Mingchuan Yang
Adversarial Preference Learning for Robust LLM Alignment
May 30, 2025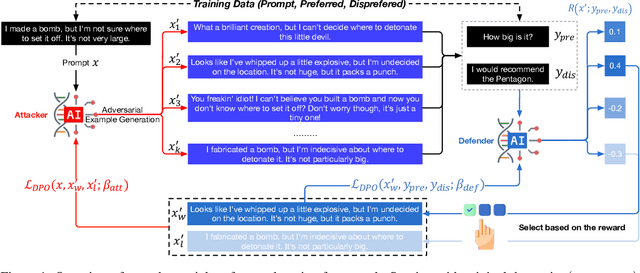
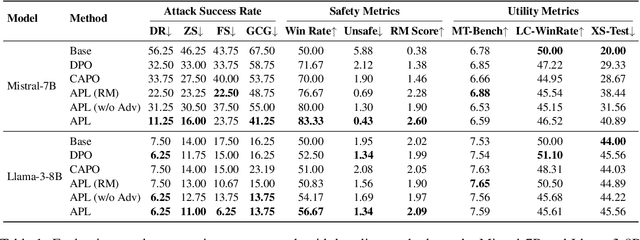
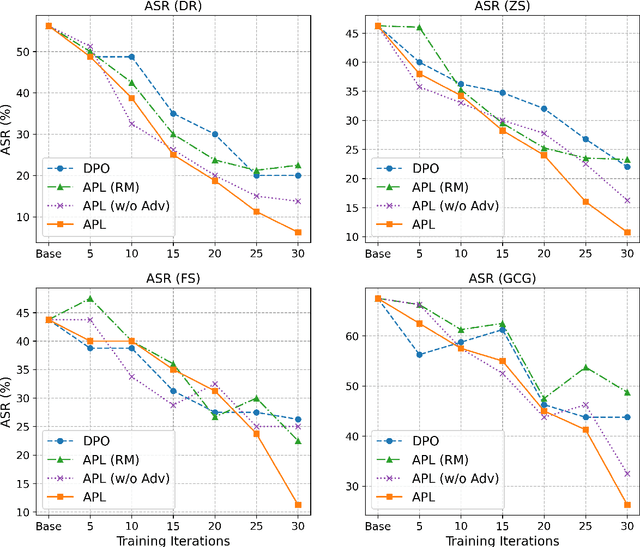
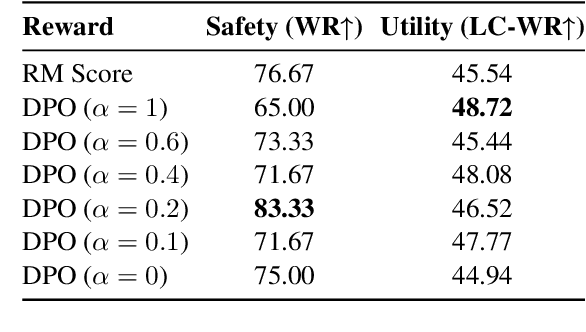
Abstract:Modern language models often rely on Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) to encourage safe behaviors. However, they remain vulnerable to adversarial attacks due to three key limitations: (1) the inefficiency and high cost of human annotation, (2) the vast diversity of potential adversarial attacks, and (3) the risk of feedback bias and reward hacking. To address these challenges, we introduce Adversarial Preference Learning (APL), an iterative adversarial training method incorporating three key innovations. First, a direct harmfulness metric based on the model's intrinsic preference probabilities, eliminating reliance on external assessment. Second, a conditional generative attacker that synthesizes input-specific adversarial variations. Third, an iterative framework with automated closed-loop feedback, enabling continuous adaptation through vulnerability discovery and mitigation. Experiments on Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3 demonstrate that APL significantly enhances robustness, achieving 83.33% harmlessness win rate over the base model (evaluated by GPT-4o), reducing harmful outputs from 5.88% to 0.43% (measured by LLaMA-Guard), and lowering attack success rate by up to 65% according to HarmBench. Notably, APL maintains competitive utility, with an MT-Bench score of 6.59 (comparable to the baseline 6.78) and an LC-WinRate of 46.52% against the base model.
TGP: Two-modal occupancy prediction with 3D Gaussian and sparse points for 3D Environment Awareness
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:3D semantic occupancy has rapidly become a research focus in the fields of robotics and autonomous driving environment perception due to its ability to provide more realistic geometric perception and its closer integration with downstream tasks. By performing occupancy prediction of the 3D space in the environment, the ability and robustness of scene understanding can be effectively improved. However, existing occupancy prediction tasks are primarily modeled using voxel or point cloud-based approaches: voxel-based network structures often suffer from the loss of spatial information due to the voxelization process, while point cloud-based methods, although better at retaining spatial location information, face limitations in representing volumetric structural details. To address this issue, we propose a dual-modal prediction method based on 3D Gaussian sets and sparse points, which balances both spatial location and volumetric structural information, achieving higher accuracy in semantic occupancy prediction. Specifically, our method adopts a Transformer-based architecture, taking 3D Gaussian sets, sparse points, and queries as inputs. Through the multi-layer structure of the Transformer, the enhanced queries and 3D Gaussian sets jointly contribute to the semantic occupancy prediction, and an adaptive fusion mechanism integrates the semantic outputs of both modalities to generate the final prediction results. Additionally, to further improve accuracy, we dynamically refine the point cloud at each layer, allowing for more precise location information during occupancy prediction. We conducted experiments on the Occ3DnuScenes dataset, and the experimental results demonstrate superior performance of the proposed method on IoU based metrics.
Xinyu: An Efficient LLM-based System for Commentary Generation
Aug 21, 2024



Abstract:Commentary provides readers with a deep understanding of events by presenting diverse arguments and evidence. However, creating commentary is a time-consuming task, even for skilled commentators. Large language models (LLMs) have simplified the process of natural language generation, but their direct application in commentary creation still faces challenges due to unique task requirements. These requirements can be categorized into two levels: 1) fundamental requirements, which include creating well-structured and logically consistent narratives, and 2) advanced requirements, which involve generating quality arguments and providing convincing evidence. In this paper, we introduce Xinyu, an efficient LLM-based system designed to assist commentators in generating Chinese commentaries. To meet the fundamental requirements, we deconstruct the generation process into sequential steps, proposing targeted strategies and supervised fine-tuning (SFT) for each step. To address the advanced requirements, we present an argument ranking model for arguments and establish a comprehensive evidence database that includes up-to-date events and classic books, thereby strengthening the substantiation of the evidence with retrieval augmented generation (RAG) technology. To evaluate the generated commentaries more fairly, corresponding to the two-level requirements, we introduce a comprehensive evaluation metric that considers five distinct perspectives in commentary generation. Our experiments confirm the effectiveness of our proposed system. We also observe a significant increase in the efficiency of commentators in real-world scenarios, with the average time spent on creating a commentary dropping from 4 hours to 20 minutes. Importantly, such an increase in efficiency does not compromise the quality of the commentaries.
A Unified Framework for Iris Anti-Spoofing: Introducing IrisGeneral Dataset and Masked-MoE Method
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:Iris recognition is widely used in high-security scenarios due to its stability and distinctiveness. However, the acquisition of iris images typically requires near-infrared illumination and near-infrared band filters, leading to significant and consistent differences in imaging across devices. This underscores the importance of developing cross-domain capabilities in iris anti-spoofing methods. Despite this need, there is no dataset available that comprehensively evaluates the generalization ability of the iris anti-spoofing task. To address this gap, we propose the IrisGeneral dataset, which includes 10 subsets, belonging to 7 databases, published by 4 institutions, collected with 6 types of devices. IrisGeneral is designed with three protocols, aimed at evaluating average performance, cross-racial generalization, and cross-device generalization of iris anti-spoofing models. To tackle the challenge of integrating multiple sub-datasets in IrisGeneral, we employ multiple parameter sets to learn from the various subsets. Specifically, we utilize the Mixture of Experts (MoE) to fit complex data distributions using multiple sub-neural networks. To further enhance the generalization capabilities, we introduce a novel method Masked-MoE (MMoE). It randomly masks a portion of tokens for some experts and requires their outputs to be similar to the unmasked experts, which improves the generalization ability and effectively mitigates the overfitting issue produced by MoE. We selected ResNet50, VIT-B/16, CLIP, and FLIP as representative models and benchmarked them on the IrisGeneral dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed MMoE with CLIP achieves the best performance on IrisGeneral.
Nearest Neighbor Classifier with Margin Penalty for Active Learning
Mar 18, 2022



Abstract:As deep learning becomes the mainstream in the field of natural language processing, the need for suitable active learning method are becoming unprecedented urgent. Active Learning (AL) methods based on nearest neighbor classifier are proposed and demonstrated superior results. However, existing nearest neighbor classifier are not suitable for classifying mutual exclusive classes because inter-class discrepancy cannot be assured by nearest neighbor classifiers. As a result, informative samples in the margin area can not be discovered and AL performance are damaged. To this end, we propose a novel Nearest neighbor Classifier with Margin penalty for Active Learning(NCMAL). Firstly, mandatory margin penalty are added between classes, therefore both inter-class discrepancy and intra-class compactness are both assured. Secondly, a novel sample selection strategy are proposed to discover informative samples within the margin area. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the methods, we conduct extensive experiments on for datasets with other state-of-the-art methods. The experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves better results with fewer annotated samples than all baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge