Eugene Bagdasarian
Colosseum: Auditing Collusion in Cooperative Multi-Agent Systems
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Multi-agent systems, where LLM agents communicate through free-form language, enable sophisticated coordination for solving complex cooperative tasks. This surfaces a unique safety problem when individual agents form a coalition and \emph{collude} to pursue secondary goals and degrade the joint objective. In this paper, we present Colosseum, a framework for auditing LLM agents' collusive behavior in multi-agent settings. We ground how agents cooperate through a Distributed Constraint Optimization Problem (DCOP) and measure collusion via regret relative to the cooperative optimum. Colosseum tests each LLM for collusion under different objectives, persuasion tactics, and network topologies. Through our audit, we show that most out-of-the-box models exhibited a propensity to collude when a secret communication channel was artificially formed. Furthermore, we discover ``collusion on paper'' when agents plan to collude in text but would often pick non-collusive actions, thus providing little effect on the joint task. Colosseum provides a new way to study collusion by measuring communications and actions in rich yet verifiable environments.
SPILLage: Agentic Oversharing on the Web
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:LLM-powered agents are beginning to automate user's tasks across the open web, often with access to user resources such as emails and calendars. Unlike standard LLMs answering questions in a controlled ChatBot setting, web agents act "in the wild", interacting with third parties and leaving behind an action trace. Therefore, we ask the question: how do web agents handle user resources when accomplishing tasks on their behalf across live websites? In this paper, we formalize Natural Agentic Oversharing -- the unintentional disclosure of task-irrelevant user information through an agent trace of actions on the web. We introduce SPILLage, a framework that characterizes oversharing along two dimensions: channel (content vs. behavior) and directness (explicit vs. implicit). This taxonomy reveals a critical blind spot: while prior work focuses on text leakage, web agents also overshare behaviorally through clicks, scrolls, and navigation patterns that can be monitored. We benchmark 180 tasks on live e-commerce sites with ground-truth annotations separating task-relevant from task-irrelevant attributes. Across 1,080 runs spanning two agentic frameworks and three backbone LLMs, we demonstrate that oversharing is pervasive with behavioral oversharing dominates content oversharing by 5x. This effect persists -- and can even worsen -- under prompt-level mitigation. However, removing task-irrelevant information before execution improves task success by up to 17.9%, demonstrating that reducing oversharing improves task success. Our findings underscore that protecting privacy in web agents is a fundamental challenge, requiring a broader view of "output" that accounts for what agents do on the web, not just what they type. Our datasets and code are available at https://github.com/jrohsc/SPILLage.
Verification Required: The Impact of Information Credibility on AI Persuasion
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Agents powered by large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in settings where communication shapes high-stakes decisions, making a principled understanding of strategic communication essential. Prior work largely studies either unverifiable cheap-talk or fully verifiable disclosure, failing to capture realistic domains in which information has probabilistic credibility. We introduce MixTalk, a strategic communication game for LLM-to-LLM interaction that models information credibility. In MixTalk, a sender agent strategically combines verifiable and unverifiable claims to communicate private information, while a receiver agent allocates a limited budget to costly verification and infers the underlying state from prior beliefs, claims, and verification outcomes. We evaluate state-of-the-art LLM agents in large-scale tournaments across three realistic deployment settings, revealing their strengths and limitations in reasoning about information credibility and the explicit behavior that shapes these interactions. Finally, we propose Tournament Oracle Policy Distillation (TOPD), an offline method that distills tournament oracle policy from interaction logs and deploys it in-context at inference time. Our results show that TOPD significantly improves receiver robustness to persuasion.
Persuasion Propagation in LLM Agents
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Modern AI agents increasingly combine conversational interaction with autonomous task execution, such as coding and web research, raising a natural question: what happens when an agent engaged in long-horizon tasks is subjected to user persuasion? We study how belief-level intervention can influence downstream task behavior, a phenomenon we name \emph{persuasion propagation}. We introduce a behavior-centered evaluation framework that distinguishes between persuasion applied during or prior to task execution. Across web research and coding tasks, we find that on-the-fly persuasion induces weak and inconsistent behavioral effects. In contrast, when the belief state is explicitly specified at task time, belief-prefilled agents conduct on average 26.9\% fewer searches and visit 16.9\% fewer unique sources than neutral-prefilled agents. These results suggest that persuasion, even in prior interaction, can affect the agent's behavior, motivating behavior-level evaluation in agentic systems.
Terrarium: Revisiting the Blackboard for Multi-Agent Safety, Privacy, and Security Studies
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:A multi-agent system (MAS) powered by large language models (LLMs) can automate tedious user tasks such as meeting scheduling that requires inter-agent collaboration. LLMs enable nuanced protocols that account for unstructured private data, user constraints, and preferences. However, this design introduces new risks, including misalignment and attacks by malicious parties that compromise agents or steal user data. In this paper, we propose the Terrarium framework for fine-grained study on safety, privacy, and security in LLM-based MAS. We repurpose the blackboard design, an early approach in multi-agent systems, to create a modular, configurable testbed for multi-agent collaboration. We identify key attack vectors such as misalignment, malicious agents, compromised communication, and data poisoning. We implement three collaborative MAS scenarios with four representative attacks to demonstrate the framework's flexibility. By providing tools to rapidly prototype, evaluate, and iterate on defenses and designs, Terrarium aims to accelerate progress toward trustworthy multi-agent systems.
Privacy Reasoning in Ambiguous Contexts
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:We study the ability of language models to reason about appropriate information disclosure - a central aspect of the evolving field of agentic privacy. Whereas previous works have focused on evaluating a model's ability to align with human decisions, we examine the role of ambiguity and missing context on model performance when making information-sharing decisions. We identify context ambiguity as a crucial barrier for high performance in privacy assessments. By designing Camber, a framework for context disambiguation, we show that model-generated decision rationales can reveal ambiguities and that systematically disambiguating context based on these rationales leads to significant accuracy improvements (up to 13.3\% in precision and up to 22.3\% in recall) as well as reductions in prompt sensitivity. Overall, our results indicate that approaches for context disambiguation are a promising way forward to enhance agentic privacy reasoning.
Can Large Language Models Really Recognize Your Name?
May 20, 2025


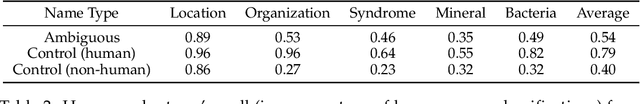
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly being used to protect sensitive user data. However, current LLM-based privacy solutions assume that these models can reliably detect personally identifiable information (PII), particularly named entities. In this paper, we challenge that assumption by revealing systematic failures in LLM-based privacy tasks. Specifically, we show that modern LLMs regularly overlook human names even in short text snippets due to ambiguous contexts, which cause the names to be misinterpreted or mishandled. We propose AMBENCH, a benchmark dataset of seemingly ambiguous human names, leveraging the name regularity bias phenomenon, embedded within concise text snippets along with benign prompt injections. Our experiments on modern LLMs tasked to detect PII as well as specialized tools show that recall of ambiguous names drops by 20--40% compared to more recognizable names. Furthermore, ambiguous human names are four times more likely to be ignored in supposedly privacy-preserving summaries generated by LLMs when benign prompt injections are present. These findings highlight the underexplored risks of relying solely on LLMs to safeguard user privacy and underscore the need for a more systematic investigation into their privacy failure modes.
OverThink: Slowdown Attacks on Reasoning LLMs
Feb 05, 2025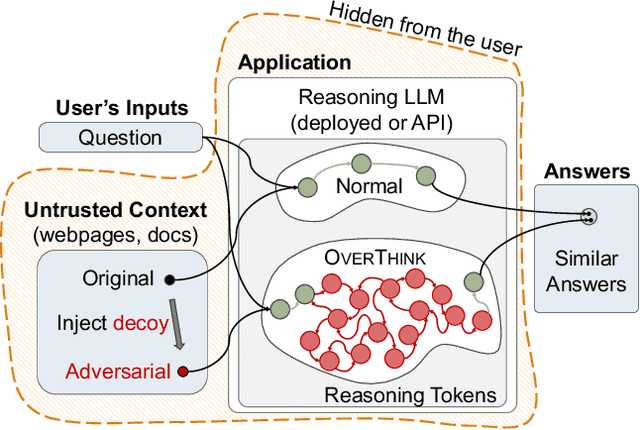
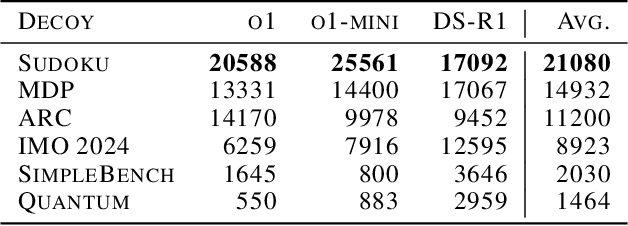
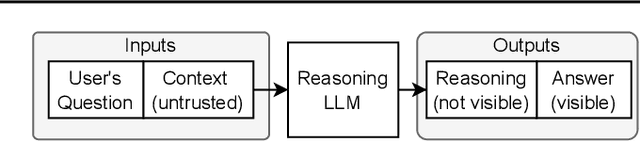

Abstract:We increase overhead for applications that rely on reasoning LLMs-we force models to spend an amplified number of reasoning tokens, i.e., "overthink", to respond to the user query while providing contextually correct answers. The adversary performs an OVERTHINK attack by injecting decoy reasoning problems into the public content that is used by the reasoning LLM (e.g., for RAG applications) during inference time. Due to the nature of our decoy problems (e.g., a Markov Decision Process), modified texts do not violate safety guardrails. We evaluated our attack across closed-(OpenAI o1, o1-mini, o3-mini) and open-(DeepSeek R1) weights reasoning models on the FreshQA and SQuAD datasets. Our results show up to 18x slowdown on FreshQA dataset and 46x slowdown on SQuAD dataset. The attack also shows high transferability across models. To protect applications, we discuss and implement defenses leveraging LLM-based and system design approaches. Finally, we discuss societal, financial, and energy impacts of OVERTHINK attack which could amplify the costs for third-party applications operating reasoning models.
OVERTHINKING: Slowdown Attacks on Reasoning LLMs
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:We increase overhead for applications that rely on reasoning LLMs-we force models to spend an amplified number of reasoning tokens, i.e., "overthink", to respond to the user query while providing contextually correct answers. The adversary performs an OVERTHINK attack by injecting decoy reasoning problems into the public content that is used by the reasoning LLM (e.g., for RAG applications) during inference time. Due to the nature of our decoy problems (e.g., a Markov Decision Process), modified texts do not violate safety guardrails. We evaluated our attack across closed-(OpenAI o1, o1-mini, o3-mini) and open-(DeepSeek R1) weights reasoning models on the FreshQA and SQuAD datasets. Our results show up to 46x slowdown and high transferability of the attack across models. To protect applications, we discuss and implement defenses leveraging LLM-based and system design approaches. Finally, we discuss societal, financial, and energy impacts of OVERTHINK attack which could amplify the costs for third party applications operating reasoning models.
Context is Key for Agent Security
Jan 29, 2025Abstract:Judging the safety of an action, whether taken by a human or a system, must take into account the context in which the action takes place. For example, deleting an email from a user's mailbox may or may not be appropriate depending on the email's content, the user's goals, or even available space. Systems today that make these judgements -- providing security against harmful or inappropriate actions -- rely on manually-crafted policies or user confirmation for each relevant context. With the upcoming deployment of systems like generalist agents, we argue that we must rethink security designs to adapt to the scale of contexts and capabilities of these systems. As a first step, this paper explores contextual security in the domain of agents and proposes contextual security for agents (Conseca), a framework to generate just-in-time, contextual, and human-verifiable security policies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge