Caixi Chen
Interleaved Scene Graph for Interleaved Text-and-Image Generation Assessment
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Many real-world user queries (e.g. "How do to make egg fried rice?") could benefit from systems capable of generating responses with both textual steps with accompanying images, similar to a cookbook. Models designed to generate interleaved text and images face challenges in ensuring consistency within and across these modalities. To address these challenges, we present ISG, a comprehensive evaluation framework for interleaved text-and-image generation. ISG leverages a scene graph structure to capture relationships between text and image blocks, evaluating responses on four levels of granularity: holistic, structural, block-level, and image-specific. This multi-tiered evaluation allows for a nuanced assessment of consistency, coherence, and accuracy, and provides interpretable question-answer feedback. In conjunction with ISG, we introduce a benchmark, ISG-Bench, encompassing 1,150 samples across 8 categories and 21 subcategories. This benchmark dataset includes complex language-vision dependencies and golden answers to evaluate models effectively on vision-centric tasks such as style transfer, a challenging area for current models. Using ISG-Bench, we demonstrate that recent unified vision-language models perform poorly on generating interleaved content. While compositional approaches that combine separate language and image models show a 111% improvement over unified models at the holistic level, their performance remains suboptimal at both block and image levels. To facilitate future work, we develop ISG-Agent, a baseline agent employing a "plan-execute-refine" pipeline to invoke tools, achieving a 122% performance improvement.
The Impact of Large Language Models in Academia: from Writing to Speaking
Sep 20, 2024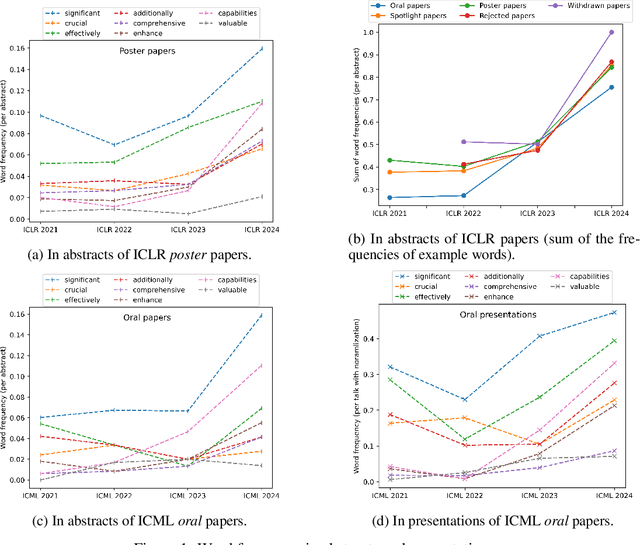

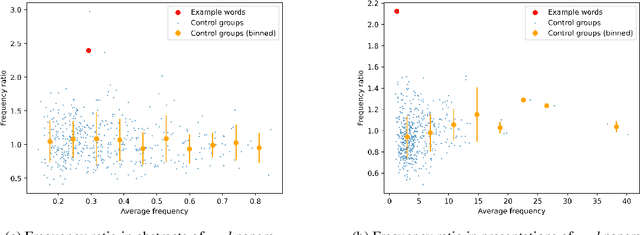

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly impacting human society, particularly in textual information. Based on more than 30,000 papers and 1,000 presentations from machine learning conferences, we examined and compared the words used in writing and speaking, representing the first large-scale investigating study of how LLMs influence the two main modes of verbal communication and expression within the same group of people. Our empirical results show that LLM-style words such as "significant" have been used more frequently in abstracts and oral presentations. The impact on speaking is beginning to emerge and is likely to grow in the future, calling attention to the implicit influence and ripple effect of LLMs on human society.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge