Guokan Shang
École Polytechnique, Linagora
GreekMMLU: A Native-Sourced Multitask Benchmark for Evaluating Language Models in Greek
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are commonly trained on multilingual corpora that include Greek, yet reliable evaluation benchmarks for Greek-particularly those based on authentic, native-sourced content-remain limited. Existing datasets are often machine-translated from English, failing to capture Greek linguistic and cultural characteristics. We introduce GreekMMLU, a native-sourced benchmark for massive multitask language understanding in Greek, comprising 21,805 multiple-choice questions across 45 subject areas, organized under a newly defined subject taxonomy and annotated with educational difficulty levels spanning primary to professional examinations. All questions are sourced or authored in Greek from academic, professional, and governmental exams. We publicly release 16,857 samples and reserve 4,948 samples for a private leaderboard to enable robust and contamination-resistant evaluation. Evaluations of over 80 open- and closed-source LLMs reveal substantial performance gaps between frontier and open-weight models, as well as between Greek-adapted models and general multilingual ones. Finally, we provide a systematic analysis of factors influencing performance-including model scale, adaptation, and prompting-and derive insights for improving LLM capabilities in Greek.
YaPO: Learnable Sparse Activation Steering Vectors for Domain Adaptation
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Steering Large Language Models (LLMs) through activation interventions has emerged as a lightweight alternative to fine-tuning for alignment and personalization. Recent work on Bi-directional Preference Optimization (BiPO) shows that dense steering vectors can be learned directly from preference data in a Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) fashion, enabling control over truthfulness, hallucinations, and safety behaviors. However, dense steering vectors often entangle multiple latent factors due to neuron multi-semanticity, limiting their effectiveness and stability in fine-grained settings such as cultural alignment, where closely related values and behaviors (e.g., among Middle Eastern cultures) must be distinguished. In this paper, we propose Yet another Policy Optimization (YaPO), a \textit{reference-free} method that learns \textit{sparse steering vectors} in the latent space of a Sparse Autoencoder (SAE). By optimizing sparse codes, YaPO produces disentangled, interpretable, and efficient steering directions. Empirically, we show that YaPO converges faster, achieves stronger performance, and exhibits improved training stability compared to dense steering baselines. Beyond cultural alignment, YaPO generalizes to a range of alignment-related behaviors, including hallucination, wealth-seeking, jailbreak, and power-seeking. Importantly, YaPO preserves general knowledge, with no measurable degradation on MMLU. Overall, our results show that YaPO provides a general recipe for efficient, stable, and fine-grained alignment of LLMs, with broad applications to controllability and domain adaptation. The associated code and data are publicly available\footnote{https://github.com/MBZUAI-Paris/YaPO}.
MixtureKit: A General Framework for Composing, Training, and Visualizing Mixture-of-Experts Models
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:We introduce MixtureKit, a modular open-source framework for constructing, training, and analyzing Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models from arbitrary pre-trained or fine-tuned models. MixtureKit currently supports three complementary methods: (i) \emph{Traditional MoE}, which uses a single router per transformer block to select experts, (ii) \emph{BTX} (Branch-Train-Mix), which introduces separate routers for each specified sub-layer enabling fine-grained token routing, and (iii) \emph{BTS} (Branch-Train-Stitch), which keeps experts fully intact and introduces trainable stitch layers for controlled information exchange between hub and experts. MixtureKit automatically modifies the model configuration, patches decoder and causal LM classes, and saves a unified checkpoint ready for inference or fine-tuning. We further provide a visualization interface to inspect per-token routing decisions, expert weight distributions, and layer-wise contributions. Experiments with multilingual code-switched data (e.g. Arabic-Latin) show that a BTX-based model trained using MixtureKit can outperform baseline dense models on multiple benchmarks. We release MixtureKit as a practical foundation for research and development of MoE-based systems across diverse domains.
Beyond Random Sampling: Efficient Language Model Pretraining via Curriculum Learning
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Curriculum learning has shown promise in improving training efficiency and generalization in various machine learning domains, yet its potential in pretraining language models remains underexplored, prompting our work as the first systematic investigation in this area. We experimented with different settings, including vanilla curriculum learning, pacing-based sampling, and interleaved curricula-guided by six difficulty metrics spanning linguistic and information-theoretic perspectives. We train models under these settings and evaluate their performance on eight diverse benchmarks. Our experiments reveal that curriculum learning consistently improves convergence in early and mid-training phases, and can yield lasting gains when used as a warmup strategy with up to $3.5\%$ improvement. Notably, we identify compression ratio, lexical diversity, and readability as effective difficulty signals across settings. Our findings highlight the importance of data ordering in large-scale pretraining and provide actionable insights for scalable, data-efficient model development under realistic training scenarios.
LLM as a Broken Telephone: Iterative Generation Distorts Information
Feb 27, 2025
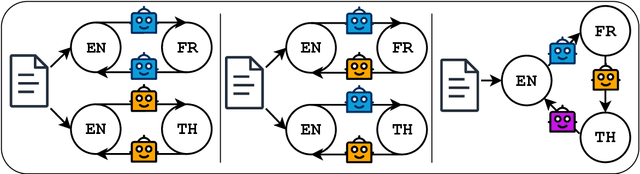
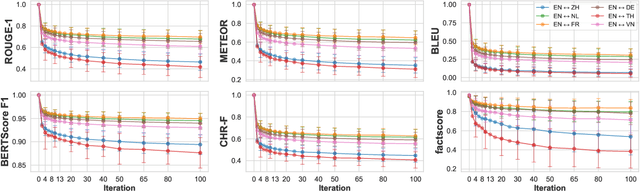
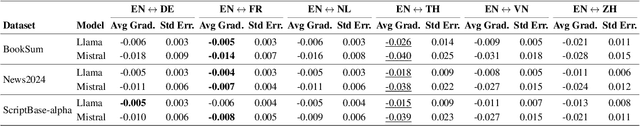
Abstract:As large language models are increasingly responsible for online content, concerns arise about the impact of repeatedly processing their own outputs. Inspired by the "broken telephone" effect in chained human communication, this study investigates whether LLMs similarly distort information through iterative generation. Through translation-based experiments, we find that distortion accumulates over time, influenced by language choice and chain complexity. While degradation is inevitable, it can be mitigated through strategic prompting techniques. These findings contribute to discussions on the long-term effects of AI-mediated information propagation, raising important questions about the reliability of LLM-generated content in iterative workflows.
Benchmarking Linguistic Diversity of Large Language Models
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:The development and evaluation of Large Language Models (LLMs) has primarily focused on their task-solving capabilities, with recent models even surpassing human performance in some areas. However, this focus often neglects whether machine-generated language matches the human level of diversity, in terms of vocabulary choice, syntactic construction, and expression of meaning, raising questions about whether the fundamentals of language generation have been fully addressed. This paper emphasizes the importance of examining the preservation of human linguistic richness by language models, given the concerning surge in online content produced or aided by LLMs. We propose a comprehensive framework for evaluating LLMs from various linguistic diversity perspectives including lexical, syntactic, and semantic dimensions. Using this framework, we benchmark several state-of-the-art LLMs across all diversity dimensions, and conduct an in-depth case study for syntactic diversity. Finally, we analyze how different development and deployment choices impact the linguistic diversity of LLM outputs.
Graph Linearization Methods for Reasoning on Graphs with Large Language Models
Oct 25, 2024



Abstract:Large language models have evolved to process multiple modalities beyond text, such as images and audio, which motivates us to explore how to effectively leverage them for graph machine learning tasks. The key question, therefore, is how to transform graphs into linear sequences of tokens, a process we term graph linearization, so that LLMs can handle graphs naturally. We consider that graphs should be linearized meaningfully to reflect certain properties of natural language text, such as local dependency and global alignment, in order to ease contemporary LLMs, trained on trillions of textual tokens, better understand graphs. To achieve this, we developed several graph linearization methods based on graph centrality, degeneracy, and node relabeling schemes. We then investigated their effect on LLM performance in graph reasoning tasks. Experimental results on synthetic graphs demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods compared to random linearization baselines. Our work introduces novel graph representations suitable for LLMs, contributing to the potential integration of graph machine learning with the trend of multi-modal processing using a unified transformer model.
Atlas-Chat: Adapting Large Language Models for Low-Resource Moroccan Arabic Dialect
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:We introduce Atlas-Chat, the first-ever collection of large language models specifically developed for dialectal Arabic. Focusing on Moroccan Arabic, also known as Darija, we construct our instruction dataset by consolidating existing Darija language resources, creating novel datasets both manually and synthetically, and translating English instructions with stringent quality control. Atlas-Chat-9B and 2B models, fine-tuned on the dataset, exhibit superior ability in following Darija instructions and performing standard NLP tasks. Notably, our models outperform both state-of-the-art and Arabic-specialized LLMs like LLaMa, Jais, and AceGPT, e.g., achieving a 13% performance boost over a larger 13B model on DarijaMMLU, in our newly introduced evaluation suite for Darija covering both discriminative and generative tasks. Furthermore, we perform an experimental analysis of various fine-tuning strategies and base model choices to determine optimal configurations. All our resources are publicly accessible, and we believe our work offers comprehensive design methodologies of instruction-tuning for low-resource language variants, which are often neglected in favor of data-rich languages by contemporary LLMs.
Leveraging Discourse Structure for Extractive Meeting Summarization
May 21, 2024Abstract:We introduce an extractive summarization system for meetings that leverages discourse structure to better identify salient information from complex multi-party discussions. Using discourse graphs to represent semantic relations between the contents of utterances in a meeting, we train a GNN-based node classification model to select the most important utterances, which are then combined to create an extractive summary. Experimental results on AMI and ICSI demonstrate that our approach surpasses existing text-based and graph-based extractive summarization systems, as measured by both classification and summarization metrics. Additionally, we conduct ablation studies on discourse structure and relation type to provide insights for future NLP applications leveraging discourse analysis theory.
FREDSum: A Dialogue Summarization Corpus for French Political Debates
Dec 08, 2023Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning, and especially the invention of encoder-decoder architectures, has significantly improved the performance of abstractive summarization systems. The majority of research has focused on written documents, however, neglecting the problem of multi-party dialogue summarization. In this paper, we present a dataset of French political debates for the purpose of enhancing resources for multi-lingual dialogue summarization. Our dataset consists of manually transcribed and annotated political debates, covering a range of topics and perspectives. We highlight the importance of high quality transcription and annotations for training accurate and effective dialogue summarization models, and emphasize the need for multilingual resources to support dialogue summarization in non-English languages. We also provide baseline experiments using state-of-the-art methods, and encourage further research in this area to advance the field of dialogue summarization. Our dataset will be made publicly available for use by the research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge