Mingmeng Geng
On the Detectability of LLM-Generated Text: What Exactly Is LLM-Generated Text?
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:With the widespread use of large language models (LLMs), many researchers have turned their attention to detecting text generated by them. However, there is no consistent or precise definition of their target, namely "LLM-generated text". Differences in usage scenarios and the diversity of LLMs further increase the difficulty of detection. What is commonly regarded as the detecting target usually represents only a subset of the text that LLMs can potentially produce. Human edits to LLM outputs, together with the subtle influences that LLMs exert on their users, are blurring the line between LLM-generated and human-written text. Existing benchmarks and evaluation approaches do not adequately address the various conditions in real-world detector applications. Hence, the numerical results of detectors are often misunderstood, and their significance is diminishing. Therefore, detectors remain useful under specific conditions, but their results should be interpreted only as references rather than decisive indicators.
code_transformed: The Influence of Large Language Models on Code
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Coding remains one of the most fundamental modes of interaction between humans and machines. With the rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs), code generation capabilities have begun to significantly reshape programming practices. This development prompts a central question: Have LLMs transformed code style, and how can such transformation be characterized? In this paper, we present a pioneering study that investigates the impact of LLMs on code style, with a focus on naming conventions, complexity, maintainability, and similarity. By analyzing code from over 19,000 GitHub repositories linked to arXiv papers published between 2020 and 2025, we identify measurable trends in the evolution of coding style that align with characteristics of LLM-generated code. For instance, the proportion of snake\_case variable names in Python code increased from 47% in Q1 2023 to 51% in Q1 2025. Furthermore, we investigate how LLMs approach algorithmic problems by examining their reasoning processes. Given the diversity of LLMs and usage scenarios, among other factors, it is difficult or even impossible to precisely estimate the proportion of code generated or assisted by LLMs. Our experimental results provide the first large-scale empirical evidence that LLMs affect real-world programming style.
Wikipedia in the Era of LLMs: Evolution and Risks
Mar 04, 2025

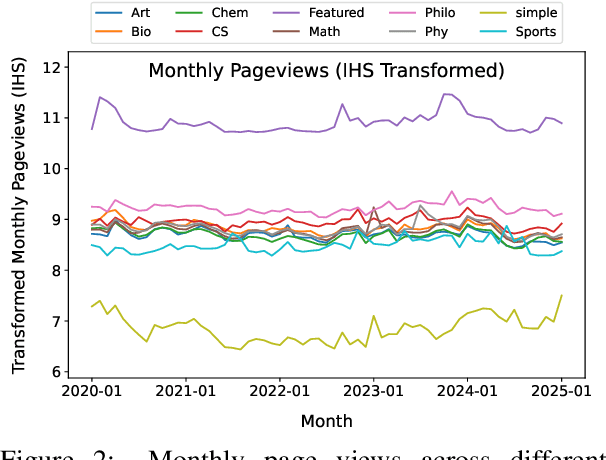

Abstract:In this paper, we present a thorough analysis of the impact of Large Language Models (LLMs) on Wikipedia, examining the evolution of Wikipedia through existing data and using simulations to explore potential risks. We begin by analyzing page views and article content to study Wikipedia's recent changes and assess the impact of LLMs. Subsequently, we evaluate how LLMs affect various Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks related to Wikipedia, including machine translation and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). Our findings and simulation results reveal that Wikipedia articles have been influenced by LLMs, with an impact of approximately 1%-2% in certain categories. If the machine translation benchmark based on Wikipedia is influenced by LLMs, the scores of the models may become inflated, and the comparative results among models might shift as well. Moreover, the effectiveness of RAG might decrease if the knowledge base becomes polluted by LLM-generated content. While LLMs have not yet fully changed Wikipedia's language and knowledge structures, we believe that our empirical findings signal the need for careful consideration of potential future risks.
LLM as a Broken Telephone: Iterative Generation Distorts Information
Feb 27, 2025
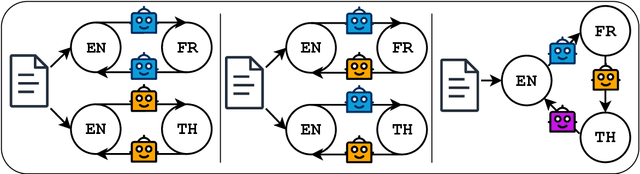
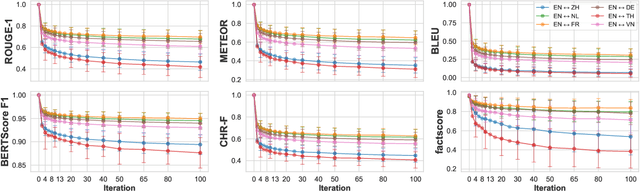
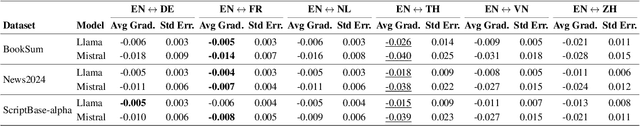
Abstract:As large language models are increasingly responsible for online content, concerns arise about the impact of repeatedly processing their own outputs. Inspired by the "broken telephone" effect in chained human communication, this study investigates whether LLMs similarly distort information through iterative generation. Through translation-based experiments, we find that distortion accumulates over time, influenced by language choice and chain complexity. While degradation is inevitable, it can be mitigated through strategic prompting techniques. These findings contribute to discussions on the long-term effects of AI-mediated information propagation, raising important questions about the reliability of LLM-generated content in iterative workflows.
Human-LLM Coevolution: Evidence from Academic Writing
Feb 13, 2025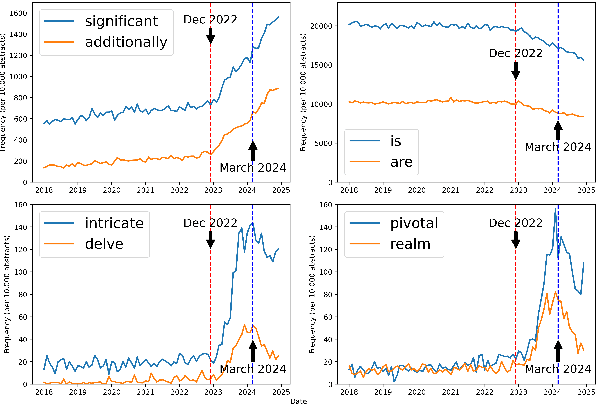

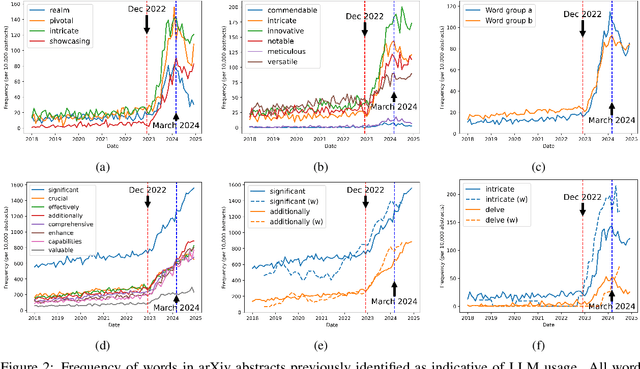
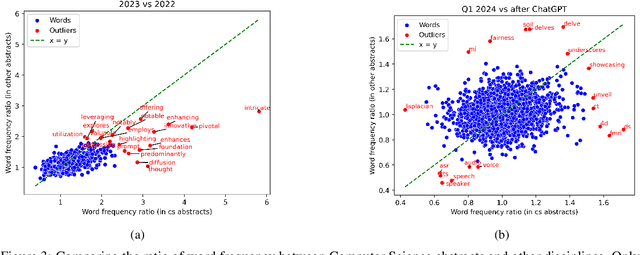
Abstract:With a statistical analysis of arXiv paper abstracts, we report a marked drop in the frequency of several words previously identified as overused by ChatGPT, such as "delve", starting soon after they were pointed out in early 2024. The frequency of certain other words favored by ChatGPT, such as "significant", has instead kept increasing. These phenomena suggest that some authors of academic papers have adapted their use of large language models (LLMs), for example, by selecting outputs or applying modifications to the LLM-generated content. Such coevolution and cooperation of humans and LLMs thus introduce additional challenges to the detection of machine-generated text in real-world scenarios. Estimating the impact of LLMs on academic writing by examining word frequency remains feasible, and more attention should be paid to words that were already frequently employed, including those that have decreased in frequency.
The Impact of Large Language Models in Academia: from Writing to Speaking
Sep 20, 2024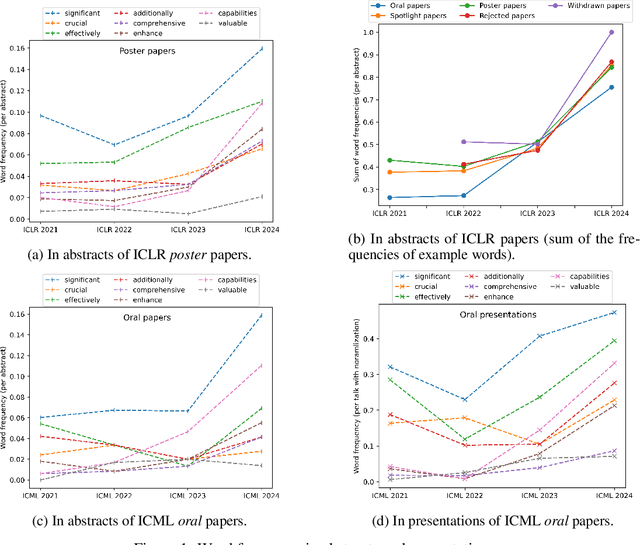

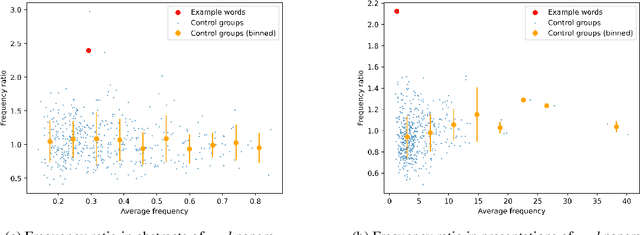

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly impacting human society, particularly in textual information. Based on more than 30,000 papers and 1,000 presentations from machine learning conferences, we examined and compared the words used in writing and speaking, representing the first large-scale investigating study of how LLMs influence the two main modes of verbal communication and expression within the same group of people. Our empirical results show that LLM-style words such as "significant" have been used more frequently in abstracts and oral presentations. The impact on speaking is beginning to emerge and is likely to grow in the future, calling attention to the implicit influence and ripple effect of LLMs on human society.
Are Large Language Models Chameleons?
May 29, 2024


Abstract:Do large language models (LLMs) have their own worldviews and personality tendencies? Simulations in which an LLM was asked to answer subjective questions were conducted more than 1 million times. Comparison of the responses from different LLMs with real data from the European Social Survey (ESS) suggests that the effect of prompts on bias and variability is fundamental, highlighting major cultural, age, and gender biases. Methods for measuring the difference between LLMs and survey data are discussed, such as calculating weighted means and a new proposed measure inspired by Jaccard similarity. We conclude that it is important to analyze the robustness and variability of prompts before using LLMs to model individual decisions or collective behavior, as their imitation abilities are approximate at best.
Is ChatGPT Transforming Academics' Writing Style?
Apr 12, 2024



Abstract:Based on one million arXiv papers submitted from May 2018 to January 2024, we assess the textual density of ChatGPT's writing style in their abstracts by means of a statistical analysis of word frequency changes. Our model is calibrated and validated on a mixture of real abstracts and ChatGPT-modified abstracts (simulated data) after a careful noise analysis. We find that ChatGPT is having an increasing impact on arXiv abstracts, especially in the field of computer science, where the fraction of ChatGPT-revised abstracts is estimated to be approximately 35%, if we take the output of one of the simplest prompts, "revise the following sentences", as a baseline. We conclude with an analysis of both positive and negative aspects of the penetration of ChatGPT into academics' writing style.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge