David Vandyke
TOAD: Task-Oriented Automatic Dialogs with Diverse Response Styles
Feb 16, 2024Abstract:In light of recent advances in large language models (LLMs), the expectations for the next generation of virtual assistants include enhanced naturalness and adaptability across diverse usage scenarios. However, the creation of high-quality annotated data for Task-Oriented Dialog (TOD) is recognized to be slow and costly. To address these challenges, we introduce Task-Oriented Automatic Dialogs (TOAD), a novel and scalable TOD dataset along with its automatic generation pipeline. The TOAD dataset simulates realistic app context interaction and provide a variety of system response style options. Two aspects of system response styles are considered, verbosity level and users' expression mirroring. We benchmark TOAD on two response generation tasks and the results show that modelling more verbose or responses without user expression mirroring is more challenging.
Languages You Know Influence Those You Learn: Impact of Language Characteristics on Multi-Lingual Text-to-Text Transfer
Dec 04, 2022



Abstract:Multi-lingual language models (LM), such as mBERT, XLM-R, mT5, mBART, have been remarkably successful in enabling natural language tasks in low-resource languages through cross-lingual transfer from high-resource ones. In this work, we try to better understand how such models, specifically mT5, transfer *any* linguistic and semantic knowledge across languages, even though no explicit cross-lingual signals are provided during pre-training. Rather, only unannotated texts from each language are presented to the model separately and independently of one another, and the model appears to implicitly learn cross-lingual connections. This raises several questions that motivate our study, such as: Are the cross-lingual connections between every language pair equally strong? What properties of source and target language impact the strength of cross-lingual transfer? Can we quantify the impact of those properties on the cross-lingual transfer? In our investigation, we analyze a pre-trained mT5 to discover the attributes of cross-lingual connections learned by the model. Through a statistical interpretation framework over 90 language pairs across three tasks, we show that transfer performance can be modeled by a few linguistic and data-derived features. These observations enable us to interpret cross-lingual understanding of the mT5 model. Through these observations, one can favorably choose the best source language for a task, and can anticipate its training data demands. A key finding of this work is that similarity of syntax, morphology and phonology are good predictors of cross-lingual transfer, significantly more than just the lexical similarity of languages. For a given language, we are able to predict zero-shot performance, that increases on a logarithmic scale with the number of few-shot target language data points.
Prompting for a conversation: How to control a dialog model?
Sep 22, 2022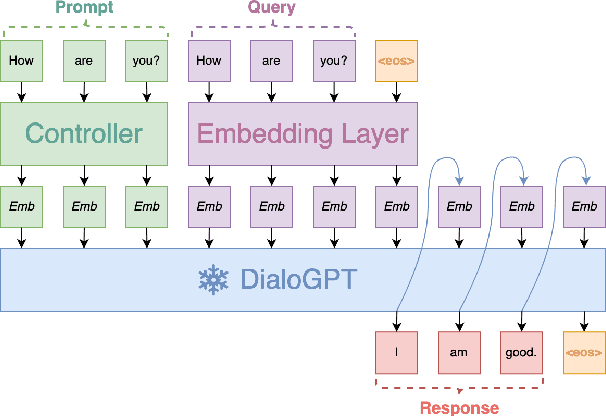
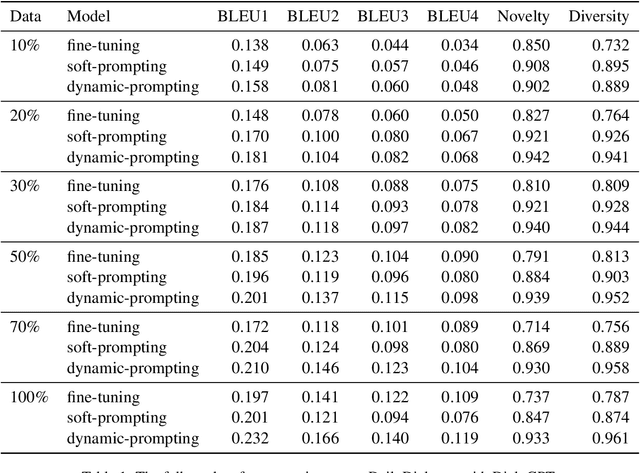
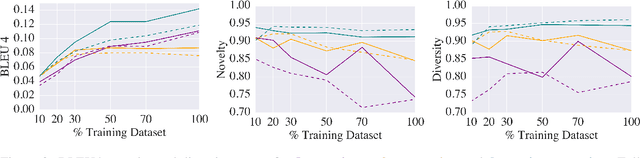
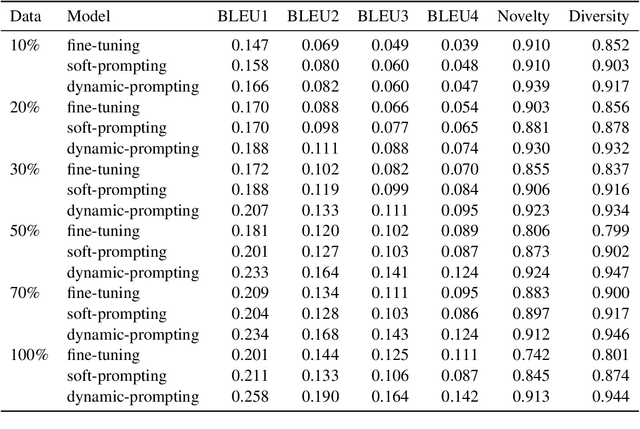
Abstract:Dialog modelling faces a difficult trade-off. Models are trained on a large amount of text, yet their responses need to be limited to a desired scope and style of a dialog agent. Because the datasets used to achieve the former contain language that is not compatible with the latter, pre-trained dialog models are fine-tuned on smaller curated datasets. However, the fine-tuning process robs them of the ability to produce diverse responses, eventually reducing them to dull conversation partners. In this paper we investigate if prompting can mitigate the above trade-off. Specifically, we experiment with conditioning the prompt on the query, rather than training a single prompt for all queries. By following the intuition that freezing the pre-trained language model will conserve its expressivity, we find that compared to fine-tuning, prompting can achieve a higher BLEU score and substantially improve the diversity and novelty of the responses.
Plan-then-Generate: Controlled Data-to-Text Generation via Planning
Aug 31, 2021



Abstract:Recent developments in neural networks have led to the advance in data-to-text generation. However, the lack of ability of neural models to control the structure of generated output can be limiting in certain real-world applications. In this study, we propose a novel Plan-then-Generate (PlanGen) framework to improve the controllability of neural data-to-text models. Extensive experiments and analyses are conducted on two benchmark datasets, ToTTo and WebNLG. The results show that our model is able to control both the intra-sentence and inter-sentence structure of the generated output. Furthermore, empirical comparisons against previous state-of-the-art methods show that our model improves the generation quality as well as the output diversity as judged by human and automatic evaluations.
Non-Autoregressive Text Generation with Pre-trained Language Models
Feb 16, 2021



Abstract:Non-autoregressive generation (NAG) has recently attracted great attention due to its fast inference speed. However, the generation quality of existing NAG models still lags behind their autoregressive counterparts. In this work, we show that BERT can be employed as the backbone of a NAG model to greatly improve performance. Additionally, we devise mechanisms to alleviate the two common problems of vanilla NAG models: the inflexibility of prefixed output length and the conditional independence of individual token predictions. Lastly, to further increase the speed advantage of the proposed model, we propose a new decoding strategy, ratio-first, for applications where the output lengths can be approximately estimated beforehand. For a comprehensive evaluation, we test the proposed model on three text generation tasks, including text summarization, sentence compression and machine translation. Experimental results show that our model significantly outperforms existing non-autoregressive baselines and achieves competitive performance with many strong autoregressive models. In addition, we also conduct extensive analysis experiments to reveal the effect of each proposed component.
A Generative Model for Joint Natural Language Understanding and Generation
Jun 12, 2020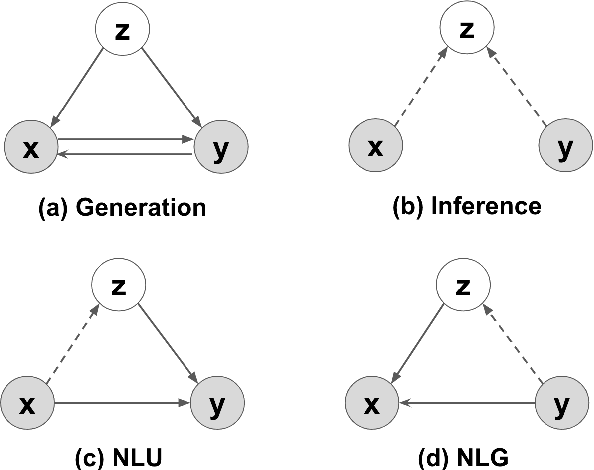

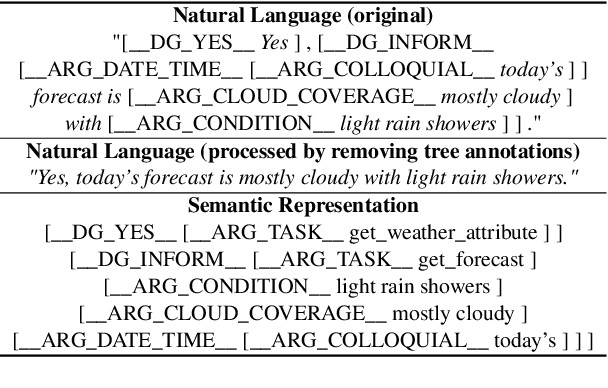
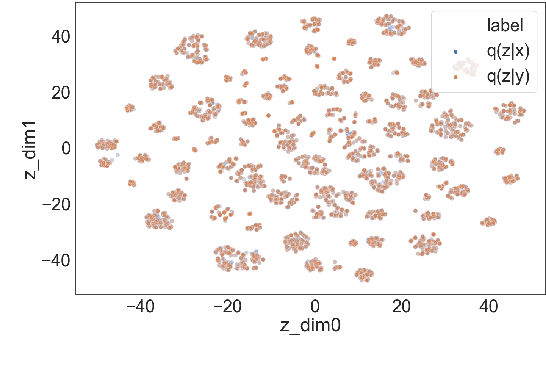
Abstract:Natural language understanding (NLU) and natural language generation (NLG) are two fundamental and related tasks in building task-oriented dialogue systems with opposite objectives: NLU tackles the transformation from natural language to formal representations, whereas NLG does the reverse. A key to success in either task is parallel training data which is expensive to obtain at a large scale. In this work, we propose a generative model which couples NLU and NLG through a shared latent variable. This approach allows us to explore both spaces of natural language and formal representations, and facilitates information sharing through the latent space to eventually benefit NLU and NLG. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on two dialogue datasets with both flat and tree-structured formal representations. We also show that the model can be trained in a semi-supervised fashion by utilising unlabelled data to boost its performance.
A Network-based End-to-End Trainable Task-oriented Dialogue System
Apr 24, 2017Abstract:Teaching machines to accomplish tasks by conversing naturally with humans is challenging. Currently, developing task-oriented dialogue systems requires creating multiple components and typically this involves either a large amount of handcrafting, or acquiring costly labelled datasets to solve a statistical learning problem for each component. In this work we introduce a neural network-based text-in, text-out end-to-end trainable goal-oriented dialogue system along with a new way of collecting dialogue data based on a novel pipe-lined Wizard-of-Oz framework. This approach allows us to develop dialogue systems easily and without making too many assumptions about the task at hand. The results show that the model can converse with human subjects naturally whilst helping them to accomplish tasks in a restaurant search domain.
Dialogue manager domain adaptation using Gaussian process reinforcement learning
Sep 09, 2016



Abstract:Spoken dialogue systems allow humans to interact with machines using natural speech. As such, they have many benefits. By using speech as the primary communication medium, a computer interface can facilitate swift, human-like acquisition of information. In recent years, speech interfaces have become ever more popular, as is evident from the rise of personal assistants such as Siri, Google Now, Cortana and Amazon Alexa. Recently, data-driven machine learning methods have been applied to dialogue modelling and the results achieved for limited-domain applications are comparable to or outperform traditional approaches. Methods based on Gaussian processes are particularly effective as they enable good models to be estimated from limited training data. Furthermore, they provide an explicit estimate of the uncertainty which is particularly useful for reinforcement learning. This article explores the additional steps that are necessary to extend these methods to model multiple dialogue domains. We show that Gaussian process reinforcement learning is an elegant framework that naturally supports a range of methods, including prior knowledge, Bayesian committee machines and multi-agent learning, for facilitating extensible and adaptable dialogue systems.
Conditional Generation and Snapshot Learning in Neural Dialogue Systems
Jun 10, 2016



Abstract:Recently a variety of LSTM-based conditional language models (LM) have been applied across a range of language generation tasks. In this work we study various model architectures and different ways to represent and aggregate the source information in an end-to-end neural dialogue system framework. A method called snapshot learning is also proposed to facilitate learning from supervised sequential signals by applying a companion cross-entropy objective function to the conditioning vector. The experimental and analytical results demonstrate firstly that competition occurs between the conditioning vector and the LM, and the differing architectures provide different trade-offs between the two. Secondly, the discriminative power and transparency of the conditioning vector is key to providing both model interpretability and better performance. Thirdly, snapshot learning leads to consistent performance improvements independent of which architecture is used.
Continuously Learning Neural Dialogue Management
Jun 08, 2016



Abstract:We describe a two-step approach for dialogue management in task-oriented spoken dialogue systems. A unified neural network framework is proposed to enable the system to first learn by supervision from a set of dialogue data and then continuously improve its behaviour via reinforcement learning, all using gradient-based algorithms on one single model. The experiments demonstrate the supervised model's effectiveness in the corpus-based evaluation, with user simulation, and with paid human subjects. The use of reinforcement learning further improves the model's performance in both interactive settings, especially under higher-noise conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge