Emmanuel Hebrard
LAAS
MurTree: Optimal Classification Trees via Dynamic Programming and Search
Jul 24, 2020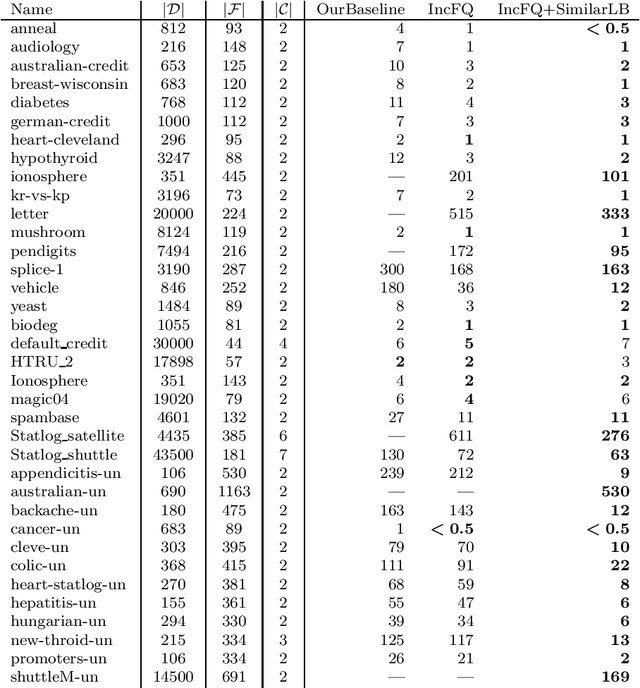
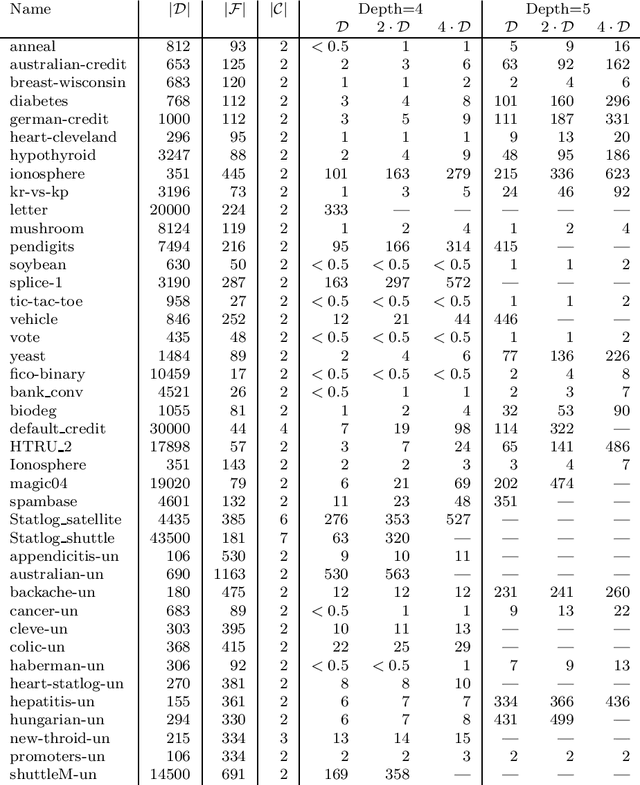

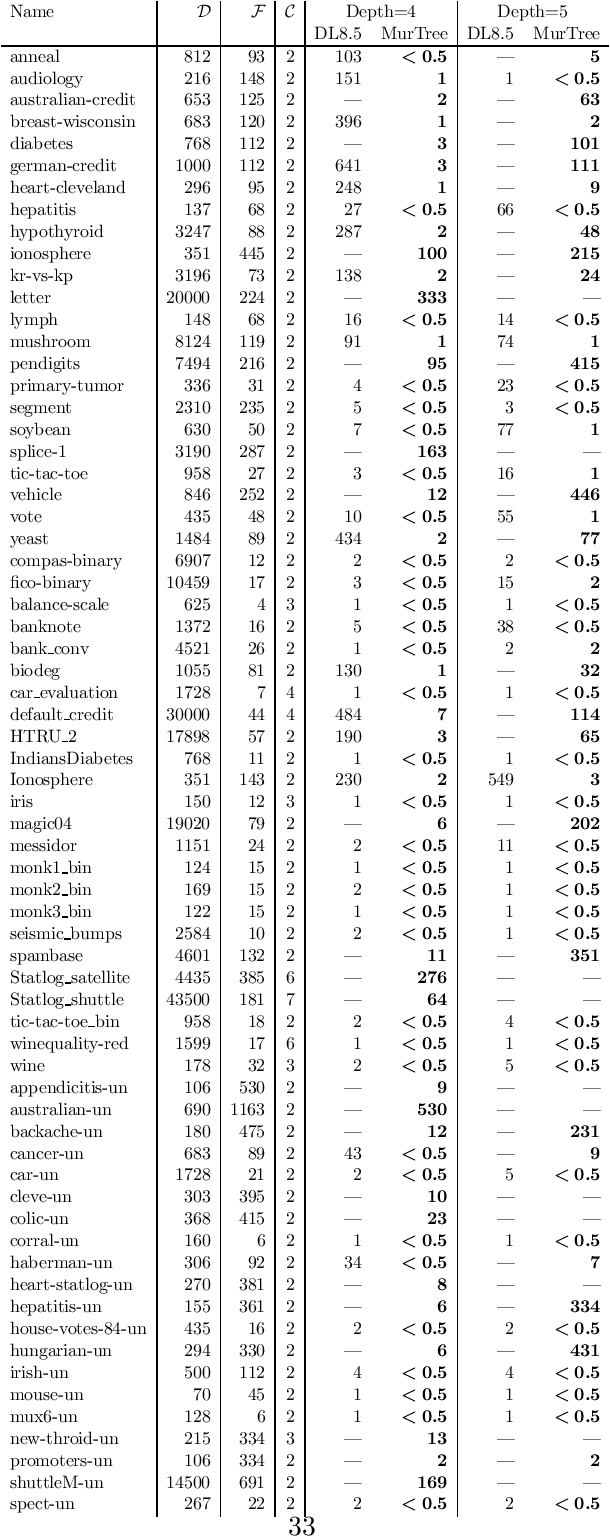
Abstract:Decision tree learning is a widely used approach in machine learning, favoured in applications that require concise and interpretable models. Heuristic methods are traditionally used to quickly produce models with reasonably high accuracy. A commonly criticised point, however, is that the resulting trees may not necessarily be the best representation of the data in terms of accuracy, size, and other considerations such as fairness. In recent years, this motivated the development of optimal classification tree algorithms that globally optimise the decision tree in contrast to heuristic methods that perform a sequence of locally optimal decisions. We follow this line of work and provide a novel algorithm for learning optimal classification trees based on dynamic programming and search. Our algorithm supports constraints on the depth of the tree and number of nodes and we argue it can be extended with other requirements. The success of our approach is attributed to a series of specialised techniques that exploit properties unique to classification trees. Whereas algorithms for optimal classification trees have traditionally been plagued by high runtimes and limited scalability, we show in a detailed experimental study that our approach uses only a fraction of the time required by the state-of-the-art and can handle datasets with tens of thousands of instances, providing several orders of magnitude improvements and notably contributing towards the practical realisation of optimal decision trees.
Partial Queries for Constraint Acquisition
Mar 14, 2020
Abstract:Learning constraint networks is known to require a number of membership queries exponential in the number of variables. In this paper, we learn constraint networks by asking the user partial queries. That is, we ask the user to classify assignments to subsets of the variables as positive or negative. We provide an algorithm, called QUACQ, that, given a negative example, focuses onto a constraint of the target network in a number of queries logarithmic in the size of the example. The whole constraint network can then be learned with a polynomial number of partial queries. We give information theoretic lower bounds for learning some simple classes of constraint networks and show that our generic algorithm is optimal in some cases.
On Backdoors To Tractable Constraint Languages
Oct 10, 2014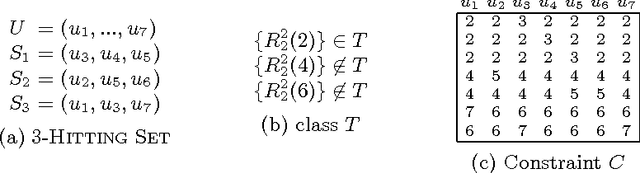
Abstract:In the context of CSPs, a strong backdoor is a subset of variables such that every complete assignment yields a residual instance guaranteed to have a specified property. If the property allows efficient solving, then a small strong backdoor provides a reasonable decomposition of the original instance into easy instances. An important challenge is the design of algorithms that can find quickly a small strong backdoor if one exists. We present a systematic study of the parameterized complexity of backdoor detection when the target property is a restricted type of constraint language defined by means of a family of polymorphisms. In particular, we show that under the weak assumption that the polymorphisms are idempotent, the problem is unlikely to be FPT when the parameter is either r (the constraint arity) or k (the size of the backdoor) unless P = NP or FPT = W[2]. When the parameter is k+r, however, we are able to identify large classes of languages for which the problem of finding a small backdoor is FPT.
Soft Constraints of Difference and Equality
Jan 16, 2014



Abstract:In many combinatorial problems one may need to model the diversity or similarity of assignments in a solution. For example, one may wish to maximise or minimise the number of distinct values in a solution. To formulate problems of this type, we can use soft variants of the well known AllDifferent and AllEqual constraints. We present a taxonomy of six soft global constraints, generated by combining the two latter ones and the two standard cost functions, which are either maximised or minimised. We characterise the complexity of achieving arc and bounds consistency on these constraints, resolving those cases for which NP-hardness was neither proven nor disproven. In particular, we explore in depth the constraint ensuring that at least k pairs of variables have a common value. We show that achieving arc consistency is NP-hard, however achieving bounds consistency can be done in polynomial time through dynamic programming. Moreover, we show that the maximum number of pairs of equal variables can be approximated by a factor 1/2 with a linear time greedy algorithm. Finally, we provide a fixed parameter tractable algorithm with respect to the number of values appearing in more than two distinct domains. Interestingly, this taxonomy shows that enforcing equality is harder than enforcing difference.
Models and Strategies for Variants of the Job Shop Scheduling Problem
Sep 27, 2011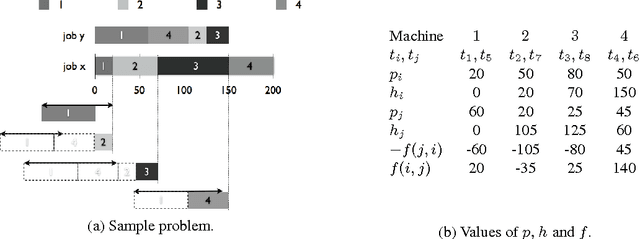
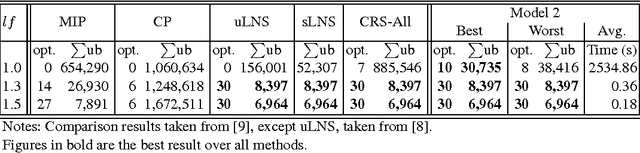
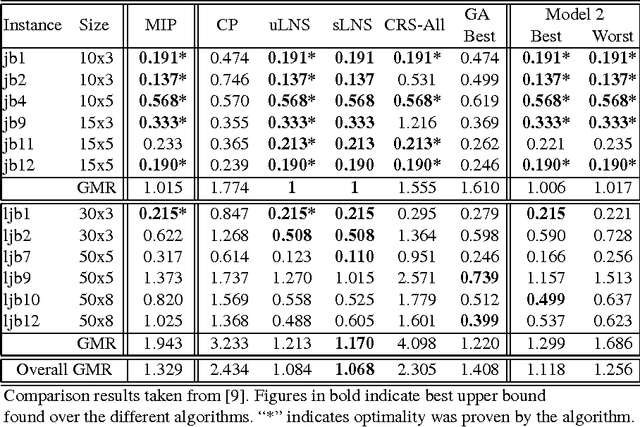
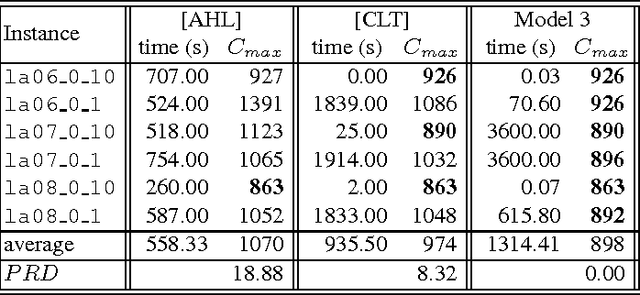
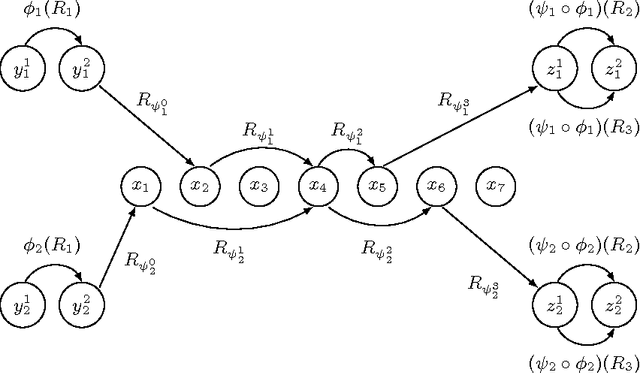
Abstract:Recently, a variety of constraint programming and Boolean satisfiability approaches to scheduling problems have been introduced. They have in common the use of relatively simple propagation mechanisms and an adaptive way to focus on the most constrained part of the problem. In some cases, these methods compare favorably to more classical constraint programming methods relying on propagation algorithms for global unary or cumulative resource constraints and dedicated search heuristics. In particular, we described an approach that combines restarting, with a generic adaptive heuristic and solution guided branching on a simple model based on a decomposition of disjunctive constraints. In this paper, we introduce an adaptation of this technique for an important subclass of job shop scheduling problems (JSPs), where the objective function involves minimization of earliness/tardiness costs. We further show that our technique can be improved by adding domain specific information for one variant of the JSP (involving time lag constraints). In particular we introduce a dedicated greedy heuristic, and an improved model for the case where the maximal time lag is 0 (also referred to as no-wait JSPs).
The Complexity of Reasoning with Global Constraints
Mar 06, 2009
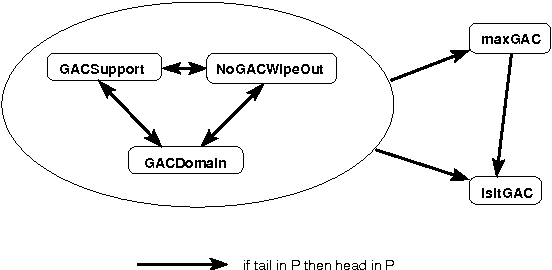
Abstract:Constraint propagation is one of the techniques central to the success of constraint programming. To reduce search, fast algorithms associated with each constraint prune the domains of variables. With global (or non-binary) constraints, the cost of such propagation may be much greater than the quadratic cost for binary constraints. We therefore study the computational complexity of reasoning with global constraints. We first characterise a number of important questions related to constraint propagation. We show that such questions are intractable in general, and identify dependencies between the tractability and intractability of the different questions. We then demonstrate how the tools of computational complexity can be used in the design and analysis of specific global constraints. In particular, we illustrate how computational complexity can be used to determine when a lesser level of local consistency should be enforced, when constraints can be safely generalized, when decomposing constraints will reduce the amount of pruning, and when combining constraints is tractable.
SLIDE: A Useful Special Case of the CARDPATH Constraint
Mar 03, 2009
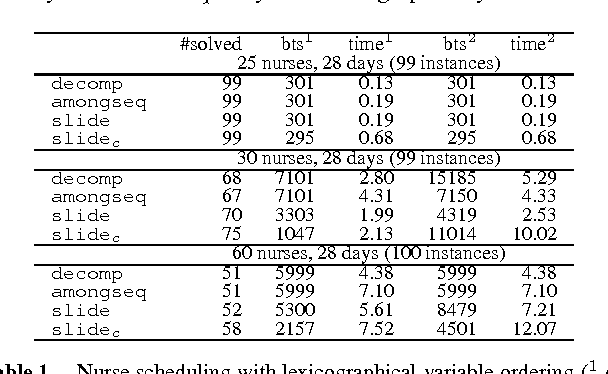
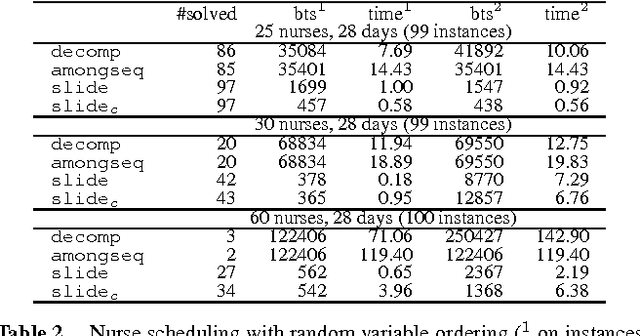
Abstract:We study the CardPath constraint. This ensures a given constraint holds a number of times down a sequence of variables. We show that SLIDE, a special case of CardPath where the slid constraint must hold always, can be used to encode a wide range of sliding sequence constraints including CardPath itself. We consider how to propagate SLIDE and provide a complete propagator for CardPath. Since propagation is NP-hard in general, we identify special cases where propagation takes polynomial time. Our experiments demonstrate that using SLIDE to encode global constraints can be as efficient and effective as specialised propagators.
* 18th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence
The Parameterized Complexity of Global Constraints
Mar 03, 2009Abstract:We argue that parameterized complexity is a useful tool with which to study global constraints. In particular, we show that many global constraints which are intractable to propagate completely have natural parameters which make them fixed-parameter tractable and which are easy to compute. This tractability tends either to be the result of a simple dynamic program or of a decomposition which has a strong backdoor of bounded size. This strong backdoor is often a cycle cutset. We also show that parameterized complexity can be used to study other aspects of constraint programming like symmetry breaking. For instance, we prove that value symmetry is fixed-parameter tractable to break in the number of symmetries. Finally, we argue that parameterized complexity can be used to derive results about the approximability of constraint propagation.
* Proceedings of the Twenty-Third AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Range and Roots: Two Common Patterns for Specifying and Propagating Counting and Occurrence Constraints
Mar 02, 2009



Abstract:We propose Range and Roots which are two common patterns useful for specifying a wide range of counting and occurrence constraints. We design specialised propagation algorithms for these two patterns. Counting and occurrence constraints specified using these patterns thus directly inherit a propagation algorithm. To illustrate the capabilities of the Range and Roots constraints, we specify a number of global constraints taken from the literature. Preliminary experiments demonstrate that propagating counting and occurrence constraints using these two patterns leads to a small loss in performance when compared to specialised global constraints and is competitive with alternative decompositions using elementary constraints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge