Seunghwan Choi
Learning to Generate Semantic Layouts for Higher Text-Image Correspondence in Text-to-Image Synthesis
Aug 16, 2023Abstract:Existing text-to-image generation approaches have set high standards for photorealism and text-image correspondence, largely benefiting from web-scale text-image datasets, which can include up to 5~billion pairs. However, text-to-image generation models trained on domain-specific datasets, such as urban scenes, medical images, and faces, still suffer from low text-image correspondence due to the lack of text-image pairs. Additionally, collecting billions of text-image pairs for a specific domain can be time-consuming and costly. Thus, ensuring high text-image correspondence without relying on web-scale text-image datasets remains a challenging task. In this paper, we present a novel approach for enhancing text-image correspondence by leveraging available semantic layouts. Specifically, we propose a Gaussian-categorical diffusion process that simultaneously generates both images and corresponding layout pairs. Our experiments reveal that we can guide text-to-image generation models to be aware of the semantics of different image regions, by training the model to generate semantic labels for each pixel. We demonstrate that our approach achieves higher text-image correspondence compared to existing text-to-image generation approaches in the Multi-Modal CelebA-HQ and the Cityscapes dataset, where text-image pairs are scarce. Codes are available in this https://pmh9960.github.io/research/GCDP
Shortcut-V2V: Compression Framework for Video-to-Video Translation based on Temporal Redundancy Reduction
Aug 15, 2023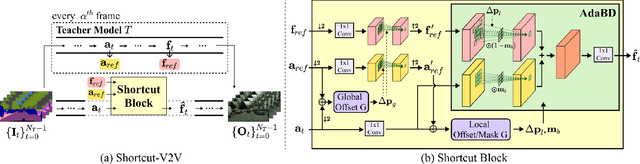



Abstract:Video-to-video translation aims to generate video frames of a target domain from an input video. Despite its usefulness, the existing networks require enormous computations, necessitating their model compression for wide use. While there exist compression methods that improve computational efficiency in various image/video tasks, a generally-applicable compression method for video-to-video translation has not been studied much. In response, we present Shortcut-V2V, a general-purpose compression framework for video-to-video translation. Shourcut-V2V avoids full inference for every neighboring video frame by approximating the intermediate features of a current frame from those of the previous frame. Moreover, in our framework, a newly-proposed block called AdaBD adaptively blends and deforms features of neighboring frames, which makes more accurate predictions of the intermediate features possible. We conduct quantitative and qualitative evaluations using well-known video-to-video translation models on various tasks to demonstrate the general applicability of our framework. The results show that Shourcut-V2V achieves comparable performance compared to the original video-to-video translation model while saving 3.2-5.7x computational cost and 7.8-44x memory at test time.
High-Resolution Virtual Try-On with Misalignment and Occlusion-Handled Conditions
Jun 28, 2022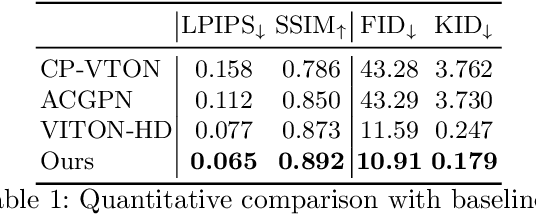
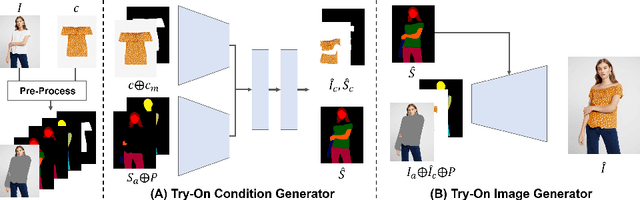
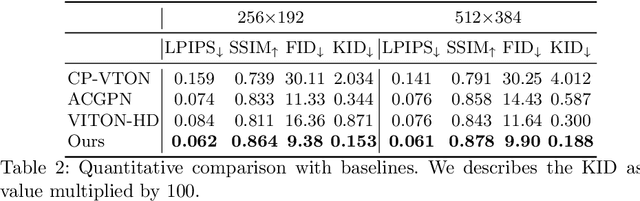
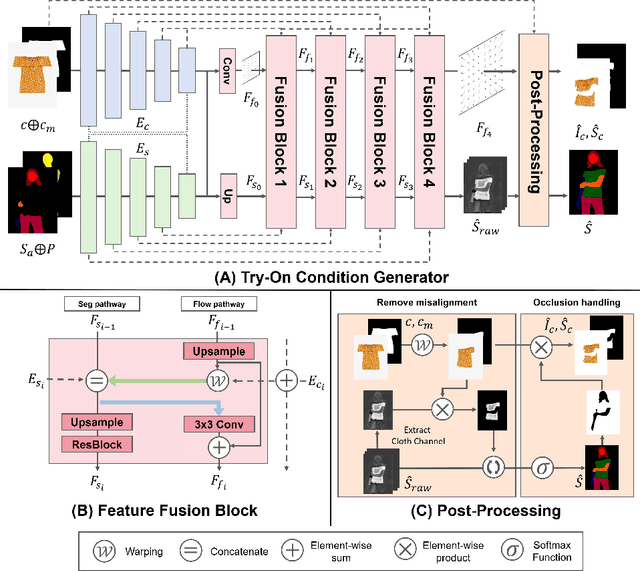
Abstract:Image-based virtual try-on aims to synthesize an image of a person wearing a given clothing item. To solve the task, the existing methods warp the clothing item to fit the person's body and generate the segmentation map of the person wearing the item, before fusing the item with the person. However, when the warping and the segmentation generation stages operate individually without information exchange, the misalignment between the warped clothes and the segmentation map occurs, which leads to the artifacts in the final image. The information disconnection also causes excessive warping near the clothing regions occluded by the body parts, so called pixel-squeezing artifacts. To settle the issues, we propose a novel try-on condition generator as a unified module of the two stages (i.e., warping and segmentation generation stages). A newly proposed feature fusion block in the condition generator implements the information exchange, and the condition generator does not create any misalignment or pixel-squeezing artifacts. We also introduce discriminator rejection that filters out the incorrect segmentation map predictions and assures the performance of virtual try-on frameworks. Experiments on a high-resolution dataset demonstrate that our model successfully handles the misalignment and the occlusion, and significantly outperforms the baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/sangyun884/HR-VITON.
HairFIT: Pose-Invariant Hairstyle Transfer via Flow-based Hair Alignment and Semantic-Region-Aware Inpainting
Jun 17, 2022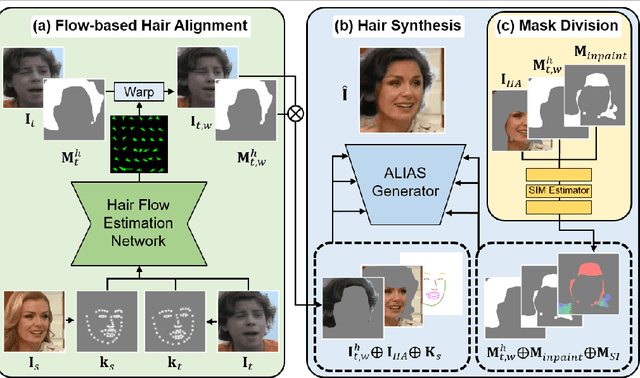

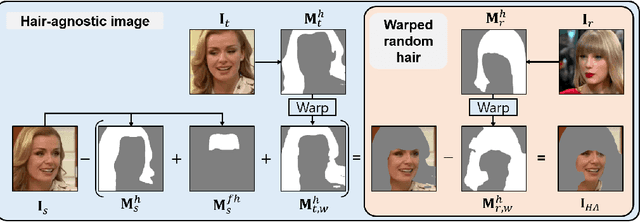

Abstract:Hairstyle transfer is the task of modifying a source hairstyle to a target one. Although recent hairstyle transfer models can reflect the delicate features of hairstyles, they still have two major limitations. First, the existing methods fail to transfer hairstyles when a source and a target image have different poses (e.g., viewing direction or face size), which is prevalent in the real world. Also, the previous models generate unrealistic images when there is a non-trivial amount of regions in the source image occluded by its original hair. When modifying long hair to short hair, shoulders or backgrounds occluded by the long hair need to be inpainted. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework for pose-invariant hairstyle transfer, HairFIT. Our model consists of two stages: 1) flow-based hair alignment and 2) hair synthesis. In the hair alignment stage, we leverage a keypoint-based optical flow estimator to align a target hairstyle with a source pose. Then, we generate a final hairstyle-transferred image in the hair synthesis stage based on Semantic-region-aware Inpainting Mask (SIM) estimator. Our SIM estimator divides the occluded regions in the source image into different semantic regions to reflect their distinct features during the inpainting. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our model, we conduct quantitative and qualitative evaluations using multi-view datasets, K-hairstyle and VoxCeleb. The results indicate that HairFIT achieves a state-of-the-art performance by successfully transferring hairstyles between images of different poses, which has never been achieved before.
Data Augmentation using Random Image Cropping for High-resolution Virtual Try-On (VITON-CROP)
Nov 16, 2021

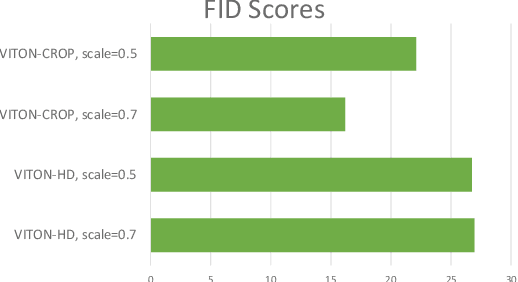
Abstract:Image-based virtual try-on provides the capacity to transfer a clothing item onto a photo of a given person, which is usually accomplished by warping the item to a given human pose and adjusting the warped item to the person. However, the results of real-world synthetic images (e.g., selfies) from the previous method is not realistic because of the limitations which result in the neck being misrepresented and significant changes to the style of the garment. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method to solve this unique issue, called VITON-CROP. VITON-CROP synthesizes images more robustly when integrated with random crop augmentation compared to the existing state-of-the-art virtual try-on models. In the experiments, we demonstrate that VITON-CROP is superior to VITON-HD both qualitatively and quantitatively.
VITON-HD: High-Resolution Virtual Try-On via Misalignment-Aware Normalization
Mar 31, 2021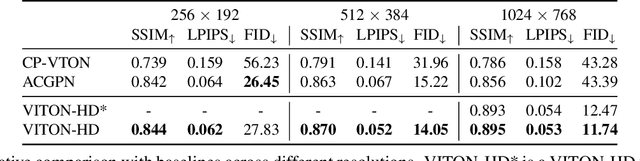

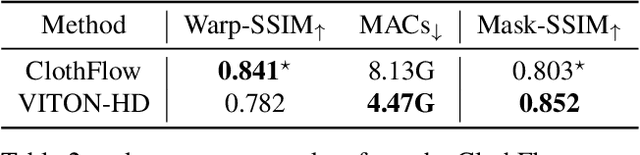
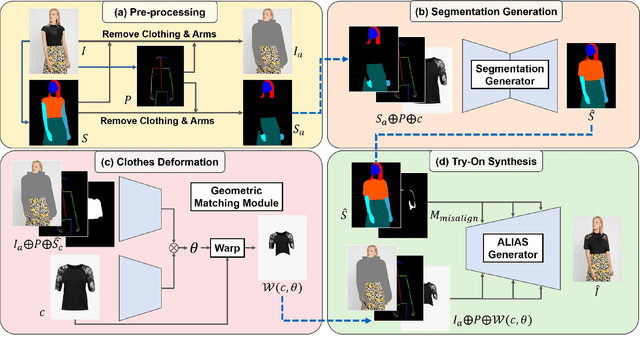
Abstract:The task of image-based virtual try-on aims to transfer a target clothing item onto the corresponding region of a person, which is commonly tackled by fitting the item to the desired body part and fusing the warped item with the person. While an increasing number of studies have been conducted, the resolution of synthesized images is still limited to low (e.g., 256x192), which acts as the critical limitation against satisfying online consumers. We argue that the limitation stems from several challenges: as the resolution increases, the artifacts in the misaligned areas between the warped clothes and the desired clothing regions become noticeable in the final results; the architectures used in existing methods have low performance in generating high-quality body parts and maintaining the texture sharpness of the clothes. To address the challenges, we propose a novel virtual try-on method called VITON-HD that successfully synthesizes 1024x768 virtual try-on images. Specifically, we first prepare the segmentation map to guide our virtual try-on synthesis, and then roughly fit the target clothing item to a given person's body. Next, we propose ALIgnment-Aware Segment (ALIAS) normalization and ALIAS generator to handle the misaligned areas and preserve the details of 1024x768 inputs. Through rigorous comparison with existing methods, we demonstrate that VITON-HD highly sur-passes the baselines in terms of synthesized image quality both qualitatively and quantitatively.
What and Where to Translate: Local Mask-based Image-to-Image Translation
Jun 09, 2019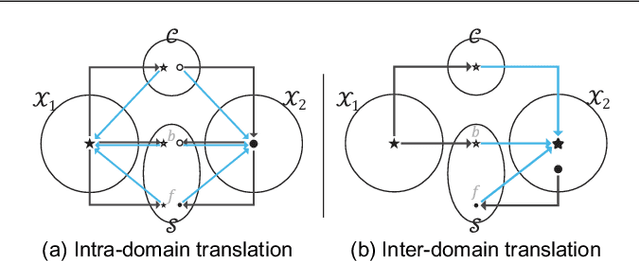
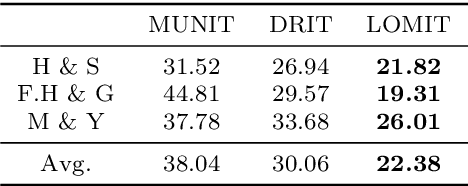
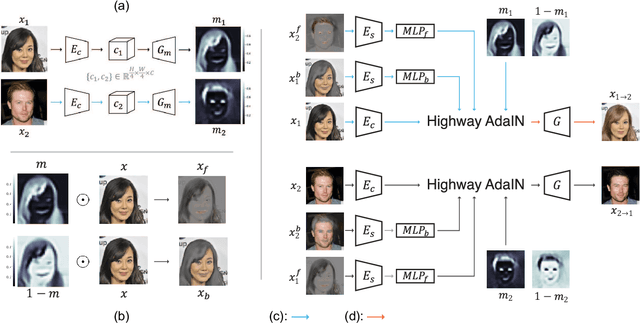

Abstract:Recently, image-to-image translation has obtained significant attention. Among many, those approaches based on an exemplar image that contains the target style information has been actively studied, due to its capability to handle multimodality as well as its applicability in practical use. However, two intrinsic problems exist in the existing methods: what and where to transfer. First, those methods extract style from an entire exemplar which includes noisy information, which impedes a translation model from properly extracting the intended style of the exemplar. That is, we need to carefully determine what to transfer from the exemplar. Second, the extracted style is applied to the entire input image, which causes unnecessary distortion in irrelevant image regions. In response, we need to decide where to transfer the extracted style. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that extracts out a local mask from the exemplar that determines what style to transfer, and another local mask from the input image that determines where to transfer the extracted style. The main novelty of this paper lies in (1) the highway adaptive instance normalization technique and (2) an end-to-end translation framework which achieves an outstanding performance in reflecting a style of an exemplar. We demonstrate the quantitative and qualitative evaluation results to confirm the advantages of our proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge