Elan van Biljon
A game-theoretic analysis of networked system control for common-pool resource management using multi-agent reinforcement learning
Oct 15, 2020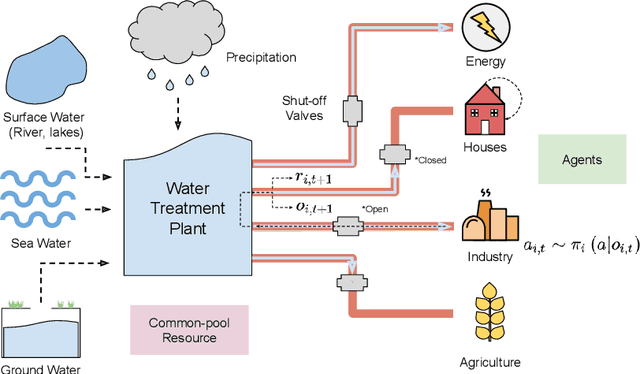
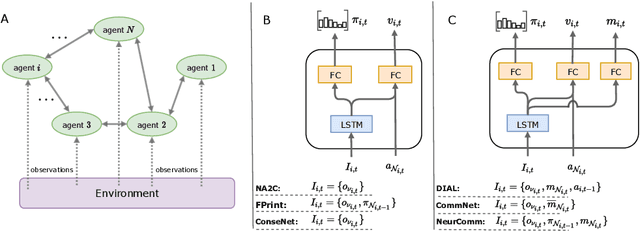
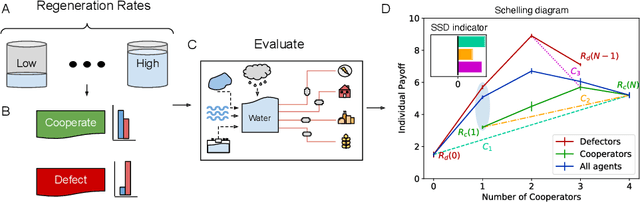
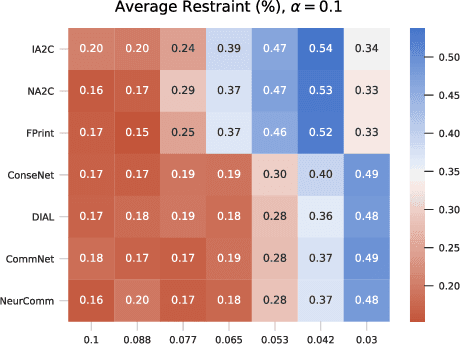
Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning has recently shown great promise as an approach to networked system control. Arguably, one of the most difficult and important tasks for which large scale networked system control is applicable is common-pool resource management. Crucial common-pool resources include arable land, fresh water, wetlands, wildlife, fish stock, forests and the atmosphere, of which proper management is related to some of society's greatest challenges such as food security, inequality and climate change. Here we take inspiration from a recent research program investigating the game-theoretic incentives of humans in social dilemma situations such as the well-known tragedy of the commons. However, instead of focusing on biologically evolved human-like agents, our concern is rather to better understand the learning and operating behaviour of engineered networked systems comprising general-purpose reinforcement learning agents, subject only to nonbiological constraints such as memory, computation and communication bandwidth. Harnessing tools from empirical game-theoretic analysis, we analyse the differences in resulting solution concepts that stem from employing different information structures in the design of networked multi-agent systems. These information structures pertain to the type of information shared between agents as well as the employed communication protocol and network topology. Our analysis contributes new insights into the consequences associated with certain design choices and provides an additional dimension of comparison between systems beyond efficiency, robustness, scalability and mean control performance.
Participatory Research for Low-resourced Machine Translation: A Case Study in African Languages
Oct 05, 2020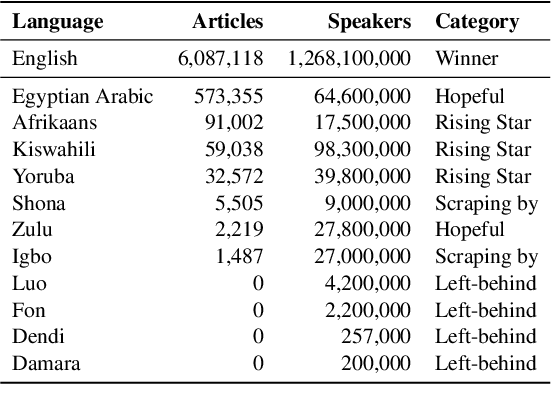
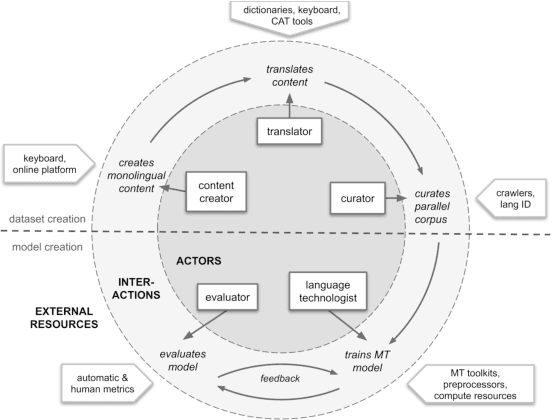
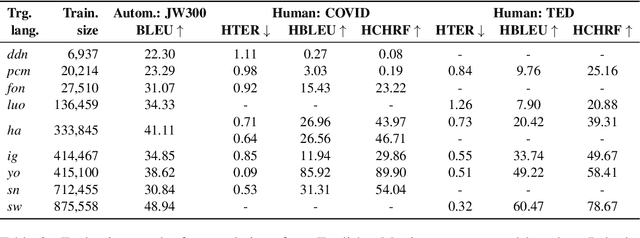
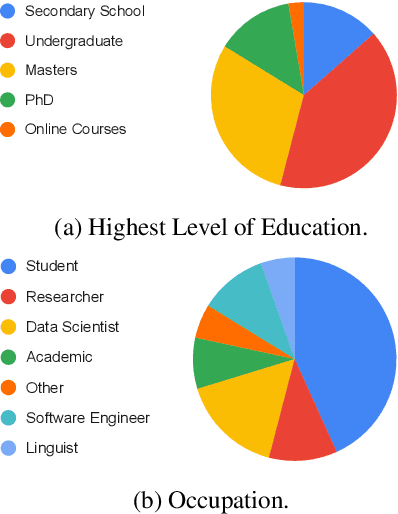
Abstract:Research in NLP lacks geographic diversity, and the question of how NLP can be scaled to low-resourced languages has not yet been adequately solved. "Low-resourced"-ness is a complex problem going beyond data availability and reflects systemic problems in society. In this paper, we focus on the task of Machine Translation (MT), that plays a crucial role for information accessibility and communication worldwide. Despite immense improvements in MT over the past decade, MT is centered around a few high-resourced languages. As MT researchers cannot solve the problem of low-resourcedness alone, we propose participatory research as a means to involve all necessary agents required in the MT development process. We demonstrate the feasibility and scalability of participatory research with a case study on MT for African languages. Its implementation leads to a collection of novel translation datasets, MT benchmarks for over 30 languages, with human evaluations for a third of them, and enables participants without formal training to make a unique scientific contribution. Benchmarks, models, data, code, and evaluation results are released under https://github.com/masakhane-io/masakhane-mt.
On Optimal Transformer Depth for Low-Resource Language Translation
Apr 14, 2020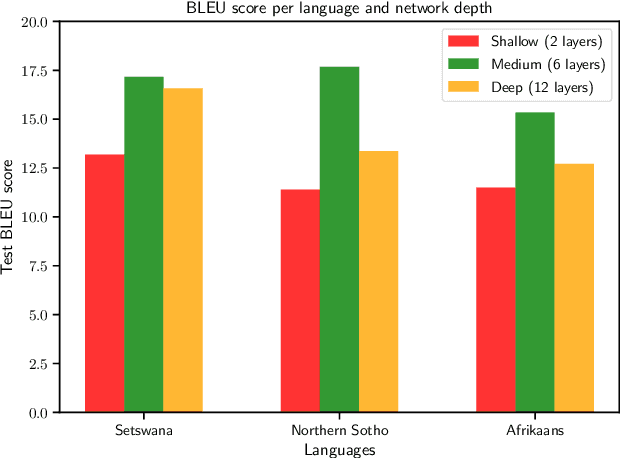
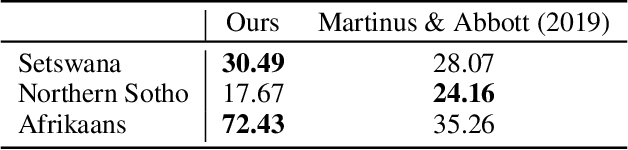
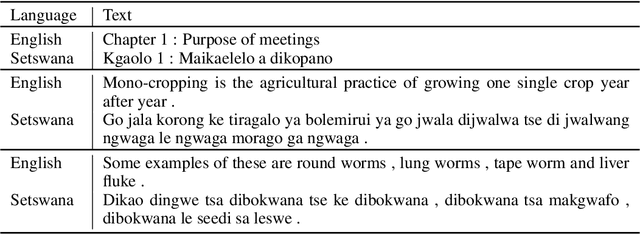

Abstract:Transformers have shown great promise as an approach to Neural Machine Translation (NMT) for low-resource languages. However, at the same time, transformer models remain difficult to optimize and require careful tuning of hyper-parameters to be useful in this setting. Many NMT toolkits come with a set of default hyper-parameters, which researchers and practitioners often adopt for the sake of convenience and avoiding tuning. These configurations, however, have been optimized for large-scale machine translation data sets with several millions of parallel sentences for European languages like English and French. In this work, we find that the current trend in the field to use very large models is detrimental for low-resource languages, since it makes training more difficult and hurts overall performance, confirming previous observations. We see our work as complementary to the Masakhane project ("Masakhane" means "We Build Together" in isiZulu.) In this spirit, low-resource NMT systems are now being built by the community who needs them the most. However, many in the community still have very limited access to the type of computational resources required for building extremely large models promoted by industrial research. Therefore, by showing that transformer models perform well (and often best) at low-to-moderate depth, we hope to convince fellow researchers to devote less computational resources, as well as time, to exploring overly large models during the development of these systems.
Masakhane -- Machine Translation For Africa
Mar 13, 2020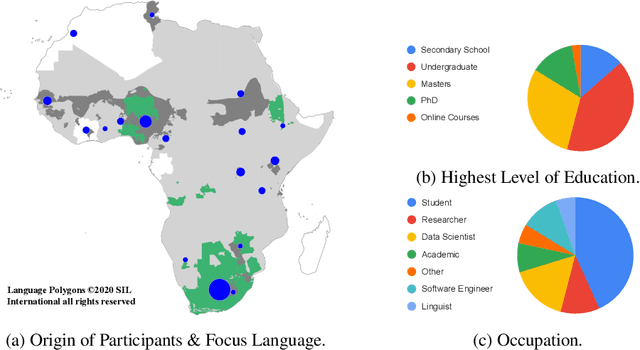
Abstract:Africa has over 2000 languages. Despite this, African languages account for a small portion of available resources and publications in Natural Language Processing (NLP). This is due to multiple factors, including: a lack of focus from government and funding, discoverability, a lack of community, sheer language complexity, difficulty in reproducing papers and no benchmarks to compare techniques. To begin to address the identified problems, MASAKHANE, an open-source, continent-wide, distributed, online research effort for machine translation for African languages, was founded. In this paper, we discuss our methodology for building the community and spurring research from the African continent, as well as outline the success of the community in terms of addressing the identified problems affecting African NLP.
If dropout limits trainable depth, does critical initialisation still matter? A large-scale statistical analysis on ReLU networks
Oct 13, 2019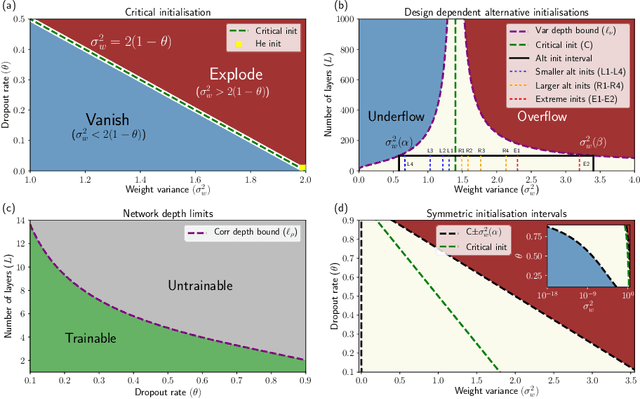
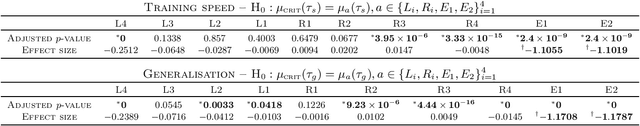
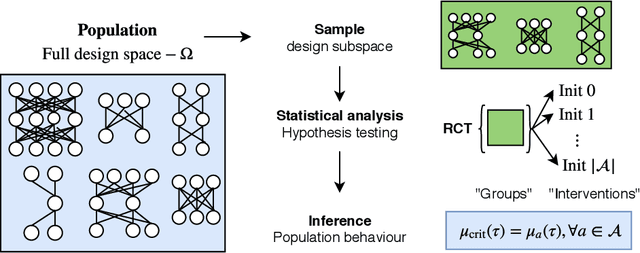
Abstract:Recent work in signal propagation theory has shown that dropout limits the depth to which information can propagate through a neural network. In this paper, we investigate the effect of initialisation on training speed and generalisation for ReLU networks within this depth limit. We ask the following research question: given that critical initialisation is crucial for training at large depth, if dropout limits the depth at which networks are trainable, does initialising critically still matter? We conduct a large-scale controlled experiment, and perform a statistical analysis of over $12000$ trained networks. We find that (1) trainable networks show no statistically significant difference in performance over a wide range of non-critical initialisations; (2) for initialisations that show a statistically significant difference, the net effect on performance is small; (3) only extreme initialisations (very small or very large) perform worse than criticality. These findings also apply to standard ReLU networks of moderate depth as a special case of zero dropout. Our results therefore suggest that, in the shallow-to-moderate depth setting, critical initialisation provides zero performance gains when compared to off-critical initialisations and that searching for off-critical initialisations that might improve training speed or generalisation, is likely to be a fruitless endeavour.
Unsupervised acoustic unit discovery for speech synthesis using discrete latent-variable neural networks
Apr 16, 2019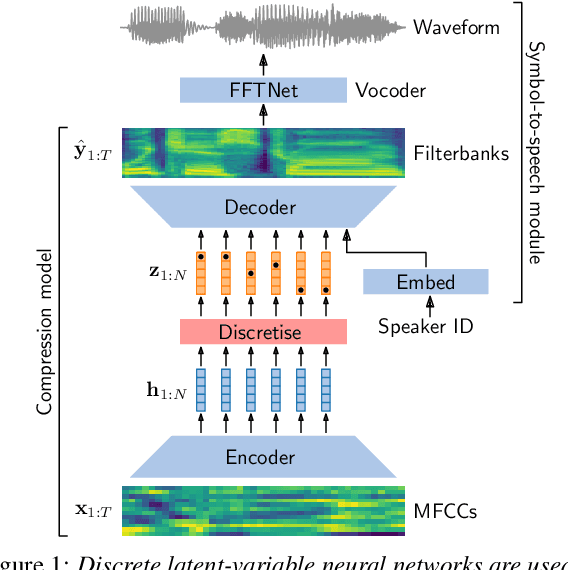
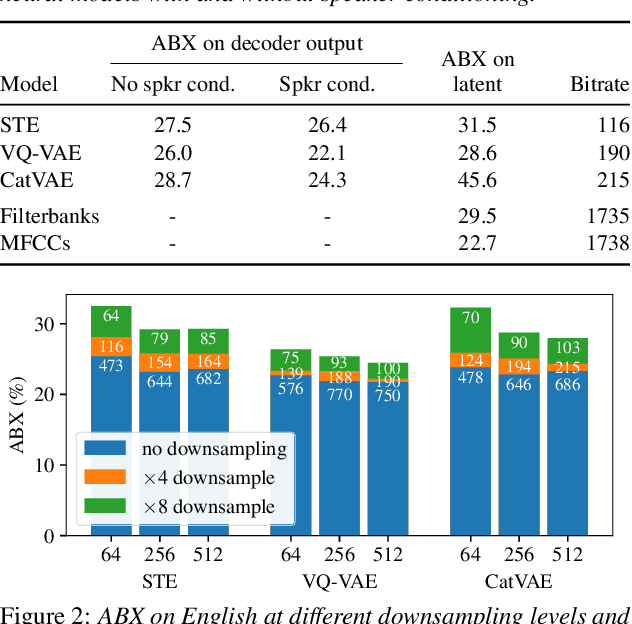
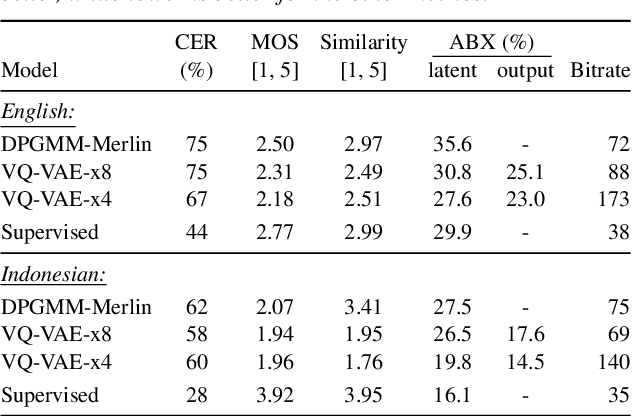
Abstract:For our submission to the ZeroSpeech 2019 challenge, we apply discrete latent-variable neural networks to unlabelled speech and use the discovered units for speech synthesis. Unsupervised discrete subword modelling could be useful for studies of phonetic category learning in infants or in low-resource speech technology requiring symbolic input. We use an autoencoder (AE) architecture with intermediate discretisation. We decouple acoustic unit discovery from speaker modelling by conditioning the AE's decoder on the training speaker identity. At test time, unit discovery is performed on speech from an unseen speaker, followed by unit decoding conditioned on a known target speaker to obtain reconstructed filterbanks. This output is fed to a neural vocoder to synthesise speech in the target speaker's voice. For discretisation, categorical variational autoencoders (CatVAEs), vector-quantised VAEs (VQ-VAEs) and straight-through estimation are compared at different compression levels on two languages. Our final model uses convolutional encoding, VQ-VAE discretisation, deconvolutional decoding and an FFTNet vocoder. We show that decoupled speaker conditioning intrinsically improves discrete acoustic representations, yielding competitive synthesis quality compared to the challenge baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge