David Keetae Park
DIVER-1 : Deep Integration of Vast Electrophysiological Recordings at Scale
Dec 22, 2025



Abstract:Electrophysiology signals such as EEG and iEEG are central to neuroscience, brain-computer interfaces, and clinical applications, yet existing foundation models remain limited in scale despite clear evidence that scaling improves performance. We introduce DIVER-1, a family of EEG and iEEG foundation models trained on the largest and most diverse corpus to date-5.3k hours of iEEG and 54k hours of EEG (1.6M channel-hours from over 17.7k subjects)-and scaled up to 1.82B parameters. We present the first systematic scaling law analysis for this domain, showing that they follow data-constrained scaling laws: for a given amount of data and compute, smaller models trained for extended epochs consistently outperform larger models trained briefly. This behavior contrasts with prior electrophysiology foundation models that emphasized model size over training duration. To achieve strong performance, we also design architectural innovations including any-variate attention, sliding temporal conditional positional encoding, and multi-domain reconstruction. DIVER-1 iEEG and EEG models each achieve state-of-the-art performance on their respective benchmarks, establishing a concrete guidelines for efficient scaling and resource allocation in electrophysiology foundation model development.
STACI: Spatio-Temporal Aleatoric Conformal Inference
May 27, 2025Abstract:Fitting Gaussian Processes (GPs) provides interpretable aleatoric uncertainty quantification for estimation of spatio-temporal fields. Spatio-temporal deep learning models, while scalable, typically assume a simplistic independent covariance matrix for the response, failing to capture the underlying correlation structure. However, spatio-temporal GPs suffer from issues of scalability and various forms of approximation bias resulting from restrictive assumptions of the covariance kernel function. We propose STACI, a novel framework consisting of a variational Bayesian neural network approximation of non-stationary spatio-temporal GP along with a novel spatio-temporal conformal inference algorithm. STACI is highly scalable, taking advantage of GPU training capabilities for neural network models, and provides statistically valid prediction intervals for uncertainty quantification. STACI outperforms competing GPs and deep methods in accurately approximating spatio-temporal processes and we show it easily scales to datasets with millions of observations.
SCENT: Robust Spatiotemporal Learning for Continuous Scientific Data via Scalable Conditioned Neural Fields
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Spatiotemporal learning is challenging due to the intricate interplay between spatial and temporal dependencies, the high dimensionality of the data, and scalability constraints. These challenges are further amplified in scientific domains, where data is often irregularly distributed (e.g., missing values from sensor failures) and high-volume (e.g., high-fidelity simulations), posing additional computational and modeling difficulties. In this paper, we present SCENT, a novel framework for scalable and continuity-informed spatiotemporal representation learning. SCENT unifies interpolation, reconstruction, and forecasting within a single architecture. Built on a transformer-based encoder-processor-decoder backbone, SCENT introduces learnable queries to enhance generalization and a query-wise cross-attention mechanism to effectively capture multi-scale dependencies. To ensure scalability in both data size and model complexity, we incorporate a sparse attention mechanism, enabling flexible output representations and efficient evaluation at arbitrary resolutions. We validate SCENT through extensive simulations and real-world experiments, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance across multiple challenging tasks while achieving superior scalability.
F^2-Softmax: Diversifying Neural Text Generation via Frequency Factorized Softmax
Oct 04, 2020



Abstract:Despite recent advances in neural text generation, encoding the rich diversity in human language remains elusive. We argue that the sub-optimal text generation is mainly attributable to the imbalanced token distribution, which particularly misdirects the learning model when trained with the maximum-likelihood objective. As a simple yet effective remedy, we propose two novel methods, F^2-Softmax and MefMax, for a balanced training even with the skewed frequency distribution. MefMax assigns tokens uniquely to frequency classes, trying to group tokens with similar frequencies and equalize frequency mass between the classes. F^2-Softmax then decomposes a probability distribution of the target token into a product of two conditional probabilities of (i) frequency class, and (ii) token from the target frequency class. Models learn more uniform probability distributions because they are confined to subsets of vocabularies. Significant performance gains on seven relevant metrics suggest the supremacy of our approach in improving not only the diversity but also the quality of generated texts.
What and Where to Translate: Local Mask-based Image-to-Image Translation
Jun 09, 2019
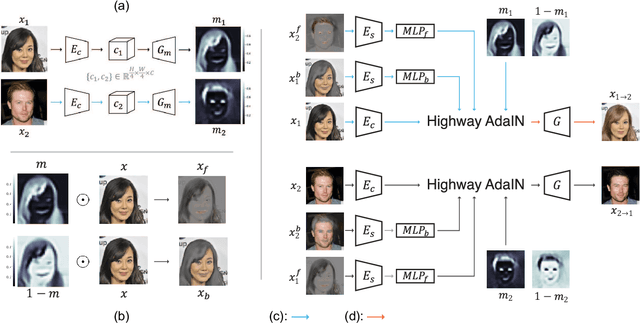

Abstract:Recently, image-to-image translation has obtained significant attention. Among many, those approaches based on an exemplar image that contains the target style information has been actively studied, due to its capability to handle multimodality as well as its applicability in practical use. However, two intrinsic problems exist in the existing methods: what and where to transfer. First, those methods extract style from an entire exemplar which includes noisy information, which impedes a translation model from properly extracting the intended style of the exemplar. That is, we need to carefully determine what to transfer from the exemplar. Second, the extracted style is applied to the entire input image, which causes unnecessary distortion in irrelevant image regions. In response, we need to decide where to transfer the extracted style. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that extracts out a local mask from the exemplar that determines what style to transfer, and another local mask from the input image that determines where to transfer the extracted style. The main novelty of this paper lies in (1) the highway adaptive instance normalization technique and (2) an end-to-end translation framework which achieves an outstanding performance in reflecting a style of an exemplar. We demonstrate the quantitative and qualitative evaluation results to confirm the advantages of our proposed approach.
Interpreting Models by Allowing to Ask
Nov 13, 2018



Abstract:Questions convey information about the questioner, namely what one does not know. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to allow a learning agent to ask what it considers as tricky to predict, in the course of producing a final output. By analyzing when and what it asks, we can make our model more transparent and interpretable. We first develop this idea to propose a general framework of deep neural networks that can ask questions, which we call asking networks. A specific architecture and training process for an asking network is proposed for the task of colorization, which is an exemplar one-to-many task and thus a task where asking questions is helpful in performing the task accurately. Our results show that the model learns to generate meaningful questions, asks difficult questions first, and utilizes the provided hint more efficiently than baseline models. We conclude that the proposed asking framework makes the learning agent reveal its weaknesses, which poses a promising new direction in developing interpretable and interactive models.
Question-Aware Sentence Gating Networks for Question and Answering
Jul 20, 2018
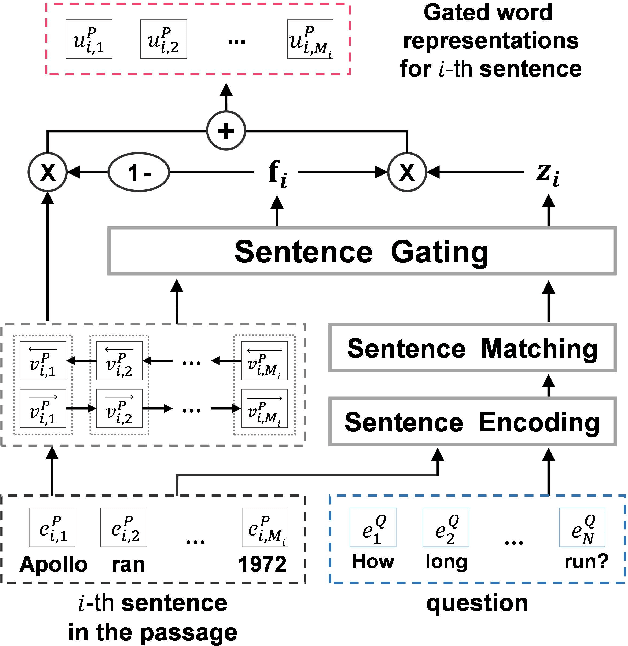

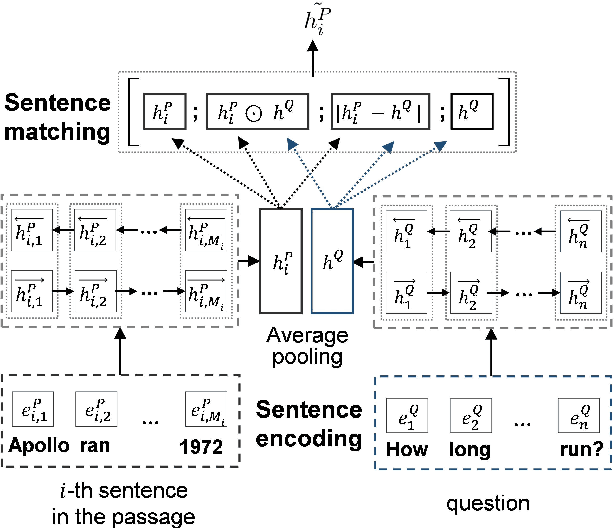
Abstract:Machine comprehension question answering, which finds an answer to the question given a passage, involves high-level reasoning processes of understanding and tracking the relevant contents across various semantic units such as words, phrases, and sentences in a document. This paper proposes the novel question-aware sentence gating networks that directly incorporate the sentence-level information into word-level encoding processes. To this end, our model first learns question-aware sentence representations and then dynamically combines them with word-level representations, resulting in semantically meaningful word representations for QA tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach consistently improves the accuracy over existing baseline approaches on various QA datasets and bears the wide applicability to other neural network-based QA models.
MEGAN: Mixture of Experts of Generative Adversarial Networks for Multimodal Image Generation
May 08, 2018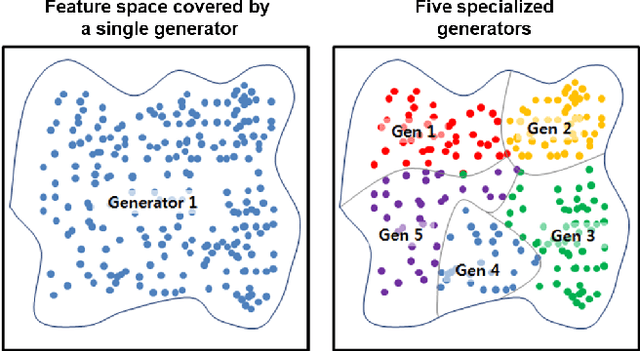
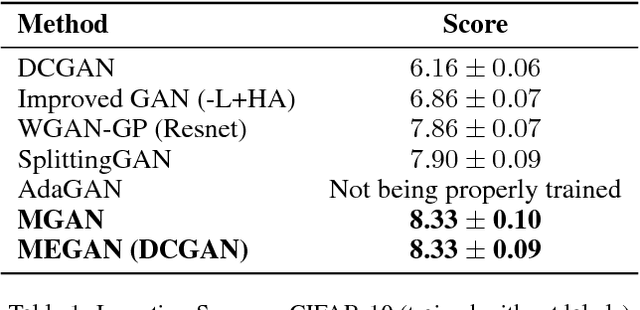
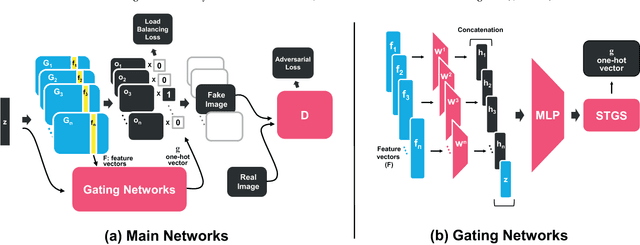
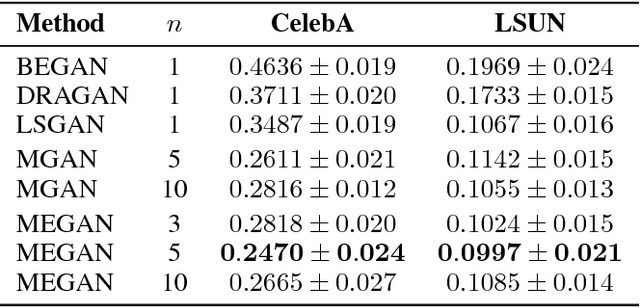
Abstract:Recently, generative adversarial networks (GANs) have shown promising performance in generating realistic images. However, they often struggle in learning complex underlying modalities in a given dataset, resulting in poor-quality generated images. To mitigate this problem, we present a novel approach called mixture of experts GAN (MEGAN), an ensemble approach of multiple generator networks. Each generator network in MEGAN specializes in generating images with a particular subset of modalities, e.g., an image class. Instead of incorporating a separate step of handcrafted clustering of multiple modalities, our proposed model is trained through an end-to-end learning of multiple generators via gating networks, which is responsible for choosing the appropriate generator network for a given condition. We adopt the categorical reparameterization trick for a categorical decision to be made in selecting a generator while maintaining the flow of the gradients. We demonstrate that individual generators learn different and salient subparts of the data and achieve a multiscale structural similarity (MS-SSIM) score of 0.2470 for CelebA and a competitive unsupervised inception score of 8.33 in CIFAR-10.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge