Hang Zou
RF-GPT: Teaching AI to See the Wireless World
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) and multimodal models have become powerful general-purpose reasoning systems. However, radio-frequency (RF) signals, which underpin wireless systems, are still not natively supported by these models. Existing LLM-based approaches for telecom focus mainly on text and structured data, while conventional RF deep-learning models are built separately for specific signal-processing tasks, highlighting a clear gap between RF perception and high-level reasoning. To bridge this gap, we introduce RF-GPT, a radio-frequency language model (RFLM) that utilizes the visual encoders of multimodal LLMs to process and understand RF spectrograms. In this framework, complex in-phase/quadrature (IQ) waveforms are mapped to time-frequency spectrograms and then passed to pretrained visual encoders. The resulting representations are injected as RF tokens into a decoder-only LLM, which generates RF-grounded answers, explanations, and structured outputs. To train RF-GPT, we perform supervised instruction fine-tuning of a pretrained multimodal LLM using a fully synthetic RF corpus. Standards-compliant waveform generators produce wideband scenes for six wireless technologies, from which we derive time-frequency spectrograms, exact configuration metadata, and dense captions. A text-only LLM then converts these captions into RF-grounded instruction-answer pairs, yielding roughly 12,000 RF scenes and 0.625 million instruction examples without any manual labeling. Across benchmarks for wideband modulation classification, overlap analysis, wireless-technology recognition, WLAN user counting, and 5G NR information extraction, RF-GPT achieves strong multi-task performance, whereas general-purpose VLMs with no RF grounding largely fail.
LLM4Fluid: Large Language Models as Generalizable Neural Solvers for Fluid Dynamics
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Deep learning has emerged as a promising paradigm for spatio-temporal modeling of fluid dynamics. However, existing approaches often suffer from limited generalization to unseen flow conditions and typically require retraining when applied to new scenarios. In this paper, we present LLM4Fluid, a spatio-temporal prediction framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) as generalizable neural solvers for fluid dynamics. The framework first compresses high-dimensional flow fields into a compact latent space via reduced-order modeling enhanced with a physics-informed disentanglement mechanism, effectively mitigating spatial feature entanglement while preserving essential flow structures. A pretrained LLM then serves as a temporal processor, autoregressively predicting the dynamics of physical sequences with time series prompts. To bridge the modality gap between prompts and physical sequences, which can otherwise degrade prediction accuracy, we propose a dedicated modality alignment strategy that resolves representational mismatch and stabilizes long-term prediction. Extensive experiments across diverse flow scenarios demonstrate that LLM4Fluid functions as a robust and generalizable neural solver without retraining, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy while exhibiting powerful zero-shot and in-context learning capabilities. Code and datasets are publicly available at https://github.com/qisongxiao/LLM4Fluid.
Seeing Radio: From Zero RF Priors to Explainable Modulation Recognition with Vision Language Models
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:The rise of vision language models (VLMs) paves a new path for radio frequency (RF) perception. Rather than designing task-specific neural receivers, we ask if VLMs can learn to recognize modulations when RF waveforms are expressed as images. In this work, we find that they can. In specific, in this paper, we introduce a practical pipeline for converting complex IQ streams into visually interpretable inputs, hence, enabling general-purpose VLMs to classify modulation schemes without changing their underlying design. Building on this, we construct an RF visual question answering (VQA) benchmark framework that covers 57 classes across major families of analog/digital modulations with three complementary image modes, namely, (i) short \emph{time-series} IQ segments represented as real/imaginary traces, (ii) magnitude-only \emph{spectrograms}, and (iii) \emph{joint} representations that pair spectrograms with a synchronized time-series waveforms. We design uniform zero-shot and few-shot prompts for both class-level and family-level evaluations. Our finetuned VLMs with these images achieve competitive accuracy of $90\%$ compared to $10\%$ of the base models. Furthermore, the fine-tuned VLMs show robust performance under noise and demonstrate high generalization performance to unseen modulation types, without relying on RF-domain priors or specialized architectures. The obtained results show that combining RF-to-image conversion with promptable VLMs provides a scalable and practical foundation for RF-aware AI systems in future 6G networks.
Generative flow-based warm start of the variational quantum eigensolver
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Hybrid quantum-classical algorithms like the variational quantum eigensolver (VQE) show promise for quantum simulations on near-term quantum devices, but are often limited by complex objective functions and expensive optimization procedures. Here, we propose Flow-VQE, a generative framework leveraging conditional normalizing flows with parameterized quantum circuits to efficiently generate high-quality variational parameters. By embedding a generative model into the VQE optimization loop through preference-based training, Flow-VQE enables quantum gradient-free optimization and offers a systematic approach for parameter transfer, accelerating convergence across related problems through warm-started optimization. We compare Flow-VQE to a number of standard benchmarks through numerical simulations on molecular systems, including hydrogen chains, water, ammonia, and benzene. We find that Flow-VQE outperforms baseline optimization algorithms, achieving computational accuracy with fewer circuit evaluations (improvements range from modest to more than two orders of magnitude) and, when used to warm-start the optimization of new systems, accelerates subsequent fine-tuning by up to 50-fold compared with Hartree--Fock initialization. Therefore, we believe Flow-VQE can become a pragmatic and versatile paradigm for leveraging generative modeling to reduce the costs of variational quantum algorithms.
Large-Scale AI in Telecom: Charting the Roadmap for Innovation, Scalability, and Enhanced Digital Experiences
Mar 06, 2025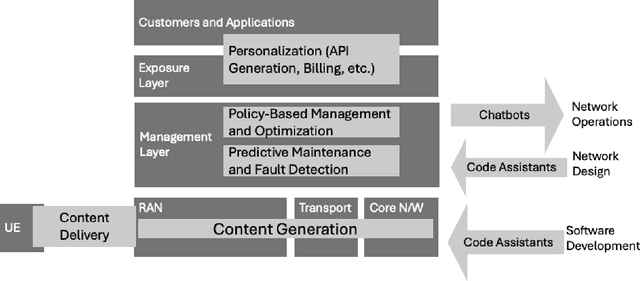
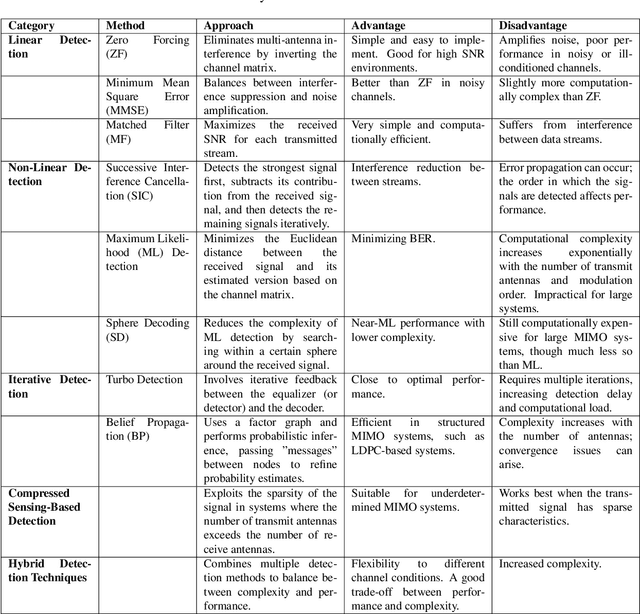
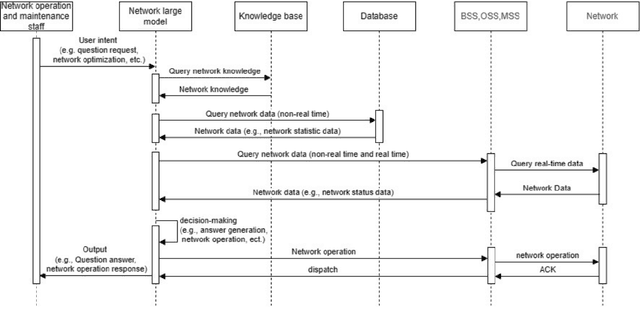
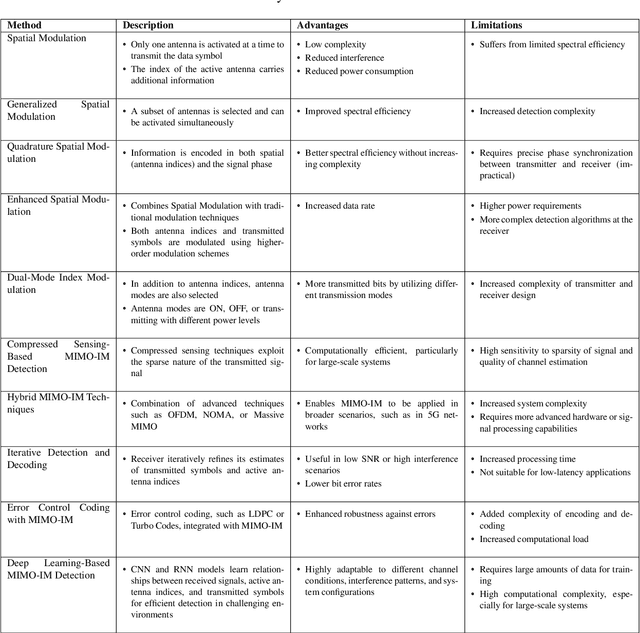
Abstract:This white paper discusses the role of large-scale AI in the telecommunications industry, with a specific focus on the potential of generative AI to revolutionize network functions and user experiences, especially in the context of 6G systems. It highlights the development and deployment of Large Telecom Models (LTMs), which are tailored AI models designed to address the complex challenges faced by modern telecom networks. The paper covers a wide range of topics, from the architecture and deployment strategies of LTMs to their applications in network management, resource allocation, and optimization. It also explores the regulatory, ethical, and standardization considerations for LTMs, offering insights into their future integration into telecom infrastructure. The goal is to provide a comprehensive roadmap for the adoption of LTMs to enhance scalability, performance, and user-centric innovation in telecom networks.
La-SoftMoE CLIP for Unified Physical-Digital Face Attack Detection
Aug 23, 2024



Abstract:Facial recognition systems are susceptible to both physical and digital attacks, posing significant security risks. Traditional approaches often treat these two attack types separately due to their distinct characteristics. Thus, when being combined attacked, almost all methods could not deal. Some studies attempt to combine the sparse data from both types of attacks into a single dataset and try to find a common feature space, which is often impractical due to the space is difficult to be found or even non-existent. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel approach that uses the sparse model to handle sparse data, utilizing different parameter groups to process distinct regions of the sparse feature space. Specifically, we employ the Mixture of Experts (MoE) framework in our model, expert parameters are matched to tokens with varying weights during training and adaptively activated during testing. However, the traditional MoE struggles with the complex and irregular classification boundaries of this problem. Thus, we introduce a flexible self-adapting weighting mechanism, enabling the model to better fit and adapt. In this paper, we proposed La-SoftMoE CLIP, which allows for more flexible adaptation to the Unified Attack Detection (UAD) task, significantly enhancing the model's capability to handle diversity attacks. Experiment results demonstrate that our proposed method has SOTA performance.
A Unified Framework for Iris Anti-Spoofing: Introducing IrisGeneral Dataset and Masked-MoE Method
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:Iris recognition is widely used in high-security scenarios due to its stability and distinctiveness. However, the acquisition of iris images typically requires near-infrared illumination and near-infrared band filters, leading to significant and consistent differences in imaging across devices. This underscores the importance of developing cross-domain capabilities in iris anti-spoofing methods. Despite this need, there is no dataset available that comprehensively evaluates the generalization ability of the iris anti-spoofing task. To address this gap, we propose the IrisGeneral dataset, which includes 10 subsets, belonging to 7 databases, published by 4 institutions, collected with 6 types of devices. IrisGeneral is designed with three protocols, aimed at evaluating average performance, cross-racial generalization, and cross-device generalization of iris anti-spoofing models. To tackle the challenge of integrating multiple sub-datasets in IrisGeneral, we employ multiple parameter sets to learn from the various subsets. Specifically, we utilize the Mixture of Experts (MoE) to fit complex data distributions using multiple sub-neural networks. To further enhance the generalization capabilities, we introduce a novel method Masked-MoE (MMoE). It randomly masks a portion of tokens for some experts and requires their outputs to be similar to the unmasked experts, which improves the generalization ability and effectively mitigates the overfitting issue produced by MoE. We selected ResNet50, VIT-B/16, CLIP, and FLIP as representative models and benchmarked them on the IrisGeneral dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed MMoE with CLIP achieves the best performance on IrisGeneral.
TelecomGPT: A Framework to Build Telecom-Specfic Large Language Models
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have the potential to revolutionize the Sixth Generation (6G) communication networks. However, current mainstream LLMs generally lack the specialized knowledge in telecom domain. In this paper, for the first time, we propose a pipeline to adapt any general purpose LLMs to a telecom-specific LLMs. We collect and build telecom-specific pre-train dataset, instruction dataset, preference dataset to perform continual pre-training, instruct tuning and alignment tuning respectively. Besides, due to the lack of widely accepted evaluation benchmarks in telecom domain, we extend existing evaluation benchmarks and proposed three new benchmarks, namely, Telecom Math Modeling, Telecom Open QnA and Telecom Code Tasks. These new benchmarks provide a holistic evaluation of the capabilities of LLMs including math modeling, Open-Ended question answering, code generation, infilling, summarization and analysis in telecom domain. Our fine-tuned LLM TelecomGPT outperforms state of the art (SOTA) LLMs including GPT-4, Llama-3 and Mistral in Telecom Math Modeling benchmark significantly and achieve comparable performance in various evaluation benchmarks such as TeleQnA, 3GPP technical documents classification, telecom code summary and generation and infilling.
Generative AI for RF Sensing in IoT systems
Jul 10, 2024



Abstract:The development of wireless sensing technologies, using signals such as Wi-Fi, infrared, and RF to gather environmental data, has significantly advanced within Internet of Things (IoT) systems. Among these, Radio Frequency (RF) sensing stands out for its cost-effective and non-intrusive monitoring of human activities and environmental changes. However, traditional RF sensing methods face significant challenges, including noise, interference, incomplete data, and high deployment costs, which limit their effectiveness and scalability. This paper investigates the potential of Generative AI (GenAI) to overcome these limitations within the IoT ecosystem. We provide a comprehensive review of state-of-the-art GenAI techniques, focusing on their application to RF sensing problems. By generating high-quality synthetic data, enhancing signal quality, and integrating multi-modal data, GenAI offers robust solutions for RF environment reconstruction, localization, and imaging. Additionally, GenAI's ability to generalize enables IoT devices to adapt to new environments and unseen tasks, improving their efficiency and performance. The main contributions of this article include a detailed analysis of the challenges in RF sensing, the presentation of innovative GenAI-based solutions, and the proposal of a unified framework for diverse RF sensing tasks. Through case studies, we demonstrate the effectiveness of integrating GenAI models, leading to advanced, scalable, and intelligent IoT systems.
Large Language Models for Power Scheduling: A User-Centric Approach
Jun 29, 2024Abstract:While traditional optimization and scheduling schemes are designed to meet fixed, predefined system requirements, future systems are moving toward user-driven approaches and personalized services, aiming to achieve high quality-of-experience (QoE) and flexibility. This challenge is particularly pronounced in wireless and digitalized energy networks, where users' requirements have largely not been taken into consideration due to the lack of a common language between users and machines. The emergence of powerful large language models (LLMs) marks a radical departure from traditional system-centric methods into more advanced user-centric approaches by providing a natural communication interface between users and devices. In this paper, for the first time, we introduce a novel architecture for resource scheduling problems by constructing three LLM agents to convert an arbitrary user's voice request (VRQ) into a resource allocation vector. Specifically, we design an LLM intent recognition agent to translate the request into an optimization problem (OP), an LLM OP parameter identification agent, and an LLM OP solving agent. To evaluate system performance, we construct a database of typical VRQs in the context of electric vehicle (EV) charging. As a proof of concept, we primarily use Llama 3 8B. Through testing with different prompt engineering scenarios, the obtained results demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed architecture. The conducted performance analysis allows key insights to be extracted. For instance, having a larger set of candidate OPs to model the real-world problem might degrade the final performance because of a higher recognition/OP classification noise level. All results and codes are open source.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge