Faez Ahmed
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
TabPFN for Zero-shot Parametric Engineering Design Generation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Deep generative models for engineering design often require substantial computational cost, large training datasets, and extensive retraining when design requirements or datasets change, limiting their applicability in real-world engineering design workflow. In this work, we propose a zero-shot generation framework for parametric engineering design based on TabPFN, enabling conditional design generation using only a limited number of reference samples and without any task-specific model training or fine-tuning. The proposed method generates design parameters sequentially conditioned on target performance indicators, providing a flexible alternative to conventional generative models. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is evaluated on three engineering design datasets, i.e., ship hull design, BlendedNet aircraft, and UIUC airfoil. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves competitive diversity across highly structured parametric design spaces, remains robust to variations in sampling, resolution and parameter dimensionality of geometry generation, and achieves a low performance error (e.g., less than 2% in generated ship hull designs' performance). Compared with diffusion-based generative models, the proposed framework significantly reduces computational overhead and data requirements while preserving reliable generation performance. These results highlight the potential of zero-shot, data-efficient generation as a practical and efficient tool for engineering design, enabling rapid deployment, flexible adaptation to new design settings, and ease of integration into real-world engineering workflows.
FIRE: Multi-fidelity Regression with Distribution-conditioned In-context Learning using Tabular Foundation Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Multi-fidelity (MF) regression often operates in regimes of extreme data imbalance, where the commonly-used Gaussian-process (GP) surrogates struggle with cubic scaling costs and overfit to sparse high-fidelity observations, limiting efficiency and generalization in real-world applications. We introduce FIRE, a training-free MF framework that couples tabular foundation models (TFMs) to perform zero-shot in-context Bayesian inference via a high-fidelity correction model conditioned on the low-fidelity model's posterior predictive distributions. This cross-fidelity information transfer via distributional summaries captures heteroscedastic errors, enabling robust residual learning without model retraining. Across 31 benchmark problems spanning synthetic and real-world tasks (e.g., DrivAerNet, LCBench), FIRE delivers a stronger performance-time trade-off than seven state-of-the-art GP-based or deep learning MF regression methods, ranking highest in accuracy and uncertainty quantification with runtime advantages. Limitations include context window constraints and dependence on the quality of the pre-trained TFM's.
AI-Guided Human-In-the-Loop Inverse Design of High Performance Engineering Structures
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Inverse design tools such as Topology Optimization (TO) can achieve new levels of improvement for high-performance engineered structures. However, widespread use is hindered by high computational times and a black-box nature that inhibits user interaction. Human-in-the-loop TO approaches are emerging that integrate human intuition into the design generation process. However, these rely on the time-consuming bottleneck of iterative region selection for design modifications. To reduce the number of iterative trials, this contribution presents an AI co-pilot that uses machine learning to predict the user's preferred regions. The prediction model is configured as an image segmentation task with a U-Net architecture. It is trained on synthetic datasets where human preferences either identify the longest topological member or the most complex structural connection. The model successfully predicts plausible regions for modification and presents them to the user as AI recommendations. The human preference model demonstrates generalization across diverse and non-standard TO problems and exhibits emergent behavior outside the single-region selection training data. Demonstration examples show that the new human-in-the-loop TO approach that integrates the AI co-pilot can improve manufacturability or improve the linear buckling load by 39% while only increasing the total design time by 15 sec compared to conventional simplistic TO.
LAMP: Data-Efficient Linear Affine Weight-Space Models for Parameter-Controlled 3D Shape Generation and Extrapolation
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Generating high-fidelity 3D geometries that satisfy specific parameter constraints has broad applications in design and engineering. However, current methods typically rely on large training datasets and struggle with controllability and generalization beyond the training distributions. To overcome these limitations, we introduce LAMP (Linear Affine Mixing of Parametric shapes), a data-efficient framework for controllable and interpretable 3D generation. LAMP first aligns signed distance function (SDF) decoders by overfitting each exemplar from a shared initialization, then synthesizes new geometries by solving a parameter-constrained mixing problem in the aligned weight space. To ensure robustness, we further propose a safety metric that detects geometry validity via linearity mismatch. We evaluate LAMP on two 3D parametric benchmarks: DrivAerNet++ and BlendedNet. We found that LAMP enables (i) controlled interpolation within bounds with as few as 100 samples, (ii) safe extrapolation by up to 100% parameter difference beyond training ranges, (iii) physics performance-guided optimization under fixed parameters. LAMP significantly outperforms conditional autoencoder and Deep Network Interpolation (DNI) baselines in both extrapolation and data efficiency. Our results demonstrate that LAMP advances controllable, data-efficient, and safe 3D generation for design exploration, dataset generation, and performance-driven optimization.
GenCAD-3D: CAD Program Generation using Multimodal Latent Space Alignment and Synthetic Dataset Balancing
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:CAD programs, structured as parametric sequences of commands that compile into precise 3D geometries, are fundamental to accurate and efficient engineering design processes. Generating these programs from nonparametric data such as point clouds and meshes remains a crucial yet challenging task, typically requiring extensive manual intervention. Current deep generative models aimed at automating CAD generation are significantly limited by imbalanced and insufficiently large datasets, particularly those lacking representation for complex CAD programs. To address this, we introduce GenCAD-3D, a multimodal generative framework utilizing contrastive learning for aligning latent embeddings between CAD and geometric encoders, combined with latent diffusion models for CAD sequence generation and retrieval. Additionally, we present SynthBal, a synthetic data augmentation strategy specifically designed to balance and expand datasets, notably enhancing representation of complex CAD geometries. Our experiments show that SynthBal significantly boosts reconstruction accuracy, reduces the generation of invalid CAD models, and markedly improves performance on high-complexity geometries, surpassing existing benchmarks. These advancements hold substantial implications for streamlining reverse engineering and enhancing automation in engineering design. We will publicly release our datasets and code, including a set of 51 3D-printed and laser-scanned parts on our project site.
BlendedNet: A Blended Wing Body Aircraft Dataset and Surrogate Model for Aerodynamic Predictions
Sep 10, 2025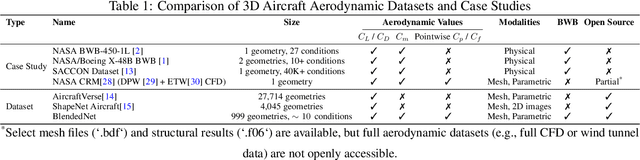
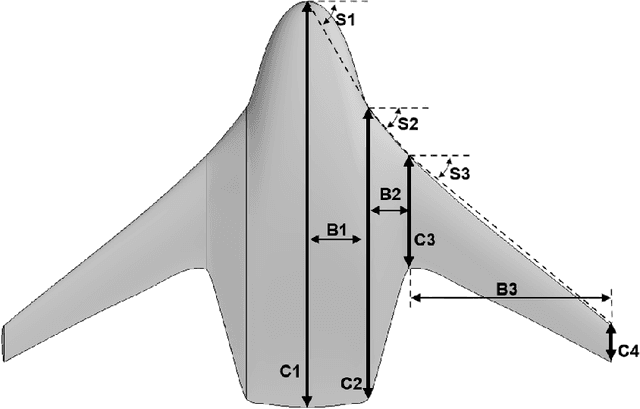
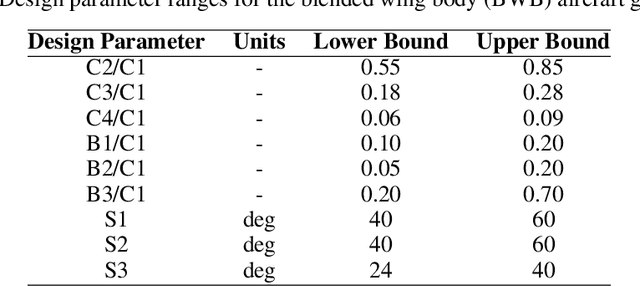
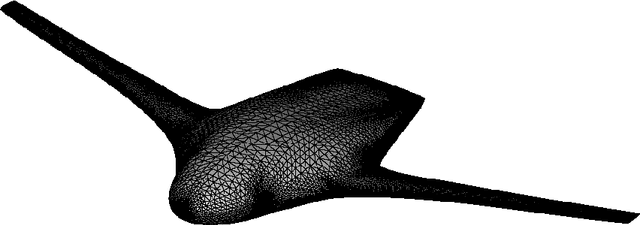
Abstract:BlendedNet is a publicly available aerodynamic dataset of 999 blended wing body (BWB) geometries. Each geometry is simulated across about nine flight conditions, yielding 8830 converged RANS cases with the Spalart-Allmaras model and 9 to 14 million cells per case. The dataset is generated by sampling geometric design parameters and flight conditions, and includes detailed pointwise surface quantities needed to study lift and drag. We also introduce an end-to-end surrogate framework for pointwise aerodynamic prediction. The pipeline first uses a permutation-invariant PointNet regressor to predict geometric parameters from sampled surface point clouds, then conditions a Feature-wise Linear Modulation (FiLM) network on the predicted parameters and flight conditions to predict pointwise coefficients Cp, Cfx, and Cfz. Experiments show low errors in surface predictions across diverse BWBs. BlendedNet addresses data scarcity for unconventional configurations and enables research on data-driven surrogate modeling for aerodynamic design.
VideoCAD: A Large-Scale Video Dataset for Learning UI Interactions and 3D Reasoning from CAD Software
May 30, 2025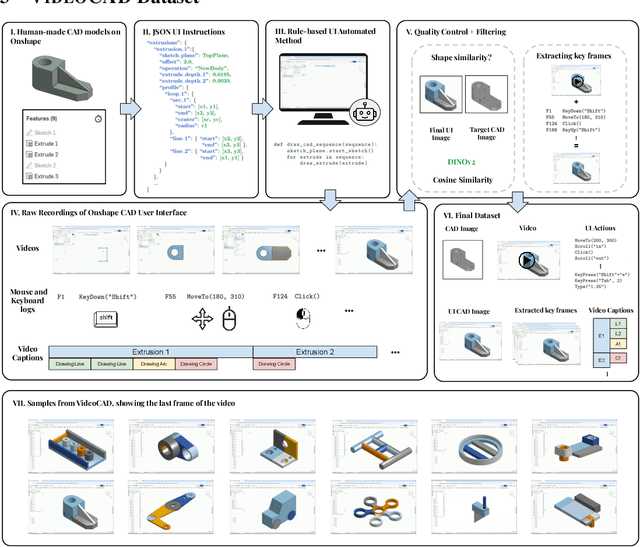

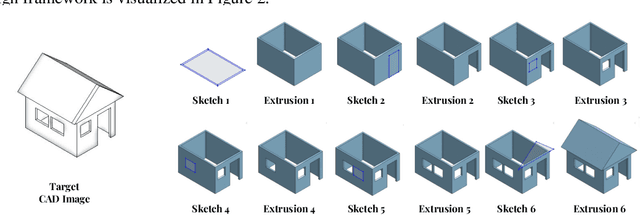
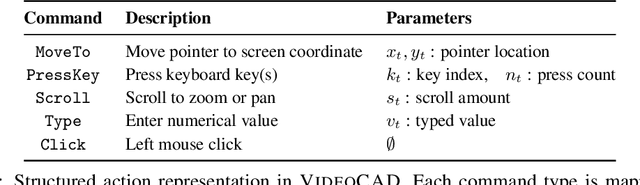
Abstract:Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is a time-consuming and complex process, requiring precise, long-horizon user interactions with intricate 3D interfaces. While recent advances in AI-driven user interface (UI) agents show promise, most existing datasets and methods focus on short, low-complexity tasks in mobile or web applications, failing to capture the demands of professional engineering tools. In this work, we introduce VideoCAD, the first attempt at engineering UI interaction learning for precision tasks. Specifically, VideoCAD is a large-scale synthetic dataset consisting of over 41K annotated video recordings of CAD operations, generated using an automated framework for collecting high-fidelity UI action data from human-made CAD designs. Compared to existing datasets, VideoCAD offers an order of magnitude higher complexity in UI interaction learning for real-world engineering tasks, having up to a 20x longer time horizon than other datasets. We show two important downstream applications of VideoCAD: learning UI interactions from professional precision 3D CAD tools and a visual question-answering (VQA) benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal large language models' (LLM) spatial reasoning and video understanding abilities. To learn the UI interactions, we propose VideoCADFormer - a state-of-the-art model in learning CAD interactions directly from video, which outperforms multiple behavior cloning baselines. Both VideoCADFormer and the VQA benchmark derived from VideoCAD reveal key challenges in the current state of video-based UI understanding, including the need for precise action grounding, multi-modal and spatial reasoning, and long-horizon dependencies.
CAD-Coder: An Open-Source Vision-Language Model for Computer-Aided Design Code Generation
May 20, 2025Abstract:Efficient creation of accurate and editable 3D CAD models is critical in engineering design, significantly impacting cost and time-to-market in product innovation. Current manual workflows remain highly time-consuming and demand extensive user expertise. While recent developments in AI-driven CAD generation show promise, existing models are limited by incomplete representations of CAD operations, inability to generalize to real-world images, and low output accuracy. This paper introduces CAD-Coder, an open-source Vision-Language Model (VLM) explicitly fine-tuned to generate editable CAD code (CadQuery Python) directly from visual input. Leveraging a novel dataset that we created--GenCAD-Code, consisting of over 163k CAD-model image and code pairs--CAD-Coder outperforms state-of-the-art VLM baselines such as GPT-4.5 and Qwen2.5-VL-72B, achieving a 100% valid syntax rate and the highest accuracy in 3D solid similarity. Notably, our VLM demonstrates some signs of generalizability, successfully generating CAD code from real-world images and executing CAD operations unseen during fine-tuning. The performance and adaptability of CAD-Coder highlights the potential of VLMs fine-tuned on code to streamline CAD workflows for engineers and designers. CAD-Coder is publicly available at: https://github.com/anniedoris/CAD-Coder.
Continual Learning Strategies for 3D Engineering Regression Problems: A Benchmarking Study
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Engineering problems that apply machine learning often involve computationally intensive methods but rely on limited datasets. As engineering data evolves with new designs and constraints, models must incorporate new knowledge over time. However, high computational costs make retraining models from scratch infeasible. Continual learning (CL) offers a promising solution by enabling models to learn from sequential data while mitigating catastrophic forgetting, where a model forgets previously learned mappings. This work introduces CL to engineering design by benchmarking several CL methods on representative regression tasks. We apply these strategies to five engineering datasets and construct nine new engineering CL benchmarks to evaluate their ability to address forgetting and improve generalization. Preliminary results show that applying existing CL methods to these tasks improves performance over naive baselines. In particular, the Replay strategy achieved performance comparable to retraining in several benchmarks while reducing training time by nearly half, demonstrating its potential for real-world engineering workflows. The code and datasets used in this work will be available at: https://github.com/kmsamuel/cl-for-engineering-release.
AI Judges in Design: Statistical Perspectives on Achieving Human Expert Equivalence With Vision-Language Models
Apr 01, 2025



Abstract:The subjective evaluation of early stage engineering designs, such as conceptual sketches, traditionally relies on human experts. However, expert evaluations are time-consuming, expensive, and sometimes inconsistent. Recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) offer the potential to automate design assessments, but it is crucial to ensure that these AI ``judges'' perform on par with human experts. However, no existing framework assesses expert equivalence. This paper introduces a rigorous statistical framework to determine whether an AI judge's ratings match those of human experts. We apply this framework in a case study evaluating four VLM-based judges on key design metrics (uniqueness, creativity, usefulness, and drawing quality). These AI judges employ various in-context learning (ICL) techniques, including uni- vs. multimodal prompts and inference-time reasoning. The same statistical framework is used to assess three trained novices for expert-equivalence. Results show that the top-performing AI judge, using text- and image-based ICL with reasoning, achieves expert-level agreement for uniqueness and drawing quality and outperforms or matches trained novices across all metrics. In 6/6 runs for both uniqueness and creativity, and 5/6 runs for both drawing quality and usefulness, its agreement with experts meets or exceeds that of the majority of trained novices. These findings suggest that reasoning-supported VLM models can achieve human-expert equivalence in design evaluation. This has implications for scaling design evaluation in education and practice, and provides a general statistical framework for validating AI judges in other domains requiring subjective content evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge