of the data. This contribution lays the foundation for co-designing a validity protocol, in collaboration with real-world stakeholders, including decision-makers, modelers, and members of potentially impacted communities, to critically evaluate the justifiability of specific designs and uses of data-driven algorithmic systems.
Improving Human-AI Partnerships in Child Welfare: Understanding Worker Practices, Challenges, and Desires for Algorithmic Decision Support
Apr 05, 2022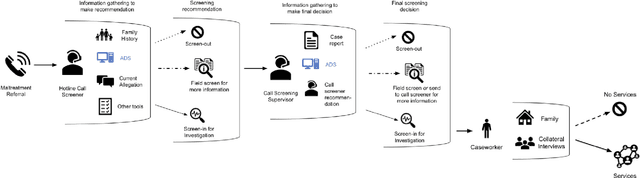
Abstract:AI-based decision support tools (ADS) are increasingly used to augment human decision-making in high-stakes, social contexts. As public sector agencies begin to adopt ADS, it is critical that we understand workers' experiences with these systems in practice. In this paper, we present findings from a series of interviews and contextual inquiries at a child welfare agency, to understand how they currently make AI-assisted child maltreatment screening decisions. Overall, we observe how workers' reliance upon the ADS is guided by (1) their knowledge of rich, contextual information beyond what the AI model captures, (2) their beliefs about the ADS's capabilities and limitations relative to their own, (3) organizational pressures and incentives around the use of the ADS, and (4) awareness of misalignments between algorithmic predictions and their own decision-making objectives. Drawing upon these findings, we discuss design implications towards supporting more effective human-AI decision-making.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge