David Haws
Granite-speech: open-source speech-aware LLMs with strong English ASR capabilities
May 14, 2025Abstract:Granite-speech LLMs are compact and efficient speech language models specifically designed for English ASR and automatic speech translation (AST). The models were trained by modality aligning the 2B and 8B parameter variants of granite-3.3-instruct to speech on publicly available open-source corpora containing audio inputs and text targets consisting of either human transcripts for ASR or automatically generated translations for AST. Comprehensive benchmarking shows that on English ASR, which was our primary focus, they outperform several competitors' models that were trained on orders of magnitude more proprietary data, and they keep pace on English-to-X AST for major European languages, Japanese, and Chinese. The speech-specific components are: a conformer acoustic encoder using block attention and self-conditioning trained with connectionist temporal classification, a windowed query-transformer speech modality adapter used to do temporal downsampling of the acoustic embeddings and map them to the LLM text embedding space, and LoRA adapters to further fine-tune the text LLM. Granite-speech-3.3 operates in two modes: in speech mode, it performs ASR and AST by activating the encoder, projector, and LoRA adapters; in text mode, it calls the underlying granite-3.3-instruct model directly (without LoRA), essentially preserving all the text LLM capabilities and safety. Both models are freely available on HuggingFace (https://huggingface.co/ibm-granite/granite-speech-3.3-2b and https://huggingface.co/ibm-granite/granite-speech-3.3-8b) and can be used for both research and commercial purposes under a permissive Apache 2.0 license.
Continuous Speech Synthesis using per-token Latent Diffusion
Oct 21, 2024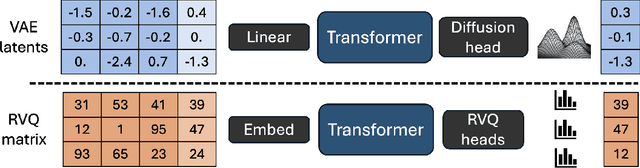
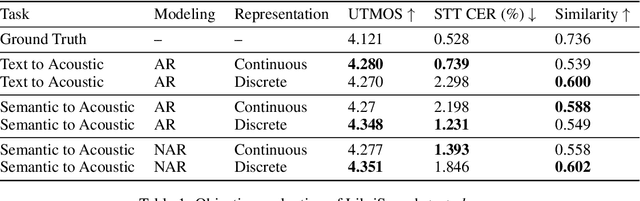
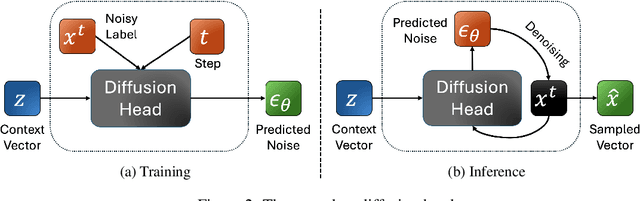

Abstract:The success of autoregressive transformer models with discrete tokens has inspired quantization-based approaches for continuous modalities, though these often limit reconstruction quality. We therefore introduce SALAD, a per-token latent diffusion model for zero-shot text-to-speech, that operates on continuous representations. SALAD builds upon the recently proposed expressive diffusion head for image generation, and extends it to generate variable-length outputs. Our approach utilizes semantic tokens for providing contextual information and determining the stopping condition. We suggest three continuous variants for our method, extending popular discrete speech synthesis techniques. Additionally, we implement discrete baselines for each variant and conduct a comparative analysis of discrete versus continuous speech modeling techniques. Our results demonstrate that both continuous and discrete approaches are highly competent, and that SALAD achieves a superior intelligibility score while obtaining speech quality and speaker similarity on par with the ground-truth audio.
Speak While You Think: Streaming Speech Synthesis During Text Generation
Sep 20, 2023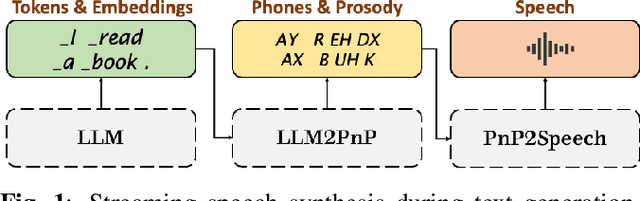
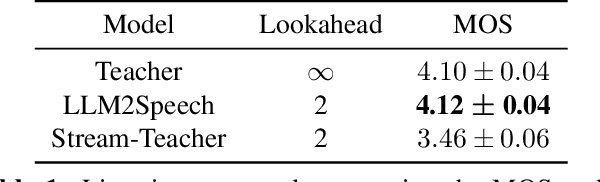
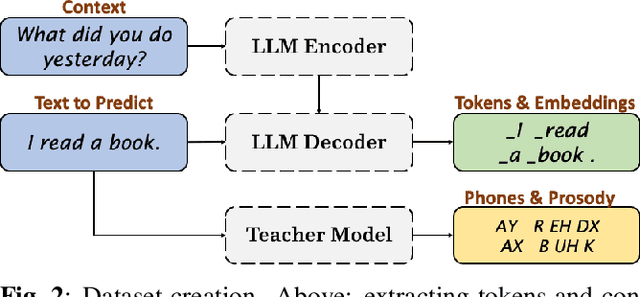
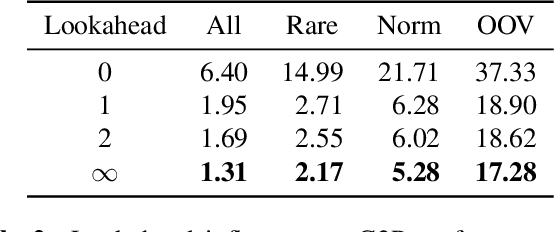
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive capabilities, yet interaction with these models is mostly facilitated through text. Using Text-To-Speech to synthesize LLM outputs typically results in notable latency, which is impractical for fluent voice conversations. We propose LLM2Speech, an architecture to synthesize speech while text is being generated by an LLM which yields significant latency reduction. LLM2Speech mimics the predictions of a non-streaming teacher model while limiting the exposure to future context in order to enable streaming. It exploits the hidden embeddings of the LLM, a by-product of the text generation that contains informative semantic context. Experimental results show that LLM2Speech maintains the teacher's quality while reducing the latency to enable natural conversations.
VQ-T: RNN Transducers using Vector-Quantized Prediction Network States
Aug 03, 2022
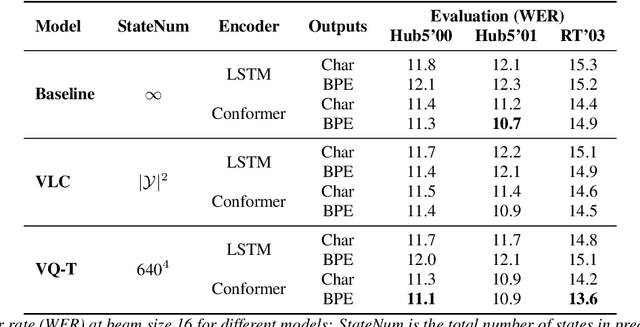


Abstract:Beam search, which is the dominant ASR decoding algorithm for end-to-end models, generates tree-structured hypotheses. However, recent studies have shown that decoding with hypothesis merging can achieve a more efficient search with comparable or better performance. But, the full context in recurrent networks is not compatible with hypothesis merging. We propose to use vector-quantized long short-term memory units (VQ-LSTM) in the prediction network of RNN transducers. By training the discrete representation jointly with the ASR network, hypotheses can be actively merged for lattice generation. Our experiments on the Switchboard corpus show that the proposed VQ RNN transducers improve ASR performance over transducers with regular prediction networks while also producing denser lattices with a very low oracle word error rate (WER) for the same beam size. Additional language model rescoring experiments also demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed lattice generation scheme.
Transplantation of Conversational Speaking Style with Interjections in Sequence-to-Sequence Speech Synthesis
Jul 25, 2022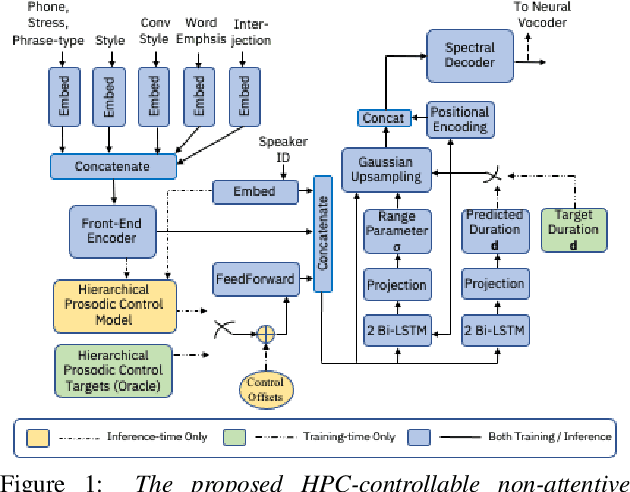

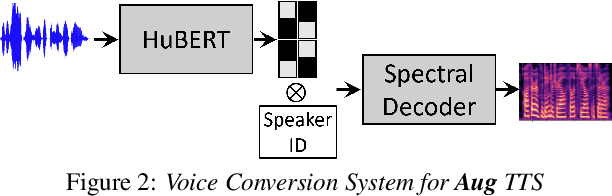

Abstract:Sequence-to-Sequence Text-to-Speech architectures that directly generate low level acoustic features from phonetic sequences are known to produce natural and expressive speech when provided with adequate amounts of training data. Such systems can learn and transfer desired speaking styles from one seen speaker to another (in multi-style multi-speaker settings), which is highly desirable for creating scalable and customizable Human-Computer Interaction systems. In this work we explore one-to-many style transfer from a dedicated single-speaker conversational corpus with style nuances and interjections. We elaborate on the corpus design and explore the feasibility of such style transfer when assisted with Voice-Conversion-based data augmentation. In a set of subjective listening experiments, this approach resulted in high-fidelity style transfer with no quality degradation. However, a certain voice persona shift was observed, requiring further improvements in voice conversion.
Reducing Exposure Bias in Training Recurrent Neural Network Transducers
Aug 24, 2021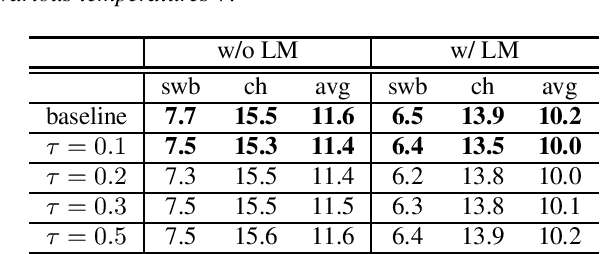
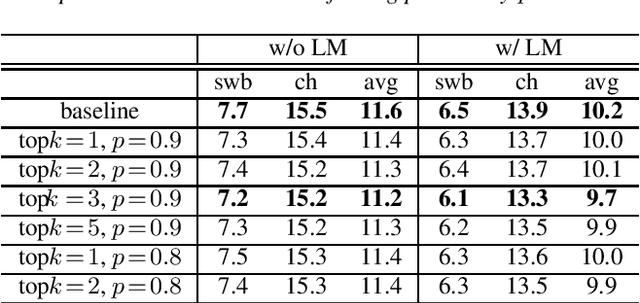
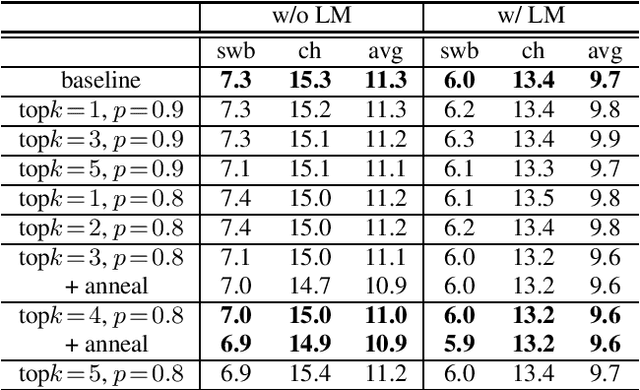
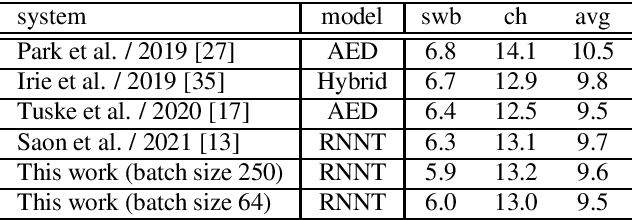
Abstract:When recurrent neural network transducers (RNNTs) are trained using the typical maximum likelihood criterion, the prediction network is trained only on ground truth label sequences. This leads to a mismatch during inference, known as exposure bias, when the model must deal with label sequences containing errors. In this paper we investigate approaches to reducing exposure bias in training to improve the generalization of RNNT models for automatic speech recognition (ASR). A label-preserving input perturbation to the prediction network is introduced. The input token sequences are perturbed using SwitchOut and scheduled sampling based on an additional token language model. Experiments conducted on the 300-hour Switchboard dataset demonstrate their effectiveness. By reducing the exposure bias, we show that we can further improve the accuracy of a high-performance RNNT ASR model and obtain state-of-the-art results on the 300-hour Switchboard dataset.
Supervised and Unsupervised Approaches for Controlling Narrow Lexical Focus in Sequence-to-Sequence Speech Synthesis
Jan 25, 2021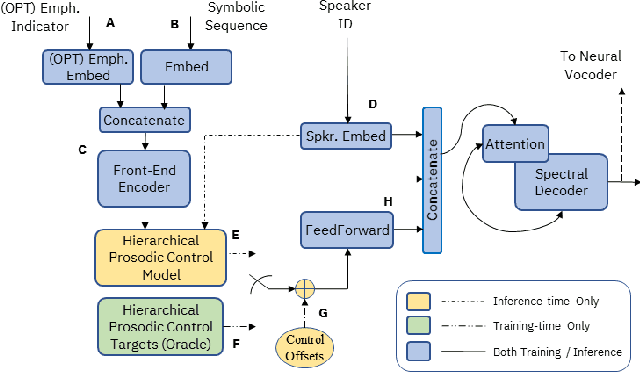
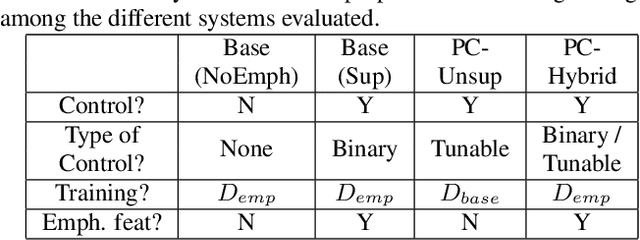
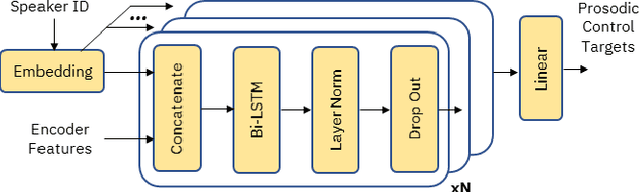
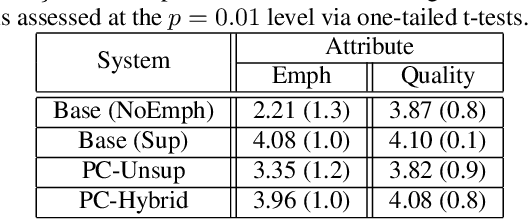
Abstract:Although Sequence-to-Sequence (S2S) architectures have become state-of-the-art in speech synthesis, capable of generating outputs that approach the perceptual quality of natural samples, they are limited by a lack of flexibility when it comes to controlling the output. In this work we present a framework capable of controlling the prosodic output via a set of concise, interpretable, disentangled parameters. We apply this framework to the realization of emphatic lexical focus, proposing a variety of architectures designed to exploit different levels of supervision based on the availability of labeled resources. We evaluate these approaches via listening tests that demonstrate we are able to successfully realize controllable focus while maintaining the same, or higher, naturalness over an established baseline, and we explore how the different approaches compare when synthesizing in a target voice with or without labeled data.
MINT: Mutual Information based Transductive Feature Selection for Genetic Trait Prediction
Oct 07, 2013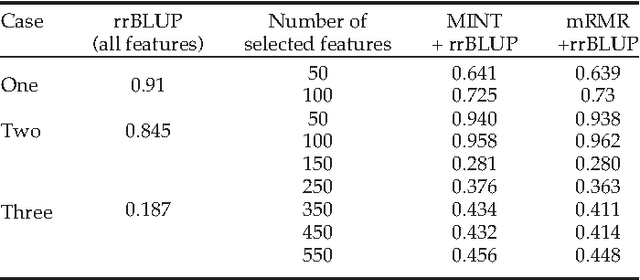
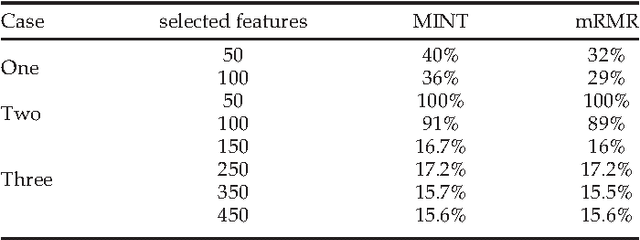
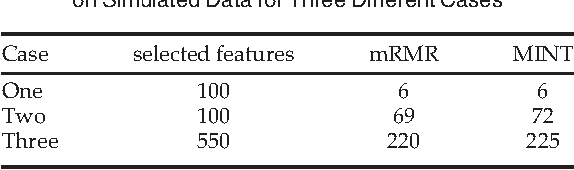

Abstract:Whole genome prediction of complex phenotypic traits using high-density genotyping arrays has attracted a great deal of attention, as it is relevant to the fields of plant and animal breeding and genetic epidemiology. As the number of genotypes is generally much bigger than the number of samples, predictive models suffer from the curse-of-dimensionality. The curse-of-dimensionality problem not only affects the computational efficiency of a particular genomic selection method, but can also lead to poor performance, mainly due to correlation among markers. In this work we proposed the first transductive feature selection method based on the MRMR (Max-Relevance and Min-Redundancy) criterion which we call MINT. We applied MINT on genetic trait prediction problems and showed that in general MINT is a better feature selection method than the state-of-the-art inductive method mRMR.
Bayes estimators for phylogenetic reconstruction
Nov 22, 2009
Abstract:Tree reconstruction methods are often judged by their accuracy, measured by how close they get to the true tree. Yet most reconstruction methods like ML do not explicitly maximize this accuracy. To address this problem, we propose a Bayesian solution. Given tree samples, we propose finding the tree estimate which is closest on average to the samples. This ``median'' tree is known as the Bayes estimator (BE). The BE literally maximizes posterior expected accuracy, measured in terms of closeness (distance) to the true tree. We discuss a unified framework of BE trees, focusing especially on tree distances which are expressible as squared euclidean distances. Notable examples include Robinson--Foulds distance, quartet distance, and squared path difference. Using simulated data, we show Bayes estimators can be efficiently computed in practice by hill climbing. We also show that Bayes estimators achieve higher accuracy, compared to maximum likelihood and neighbor joining.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge