Md Ferdous Alam
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
AI-Guided Human-In-the-Loop Inverse Design of High Performance Engineering Structures
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Inverse design tools such as Topology Optimization (TO) can achieve new levels of improvement for high-performance engineered structures. However, widespread use is hindered by high computational times and a black-box nature that inhibits user interaction. Human-in-the-loop TO approaches are emerging that integrate human intuition into the design generation process. However, these rely on the time-consuming bottleneck of iterative region selection for design modifications. To reduce the number of iterative trials, this contribution presents an AI co-pilot that uses machine learning to predict the user's preferred regions. The prediction model is configured as an image segmentation task with a U-Net architecture. It is trained on synthetic datasets where human preferences either identify the longest topological member or the most complex structural connection. The model successfully predicts plausible regions for modification and presents them to the user as AI recommendations. The human preference model demonstrates generalization across diverse and non-standard TO problems and exhibits emergent behavior outside the single-region selection training data. Demonstration examples show that the new human-in-the-loop TO approach that integrates the AI co-pilot can improve manufacturability or improve the linear buckling load by 39% while only increasing the total design time by 15 sec compared to conventional simplistic TO.
GenCAD-3D: CAD Program Generation using Multimodal Latent Space Alignment and Synthetic Dataset Balancing
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:CAD programs, structured as parametric sequences of commands that compile into precise 3D geometries, are fundamental to accurate and efficient engineering design processes. Generating these programs from nonparametric data such as point clouds and meshes remains a crucial yet challenging task, typically requiring extensive manual intervention. Current deep generative models aimed at automating CAD generation are significantly limited by imbalanced and insufficiently large datasets, particularly those lacking representation for complex CAD programs. To address this, we introduce GenCAD-3D, a multimodal generative framework utilizing contrastive learning for aligning latent embeddings between CAD and geometric encoders, combined with latent diffusion models for CAD sequence generation and retrieval. Additionally, we present SynthBal, a synthetic data augmentation strategy specifically designed to balance and expand datasets, notably enhancing representation of complex CAD geometries. Our experiments show that SynthBal significantly boosts reconstruction accuracy, reduces the generation of invalid CAD models, and markedly improves performance on high-complexity geometries, surpassing existing benchmarks. These advancements hold substantial implications for streamlining reverse engineering and enhancing automation in engineering design. We will publicly release our datasets and code, including a set of 51 3D-printed and laser-scanned parts on our project site.
VideoCAD: A Large-Scale Video Dataset for Learning UI Interactions and 3D Reasoning from CAD Software
May 30, 2025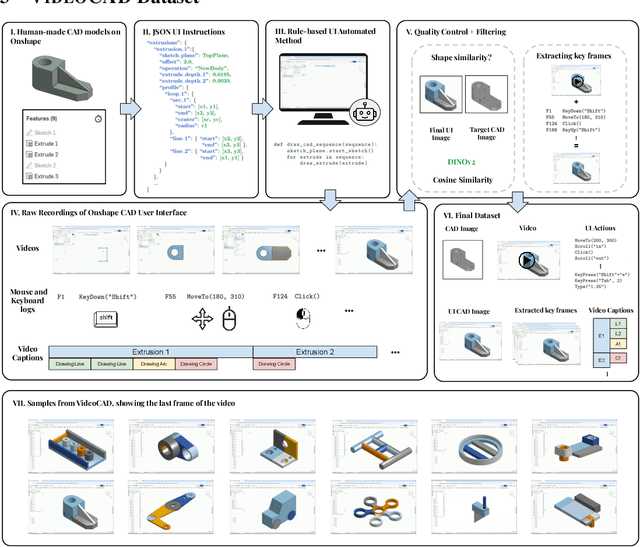

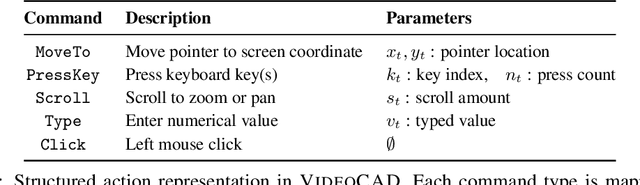
Abstract:Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is a time-consuming and complex process, requiring precise, long-horizon user interactions with intricate 3D interfaces. While recent advances in AI-driven user interface (UI) agents show promise, most existing datasets and methods focus on short, low-complexity tasks in mobile or web applications, failing to capture the demands of professional engineering tools. In this work, we introduce VideoCAD, the first attempt at engineering UI interaction learning for precision tasks. Specifically, VideoCAD is a large-scale synthetic dataset consisting of over 41K annotated video recordings of CAD operations, generated using an automated framework for collecting high-fidelity UI action data from human-made CAD designs. Compared to existing datasets, VideoCAD offers an order of magnitude higher complexity in UI interaction learning for real-world engineering tasks, having up to a 20x longer time horizon than other datasets. We show two important downstream applications of VideoCAD: learning UI interactions from professional precision 3D CAD tools and a visual question-answering (VQA) benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal large language models' (LLM) spatial reasoning and video understanding abilities. To learn the UI interactions, we propose VideoCADFormer - a state-of-the-art model in learning CAD interactions directly from video, which outperforms multiple behavior cloning baselines. Both VideoCADFormer and the VQA benchmark derived from VideoCAD reveal key challenges in the current state of video-based UI understanding, including the need for precise action grounding, multi-modal and spatial reasoning, and long-horizon dependencies.
GenCAD-Self-Repairing: Feasibility Enhancement for 3D CAD Generation
May 29, 2025Abstract:With the advancement of generative AI, research on its application to 3D model generation has gained traction, particularly in automating the creation of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) files from images. GenCAD is a notable model in this domain, leveraging an autoregressive transformer-based architecture with a contrastive learning framework to generate CAD programs. However, a major limitation of GenCAD is its inability to consistently produce feasible boundary representations (B-reps), with approximately 10% of generated designs being infeasible. To address this, we propose GenCAD-Self-Repairing, a framework that enhances the feasibility of generative CAD models through diffusion guidance and a self-repairing pipeline. This framework integrates a guided diffusion denoising process in the latent space and a regression-based correction mechanism to refine infeasible CAD command sequences while preserving geometric accuracy. Our approach successfully converted two-thirds of infeasible designs in the baseline method into feasible ones, significantly improving the feasibility rate while simultaneously maintaining a reasonable level of geometric accuracy between the point clouds of ground truth models and generated models. By significantly improving the feasibility rate of generating CAD models, our approach helps expand the availability of high-quality training data and enhances the applicability of AI-driven CAD generation in manufacturing, architecture, and product design.
CAD-Coder: An Open-Source Vision-Language Model for Computer-Aided Design Code Generation
May 20, 2025Abstract:Efficient creation of accurate and editable 3D CAD models is critical in engineering design, significantly impacting cost and time-to-market in product innovation. Current manual workflows remain highly time-consuming and demand extensive user expertise. While recent developments in AI-driven CAD generation show promise, existing models are limited by incomplete representations of CAD operations, inability to generalize to real-world images, and low output accuracy. This paper introduces CAD-Coder, an open-source Vision-Language Model (VLM) explicitly fine-tuned to generate editable CAD code (CadQuery Python) directly from visual input. Leveraging a novel dataset that we created--GenCAD-Code, consisting of over 163k CAD-model image and code pairs--CAD-Coder outperforms state-of-the-art VLM baselines such as GPT-4.5 and Qwen2.5-VL-72B, achieving a 100% valid syntax rate and the highest accuracy in 3D solid similarity. Notably, our VLM demonstrates some signs of generalizability, successfully generating CAD code from real-world images and executing CAD operations unseen during fine-tuning. The performance and adaptability of CAD-Coder highlights the potential of VLMs fine-tuned on code to streamline CAD workflows for engineers and designers. CAD-Coder is publicly available at: https://github.com/anniedoris/CAD-Coder.
DesignQA: A Multimodal Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models' Understanding of Engineering Documentation
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:This research introduces DesignQA, a novel benchmark aimed at evaluating the proficiency of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) in comprehending and applying engineering requirements in technical documentation. Developed with a focus on real-world engineering challenges, DesignQA uniquely combines multimodal data-including textual design requirements, CAD images, and engineering drawings-derived from the Formula SAE student competition. Different from many existing MLLM benchmarks, DesignQA contains document-grounded visual questions where the input image and input document come from different sources. The benchmark features automatic evaluation metrics and is divided into segments-Rule Comprehension, Rule Compliance, and Rule Extraction-based on tasks that engineers perform when designing according to requirements. We evaluate state-of-the-art models like GPT4 and LLaVA against the benchmark, and our study uncovers the existing gaps in MLLMs' abilities to interpret complex engineering documentation. Key findings suggest that while MLLMs demonstrate potential in navigating technical documents, substantial limitations exist, particularly in accurately extracting and applying detailed requirements to engineering designs. This benchmark sets a foundation for future advancements in AI-supported engineering design processes. DesignQA is publicly available at: https://github.com/anniedoris/design_qa/.
From Concept to Manufacturing: Evaluating Vision-Language Models for Engineering Design
Nov 21, 2023



Abstract:Engineering Design is undergoing a transformative shift with the advent of AI, marking a new era in how we approach product, system, and service planning. Large language models have demonstrated impressive capabilities in enabling this shift. Yet, with text as their only input modality, they cannot leverage the large body of visual artifacts that engineers have used for centuries and are accustomed to. This gap is addressed with the release of multimodal vision language models, such as GPT-4V, enabling AI to impact many more types of tasks. In light of these advancements, this paper presents a comprehensive evaluation of GPT-4V, a vision language model, across a wide spectrum of engineering design tasks, categorized into four main areas: Conceptual Design, System-Level and Detailed Design, Manufacturing and Inspection, and Engineering Education Tasks. Our study assesses GPT-4V's capabilities in design tasks such as sketch similarity analysis, concept selection using Pugh Charts, material selection, engineering drawing analysis, CAD generation, topology optimization, design for additive and subtractive manufacturing, spatial reasoning challenges, and textbook problems. Through this structured evaluation, we not only explore GPT-4V's proficiency in handling complex design and manufacturing challenges but also identify its limitations in complex engineering design applications. Our research establishes a foundation for future assessments of vision language models, emphasizing their immense potential for innovating and enhancing the engineering design and manufacturing landscape. It also contributes a set of benchmark testing datasets, with more than 1000 queries, for ongoing advancements and applications in this field.
An advantage based policy transfer algorithm for reinforcement learning with metrics of transferability
Nov 12, 2023



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) can enable sequential decision-making in complex and high-dimensional environments if the acquisition of a new state-action pair is efficient, i.e., when interaction with the environment is inexpensive. However, there are a myriad of real-world applications in which a high number of interactions are infeasible. In these environments, transfer RL algorithms, which can be used for the transfer of knowledge from one or multiple source environments to a target environment, have been shown to increase learning speed and improve initial and asymptotic performance. However, most existing transfer RL algorithms are on-policy and sample inefficient, and often require heuristic choices in algorithm design. This paper proposes an off-policy Advantage-based Policy Transfer algorithm, APT-RL, for fixed domain environments. Its novelty is in using the popular notion of ``advantage'' as a regularizer, to weigh the knowledge that should be transferred from the source, relative to new knowledge learned in the target, removing the need for heuristic choices. Further, we propose a new transfer performance metric to evaluate the performance of our algorithm and unify existing transfer RL frameworks. Finally, we present a scalable, theoretically-backed task similarity measurement algorithm to illustrate the alignments between our proposed transferability metric and similarities between source and target environments. Numerical experiments on three continuous control benchmark tasks demonstrate that APT-RL outperforms existing transfer RL algorithms on most tasks, and is $10\%$ to $75\%$ more sample efficient than learning from scratch.
Representation Learning for Sequential Volumetric Design Tasks
Sep 05, 2023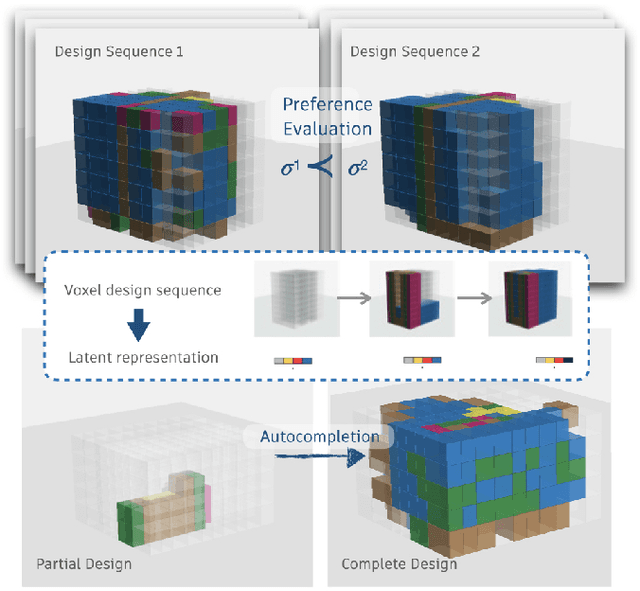



Abstract:Volumetric design, also called massing design, is the first and critical step in professional building design which is sequential in nature. As the volumetric design process is complex, the underlying sequential design process encodes valuable information for designers. Many efforts have been made to automatically generate reasonable volumetric designs, but the quality of the generated design solutions varies, and evaluating a design solution requires either a prohibitively comprehensive set of metrics or expensive human expertise. While previous approaches focused on learning only the final design instead of sequential design tasks, we propose to encode the design knowledge from a collection of expert or high-performing design sequences and extract useful representations using transformer-based models. Later we propose to utilize the learned representations for crucial downstream applications such as design preference evaluation and procedural design generation. We develop the preference model by estimating the density of the learned representations whereas we train an autoregressive transformer model for sequential design generation. We demonstrate our ideas by leveraging a novel dataset of thousands of sequential volumetric designs. Our preference model can compare two arbitrarily given design sequences and is almost 90% accurate in evaluation against random design sequences. Our autoregressive model is also capable of autocompleting a volumetric design sequence from a partial design sequence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge