Pei-Hao Su
ConvFiT: Conversational Fine-Tuning of Pretrained Language Models
Sep 21, 2021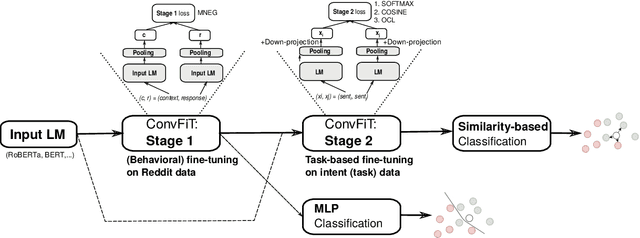

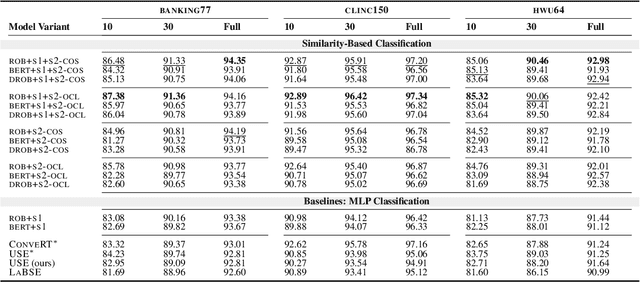
Abstract:Transformer-based language models (LMs) pretrained on large text collections are proven to store a wealth of semantic knowledge. However, 1) they are not effective as sentence encoders when used off-the-shelf, and 2) thus typically lag behind conversationally pretrained (e.g., via response selection) encoders on conversational tasks such as intent detection (ID). In this work, we propose ConvFiT, a simple and efficient two-stage procedure which turns any pretrained LM into a universal conversational encoder (after Stage 1 ConvFiT-ing) and task-specialised sentence encoder (after Stage 2). We demonstrate that 1) full-blown conversational pretraining is not required, and that LMs can be quickly transformed into effective conversational encoders with much smaller amounts of unannotated data; 2) pretrained LMs can be fine-tuned into task-specialised sentence encoders, optimised for the fine-grained semantics of a particular task. Consequently, such specialised sentence encoders allow for treating ID as a simple semantic similarity task based on interpretable nearest neighbours retrieval. We validate the robustness and versatility of the ConvFiT framework with such similarity-based inference on the standard ID evaluation sets: ConvFiT-ed LMs achieve state-of-the-art ID performance across the board, with particular gains in the most challenging, few-shot setups.
Multilingual and Cross-Lingual Intent Detection from Spoken Data
Apr 17, 2021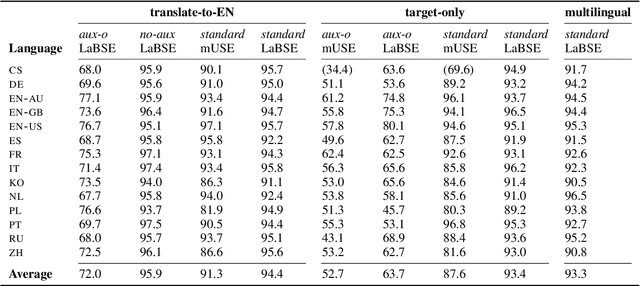
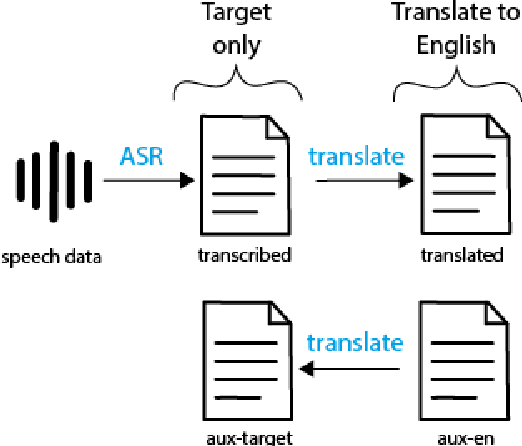
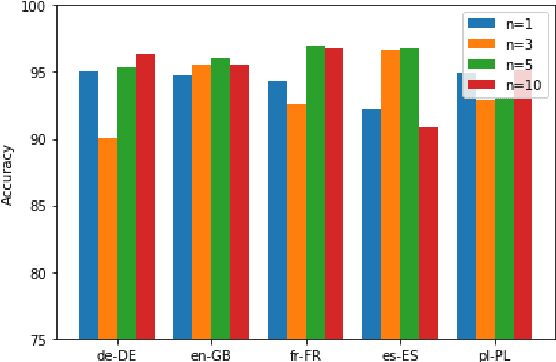
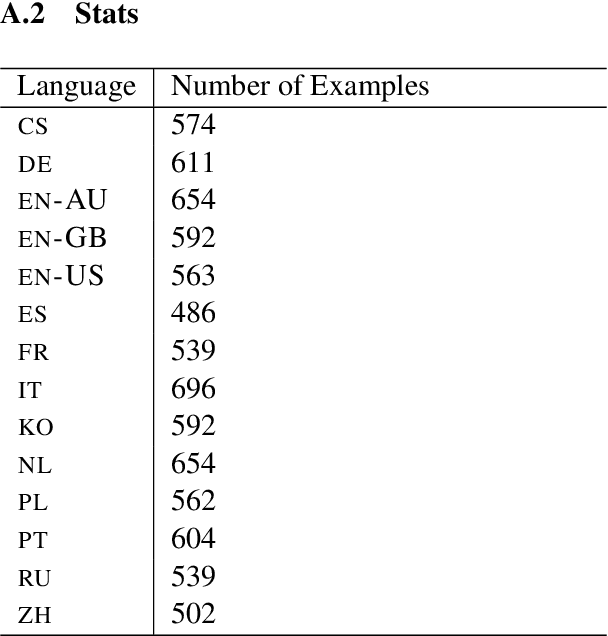
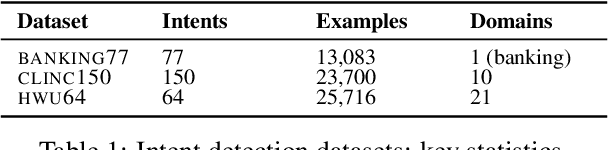
Abstract:We present a systematic study on multilingual and cross-lingual intent detection from spoken data. The study leverages a new resource put forth in this work, termed MInDS-14, a first training and evaluation resource for the intent detection task with spoken data. It covers 14 intents extracted from a commercial system in the e-banking domain, associated with spoken examples in 14 diverse language varieties. Our key results indicate that combining machine translation models with state-of-the-art multilingual sentence encoders (e.g., LaBSE) can yield strong intent detectors in the majority of target languages covered in MInDS-14, and offer comparative analyses across different axes: e.g., zero-shot versus few-shot learning, translation direction, and impact of speech recognition. We see this work as an important step towards more inclusive development and evaluation of multilingual intent detectors from spoken data, in a much wider spectrum of languages compared to prior work.
ConveRT: Efficient and Accurate Conversational Representations from Transformers
Nov 09, 2019



Abstract:General-purpose pretrained sentence encoders such as BERT are not ideal for real-world conversational AI applications; they are computationally heavy, slow, and expensive to train. We propose ConveRT (Conversational Representations from Transformers), a faster, more compact dual sentence encoder specifically optimized for dialog tasks. We pretrain using a retrieval-based response selection task, effectively leveraging quantization and subword-level parameterization in the dual encoder to build a lightweight memory- and energy-efficient model. In our evaluation, we show that ConveRT achieves state-of-the-art performance across widely established response selection tasks. We also demonstrate that the use of extended dialog history as context yields further performance gains. Finally, we show that pretrained representations from the proposed encoder can be transferred to the intent classification task, yielding strong results across three diverse data sets. ConveRT trains substantially faster than standard sentence encoders or previous state-of-the-art dual encoders. With its reduced size and superior performance, we believe this model promises wider portability and scalability for Conversational AI applications.
PolyResponse: A Rank-based Approach to Task-Oriented Dialogue with Application in Restaurant Search and Booking
Sep 03, 2019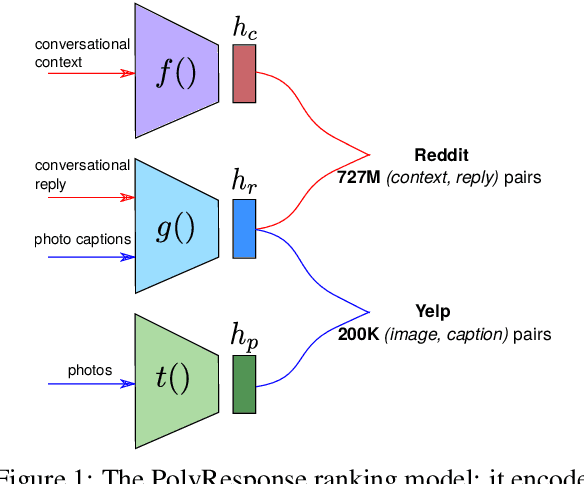
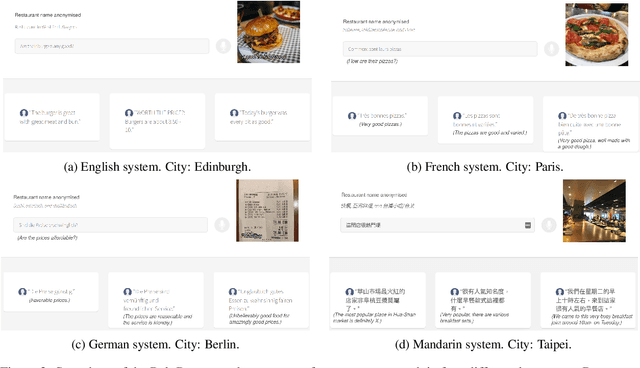
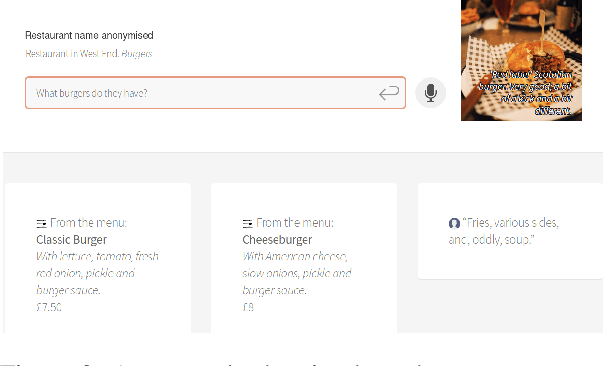
Abstract:We present PolyResponse, a conversational search engine that supports task-oriented dialogue. It is a retrieval-based approach that bypasses the complex multi-component design of traditional task-oriented dialogue systems and the use of explicit semantics in the form of task-specific ontologies. The PolyResponse engine is trained on hundreds of millions of examples extracted from real conversations: it learns what responses are appropriate in different conversational contexts. It then ranks a large index of text and visual responses according to their similarity to the given context, and narrows down the list of relevant entities during the multi-turn conversation. We introduce a restaurant search and booking system powered by the PolyResponse engine, currently available in 8 different languages.
Training Neural Response Selection for Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems
Jun 07, 2019

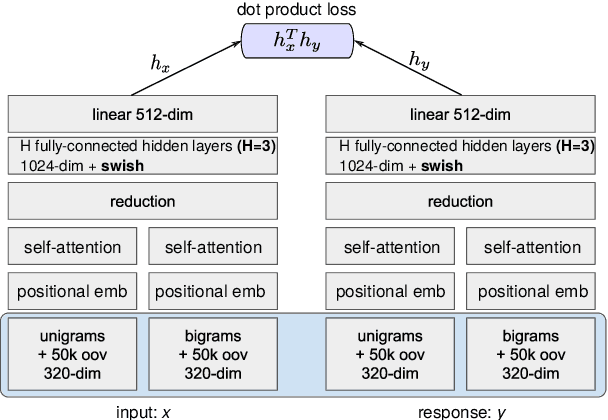
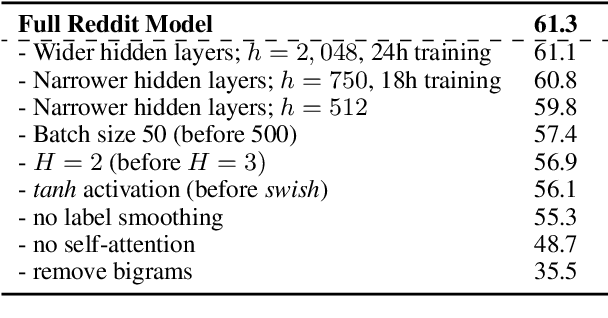
Abstract:Despite their popularity in the chatbot literature, retrieval-based models have had modest impact on task-oriented dialogue systems, with the main obstacle to their application being the low-data regime of most task-oriented dialogue tasks. Inspired by the recent success of pretraining in language modelling, we propose an effective method for deploying response selection in task-oriented dialogue. To train response selection models for task-oriented dialogue tasks, we propose a novel method which: 1) pretrains the response selection model on large general-domain conversational corpora; and then 2) fine-tunes the pretrained model for the target dialogue domain, relying only on the small in-domain dataset to capture the nuances of the given dialogue domain. Our evaluation on six diverse application domains, ranging from e-commerce to banking, demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed training method.
A Repository of Conversational Datasets
May 29, 2019
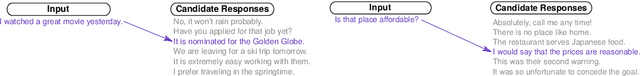
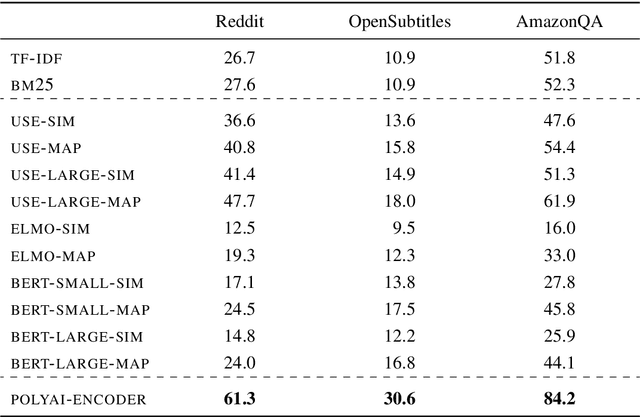

Abstract:Progress in Machine Learning is often driven by the availability of large datasets, and consistent evaluation metrics for comparing modeling approaches. To this end, we present a repository of conversational datasets consisting of hundreds of millions of examples, and a standardised evaluation procedure for conversational response selection models using '1-of-100 accuracy'. The repository contains scripts that allow researchers to reproduce the standard datasets, or to adapt the pre-processing and data filtering steps to their needs. We introduce and evaluate several competitive baselines for conversational response selection, whose implementations are shared in the repository, as well as a neural encoder model that is trained on the entire training set.
A Benchmarking Environment for Reinforcement Learning Based Task Oriented Dialogue Management
Apr 06, 2018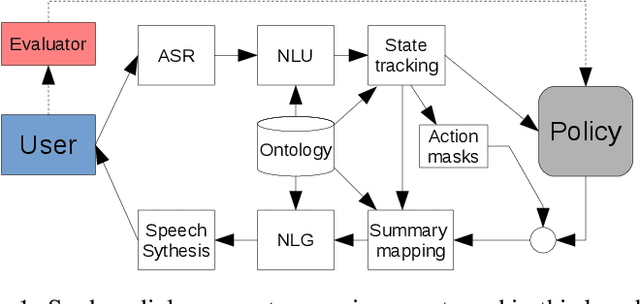
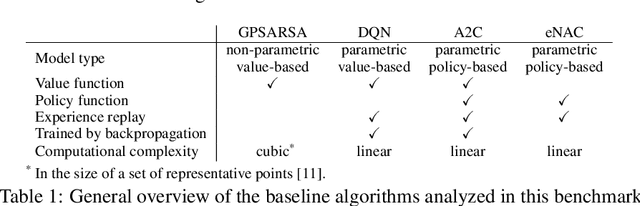
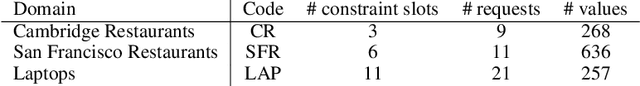
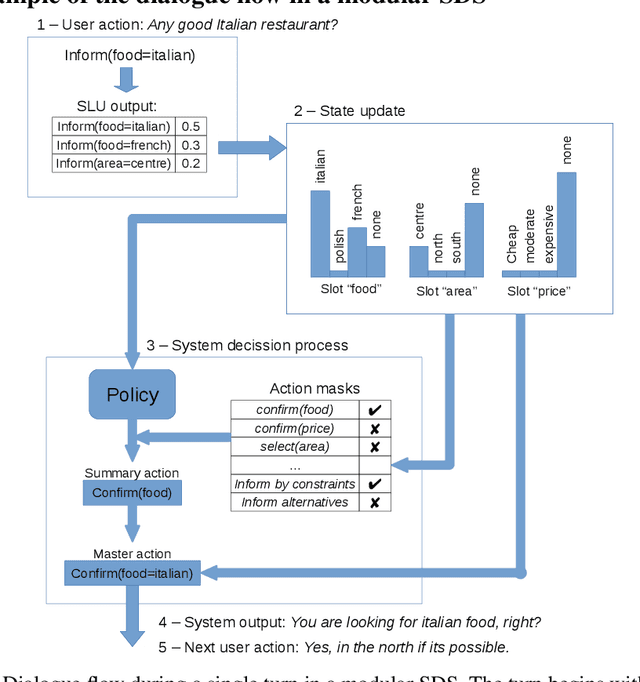
Abstract:Dialogue assistants are rapidly becoming an indispensable daily aid. To avoid the significant effort needed to hand-craft the required dialogue flow, the Dialogue Management (DM) module can be cast as a continuous Markov Decision Process (MDP) and trained through Reinforcement Learning (RL). Several RL models have been investigated over recent years. However, the lack of a common benchmarking framework makes it difficult to perform a fair comparison between different models and their capability to generalise to different environments. Therefore, this paper proposes a set of challenging simulated environments for dialogue model development and evaluation. To provide some baselines, we investigate a number of representative parametric algorithms, namely deep reinforcement learning algorithms - DQN, A2C and Natural Actor-Critic and compare them to a non-parametric model, GP-SARSA. Both the environments and policy models are implemented using the publicly available PyDial toolkit and released on-line, in order to establish a testbed framework for further experiments and to facilitate experimental reproducibility.
Feudal Reinforcement Learning for Dialogue Management in Large Domains
Mar 08, 2018



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) is a promising approach to solve dialogue policy optimisation. Traditional RL algorithms, however, fail to scale to large domains due to the curse of dimensionality. We propose a novel Dialogue Management architecture, based on Feudal RL, which decomposes the decision into two steps; a first step where a master policy selects a subset of primitive actions, and a second step where a primitive action is chosen from the selected subset. The structural information included in the domain ontology is used to abstract the dialogue state space, taking the decisions at each step using different parts of the abstracted state. This, combined with an information sharing mechanism between slots, increases the scalability to large domains. We show that an implementation of this approach, based on Deep-Q Networks, significantly outperforms previous state of the art in several dialogue domains and environments, without the need of any additional reward signal.
Sample Efficient Deep Reinforcement Learning for Dialogue Systems with Large Action Spaces
Feb 11, 2018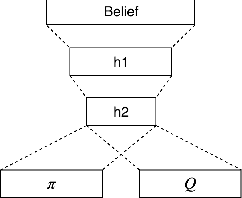
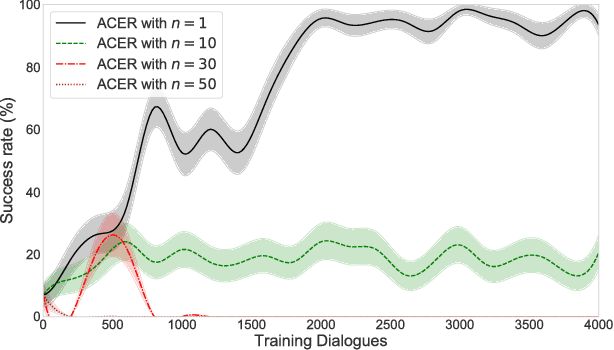
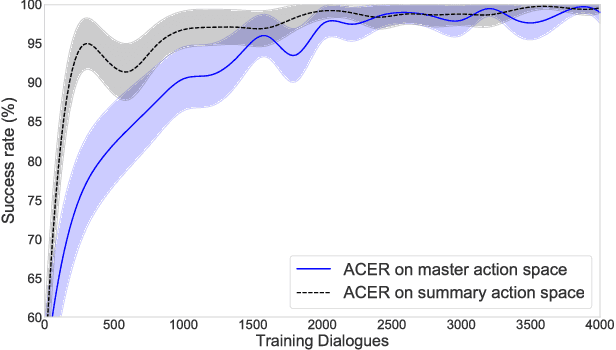
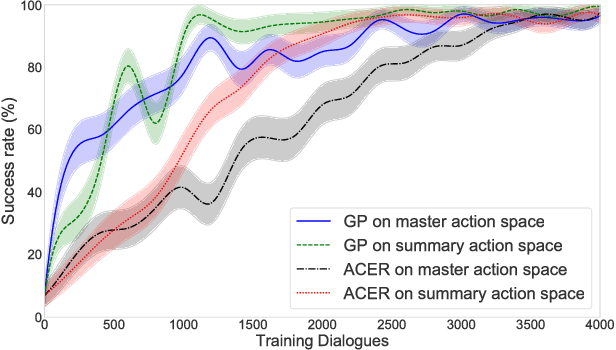
Abstract:In spoken dialogue systems, we aim to deploy artificial intelligence to build automated dialogue agents that can converse with humans. A part of this effort is the policy optimisation task, which attempts to find a policy describing how to respond to humans, in the form of a function taking the current state of the dialogue and returning the response of the system. In this paper, we investigate deep reinforcement learning approaches to solve this problem. Particular attention is given to actor-critic methods, off-policy reinforcement learning with experience replay, and various methods aimed at reducing the bias and variance of estimators. When combined, these methods result in the previously proposed ACER algorithm that gave competitive results in gaming environments. These environments however are fully observable and have a relatively small action set so in this paper we examine the application of ACER to dialogue policy optimisation. We show that this method beats the current state-of-the-art in deep learning approaches for spoken dialogue systems. This not only leads to a more sample efficient algorithm that can train faster, but also allows us to apply the algorithm in more difficult environments than before. We thus experiment with learning in a very large action space, which has two orders of magnitude more actions than previously considered. We find that ACER trains significantly faster than the current state-of-the-art.
Reward-Balancing for Statistical Spoken Dialogue Systems using Multi-objective Reinforcement Learning
Jul 19, 2017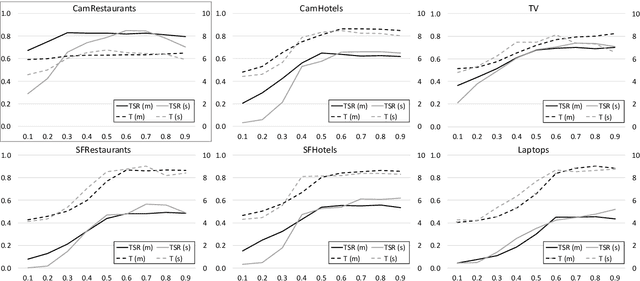
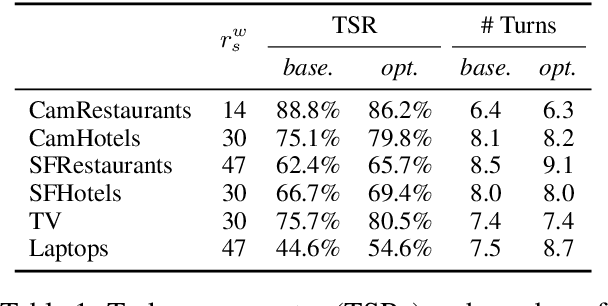
Abstract:Reinforcement learning is widely used for dialogue policy optimization where the reward function often consists of more than one component, e.g., the dialogue success and the dialogue length. In this work, we propose a structured method for finding a good balance between these components by searching for the optimal reward component weighting. To render this search feasible, we use multi-objective reinforcement learning to significantly reduce the number of training dialogues required. We apply our proposed method to find optimized component weights for six domains and compare them to a default baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge