Douglas Teodoro
Toward Global Large Language Models in Medicine
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Despite continuous advances in medical technology, the global distribution of health care resources remains uneven. The development of large language models (LLMs) has transformed the landscape of medicine and holds promise for improving health care quality and expanding access to medical information globally. However, existing LLMs are primarily trained on high-resource languages, limiting their applicability in global medical scenarios. To address this gap, we constructed GlobMed, a large multilingual medical dataset, containing over 500,000 entries spanning 12 languages, including four low-resource languages. Building on this, we established GlobMed-Bench, which systematically assesses 56 state-of-the-art proprietary and open-weight LLMs across multiple multilingual medical tasks, revealing significant performance disparities across languages, particularly for low-resource languages. Additionally, we introduced GlobMed-LLMs, a suite of multilingual medical LLMs trained on GlobMed, with parameters ranging from 1.7B to 8B. GlobMed-LLMs achieved an average performance improvement of over 40% relative to baseline models, with a more than threefold increase in performance on low-resource languages. Together, these resources provide an important foundation for advancing the equitable development and application of LLMs globally, enabling broader language communities to benefit from technological advances.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Medicine: A Scoping Review of Technical Implementations, Clinical Applications, and Ethical Considerations
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of medical knowledge and increasing complexity of clinical practice pose challenges. In this context, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated value; however, inherent limitations remain. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technologies show potential to enhance their clinical applicability. This study reviewed RAG applications in medicine. We found that research primarily relied on publicly available data, with limited application in private data. For retrieval, approaches commonly relied on English-centric embedding models, while LLMs were mostly generic, with limited use of medical-specific LLMs. For evaluation, automated metrics evaluated generation quality and task performance, whereas human evaluation focused on accuracy, completeness, relevance, and fluency, with insufficient attention to bias and safety. RAG applications were concentrated on question answering, report generation, text summarization, and information extraction. Overall, medical RAG remains at an early stage, requiring advances in clinical validation, cross-linguistic adaptation, and support for low-resource settings to enable trustworthy and responsible global use.
ICU-TSB: A Benchmark for Temporal Patient Representation Learning for Unsupervised Stratification into Patient Cohorts
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Patient stratification identifying clinically meaningful subgroups is essential for advancing personalized medicine through improved diagnostics and treatment strategies. Electronic health records (EHRs), particularly those from intensive care units (ICUs), contain rich temporal clinical data that can be leveraged for this purpose. In this work, we introduce ICU-TSB (Temporal Stratification Benchmark), the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating patient stratification based on temporal patient representation learning using three publicly available ICU EHR datasets. A key contribution of our benchmark is a novel hierarchical evaluation framework utilizing disease taxonomies to measure the alignment of discovered clusters with clinically validated disease groupings. In our experiments with ICU-TSB, we compared statistical methods and several recurrent neural networks, including LSTM and GRU, for their ability to generate effective patient representations for subsequent clustering of patient trajectories. Our results demonstrate that temporal representation learning can rediscover clinically meaningful patient cohorts; nevertheless, it remains a challenging task, with v-measuring varying from up to 0.46 at the top level of the taxonomy to up to 0.40 at the lowest level. To further enhance the practical utility of our findings, we also evaluate multiple strategies for assigning interpretable labels to the identified clusters. The experiments and benchmark are fully reproducible and available at https://github.com/ds4dh/CBMS2025stratification.
The Evolving Landscape of Generative Large Language Models and Traditional Natural Language Processing in Medicine
May 15, 2025Abstract:Natural language processing (NLP) has been traditionally applied to medicine, and generative large language models (LLMs) have become prominent recently. However, the differences between them across different medical tasks remain underexplored. We analyzed 19,123 studies, finding that generative LLMs demonstrate advantages in open-ended tasks, while traditional NLP dominates in information extraction and analysis tasks. As these technologies advance, ethical use of them is essential to ensure their potential in medical applications.
GLiNER-biomed: A Suite of Efficient Models for Open Biomedical Named Entity Recognition
Apr 01, 2025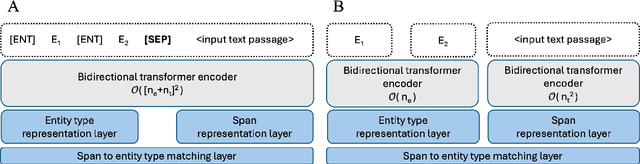



Abstract:Biomedical named entity recognition (NER) presents unique challenges due to specialized vocabularies, the sheer volume of entities, and the continuous emergence of novel entities. Traditional NER models, constrained by fixed taxonomies and human annotations, struggle to generalize beyond predefined entity types or efficiently adapt to emerging concepts. To address these issues, we introduce GLiNER-biomed, a domain-adapted suite of Generalist and Lightweight Model for NER (GLiNER) models specifically tailored for biomedical NER. In contrast to conventional approaches, GLiNER uses natural language descriptions to infer arbitrary entity types, enabling zero-shot recognition. Our approach first distills the annotation capabilities of large language models (LLMs) into a smaller, more efficient model, enabling the generation of high-coverage synthetic biomedical NER data. We subsequently train two GLiNER architectures, uni- and bi-encoder, at multiple scales to balance computational efficiency and recognition performance. Evaluations on several biomedical datasets demonstrate that GLiNER-biomed outperforms state-of-the-art GLiNER models in both zero- and few-shot scenarios, achieving 5.96% improvement in F1-score over the strongest baseline. Ablation studies highlight the effectiveness of our synthetic data generation strategy and emphasize the complementary benefits of synthetic biomedical pre-training combined with fine-tuning on high-quality general-domain annotations. All datasets, models, and training pipelines are publicly available at https://github.com/ds4dh/GLiNER-biomed.
MKG-Rank: Enhancing Large Language Models with Knowledge Graph for Multilingual Medical Question Answering
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable progress in medical question answering (QA), yet their effectiveness remains predominantly limited to English due to imbalanced multilingual training data and scarce medical resources for low-resource languages. To address this critical language gap in medical QA, we propose Multilingual Knowledge Graph-based Retrieval Ranking (MKG-Rank), a knowledge graph-enhanced framework that enables English-centric LLMs to perform multilingual medical QA. Through a word-level translation mechanism, our framework efficiently integrates comprehensive English-centric medical knowledge graphs into LLM reasoning at a low cost, mitigating cross-lingual semantic distortion and achieving precise medical QA across language barriers. To enhance efficiency, we introduce caching and multi-angle ranking strategies to optimize the retrieval process, significantly reducing response times and prioritizing relevant medical knowledge. Extensive evaluations on multilingual medical QA benchmarks across Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Swahili demonstrate that MKG-Rank consistently outperforms zero-shot LLMs, achieving maximum 35.03% increase in accuracy, while maintaining an average retrieval time of only 0.0009 seconds.
MMLU-ProX: A Multilingual Benchmark for Advanced Large Language Model Evaluation
Mar 13, 2025

Abstract:Traditional benchmarks struggle to evaluate increasingly sophisticated language models in multilingual and culturally diverse contexts. To address this gap, we introduce MMLU-ProX, a comprehensive multilingual benchmark covering 13 typologically diverse languages with approximately 11,829 questions per language. Building on the challenging reasoning-focused design of MMLU-Pro, our framework employs a semi-automatic translation process: translations generated by state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) are rigorously evaluated by expert annotators to ensure conceptual accuracy, terminological consistency, and cultural relevance. We comprehensively evaluate 25 state-of-the-art LLMs using 5-shot chain-of-thought (CoT) and zero-shot prompting strategies, analyzing their performance across linguistic and cultural boundaries. Our experiments reveal consistent performance degradation from high-resource languages to lower-resource ones, with the best models achieving over 70% accuracy on English but dropping to around 40% for languages like Swahili, highlighting persistent gaps in multilingual capabilities despite recent advances. MMLU-ProX is an ongoing project; we are expanding our benchmark by incorporating additional languages and evaluating more language models to provide a more comprehensive assessment of multilingual capabilities.
CT-ADE: An Evaluation Benchmark for Adverse Drug Event Prediction from Clinical Trial Results
Apr 19, 2024Abstract:Adverse drug events (ADEs) significantly impact clinical research and public health, contributing to failures in clinical trials and leading to increased healthcare costs. The accurate prediction and management of ADEs are crucial for improving the development of safer, more effective medications, and enhancing patient outcomes. To support this effort, we introduce CT-ADE, a novel dataset compiled to enhance the predictive modeling of ADEs. Encompassing over 12,000 instances extracted from clinical trial results, the CT-ADE dataset integrates drug, patient population, and contextual information for multilabel ADE classification tasks in monopharmacy treatments, providing a comprehensive resource for developing advanced predictive models. To mirror the complex nature of ADEs, annotations are standardized at the system organ class level of the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) ontology. Preliminary analyses using baseline models have demonstrated promising results, achieving 73.33% F1 score and 81.54% balanced accuracy, highlighting CT-ADE's potential to advance ADE prediction. CT-ADE provides an essential tool for researchers aiming to leverage the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance patient safety and minimize the impact of ADEs on pharmaceutical research and development. Researchers interested in using the CT-ADE dataset can find all necessary resources at https://github.com/xxxx/xxxx.
DS4DH at #SMM4H 2023: Zero-Shot Adverse Drug Events Normalization using Sentence Transformers and Reciprocal-Rank Fusion
Aug 15, 2023

Abstract:This paper outlines the performance evaluation of a system for adverse drug event normalization, developed by the Data Science for Digital Health group for the Social Media Mining for Health Applications 2023 shared task 5. Shared task 5 targeted the normalization of adverse drug event mentions in Twitter to standard concepts from the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities terminology. Our system hinges on a two-stage approach: BERT fine-tuning for entity recognition, followed by zero-shot normalization using sentence transformers and reciprocal-rank fusion. The approach yielded a precision of 44.9%, recall of 40.5%, and an F1-score of 42.6%. It outperformed the median performance in shared task 5 by 10% and demonstrated the highest performance among all participants. These results substantiate the effectiveness of our approach and its potential application for adverse drug event normalization in the realm of social media text mining.
Efficient Joint Learning for Clinical Named Entity Recognition and Relation Extraction Using Fourier Networks: A Use Case in Adverse Drug Events
Feb 08, 2023



Abstract:Current approaches for clinical information extraction are inefficient in terms of computational costs and memory consumption, hindering their application to process large-scale electronic health records (EHRs). We propose an efficient end-to-end model, the Joint-NER-RE-Fourier (JNRF), to jointly learn the tasks of named entity recognition and relation extraction for documents of variable length. The architecture uses positional encoding and unitary batch sizes to process variable length documents and uses a weight-shared Fourier network layer for low-complexity token mixing. Finally, we reach the theoretical computational complexity lower bound for relation extraction using a selective pooling strategy and distance-aware attention weights with trainable polynomial distance functions. We evaluated the JNRF architecture using the 2018 N2C2 ADE benchmark to jointly extract medication-related entities and relations in variable-length EHR summaries. JNRF outperforms rolling window BERT with selective pooling by 0.42%, while being twice as fast to train. Compared to state-of-the-art BiLSTM-CRF architectures on the N2C2 ADE benchmark, results show that the proposed approach trains 22 times faster and reduces GPU memory consumption by 1.75 folds, with a reasonable performance tradeoff of 90%, without the use of external tools, hand-crafted rules or post-processing. Given the significant carbon footprint of deep learning models and the current energy crises, these methods could support efficient and cleaner information extraction in EHRs and other types of large-scale document databases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge