Dario Piga
Nonlinear System Identification Nano-drone Benchmark
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:We introduce a benchmark for system identification based on 75k real-world samples from the Crazyflie 2.1 Brushless nano-quadrotor, a sub-50g aerial vehicle widely adopted in robotics research. The platform presents a challenging testbed due to its multi-input, multi-output nature, open-loop instability, and nonlinear dynamics under agile maneuvers. The dataset comprises four aggressive trajectories with synchronized 4-dimensional motor inputs and 13-dimensional output measurements. To enable fair comparison of identification methods, the benchmark includes a suite of multi-horizon prediction metrics for evaluating both one-step and multi-step error propagation. In addition to the data, we provide a detailed description of the platform and experimental setup, as well as baseline models highlighting the challenge of accurate prediction under real-world noise and actuation nonlinearities. All data, scripts, and reference implementations are released as open-source at https://github.com/idsia-robotics/nanodrone-sysid-benchmark to facilitate transparent comparison of algorithms and support research on agile, miniaturized aerial robotics.
Regularized GLISp for sensor-guided human-in-the-loop optimization
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Human-in-the-loop calibration is often addressed via preference-based optimization, where algorithms learn from pairwise comparisons rather than explicit cost evaluations. While effective, methods such as Preferential Bayesian Optimization or Global optimization based on active preference learning with radial basis functions (GLISp) treat the system as a black box and ignore informative sensor measurements. In this work, we introduce a sensor-guided regularized extension of GLISp that integrates measurable descriptors into the preference-learning loop through a physics-informed hypothesis function and a least-squares regularization term. This injects grey-box structure, combining subjective feedback with quantitative sensor information while preserving the flexibility of preference-based search. Numerical evaluations on an analytical benchmark and on a human-in-the-loop vehicle suspension tuning task show faster convergence and superior final solutions compared to baseline GLISp.
Learning Low-Dimensional Embeddings for Black-Box Optimization
May 02, 2025Abstract:When gradient-based methods are impractical, black-box optimization (BBO) provides a valuable alternative. However, BBO often struggles with high-dimensional problems and limited trial budgets. In this work, we propose a novel approach based on meta-learning to pre-compute a reduced-dimensional manifold where optimal points lie for a specific class of optimization problems. When optimizing a new problem instance sampled from the class, black-box optimization is carried out in the reduced-dimensional space, effectively reducing the effort required for finding near-optimal solutions.
Manifold meta-learning for reduced-complexity neural system identification
Apr 16, 2025



Abstract:System identification has greatly benefited from deep learning techniques, particularly for modeling complex, nonlinear dynamical systems with partially unknown physics where traditional approaches may not be feasible. However, deep learning models often require large datasets and significant computational resources at training and inference due to their high-dimensional parameterizations. To address this challenge, we propose a meta-learning framework that discovers a low-dimensional manifold within the parameter space of an over-parameterized neural network architecture. This manifold is learned from a meta-dataset of input-output sequences generated by a class of related dynamical systems, enabling efficient model training while preserving the network's expressive power for the considered system class. Unlike bilevel meta-learning approaches, our method employs an auxiliary neural network to map datasets directly onto the learned manifold, eliminating the need for costly second-order gradient computations during meta-training and reducing the number of first-order updates required in inference, which could be expensive for large models. We validate our approach on a family of Bouc-Wen oscillators, which is a well-studied nonlinear system identification benchmark. We demonstrate that we are able to learn accurate models even in small-data scenarios.
In-Context Learning for Zero-Shot Speed Estimation of BLDC motors
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Accurate speed estimation in sensorless brushless DC motors is essential for high-performance control and monitoring, yet conventional model-based approaches struggle with system nonlinearities and parameter uncertainties. In this work, we propose an in-context learning framework leveraging transformer-based models to perform zero-shot speed estimation using only electrical measurements. By training the filter offline on simulated motor trajectories, we enable real-time inference on unseen real motors without retraining, eliminating the need for explicit system identification while retaining adaptability to varying operating conditions. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms traditional Kalman filter-based estimators, especially in low-speed regimes that are crucial during motor startup.
dynoGP: Deep Gaussian Processes for dynamic system identification
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:In this work, we present a novel approach to system identification for dynamical systems, based on a specific class of Deep Gaussian Processes (Deep GPs). These models are constructed by interconnecting linear dynamic GPs (equivalent to stochastic linear time-invariant dynamical systems) and static GPs (to model static nonlinearities). Our approach combines the strengths of data-driven methods, such as those based on neural network architectures, with the ability to output a probability distribution. This offers a more comprehensive framework for system identification that includes uncertainty quantification. Using both simulated and real-world data, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Integrating Reinforcement Learning with Foundation Models for Autonomous Robotics: Methods and Perspectives
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Foundation models (FMs), large deep learning models pre-trained on vast, unlabeled datasets, exhibit powerful capabilities in understanding complex patterns and generating sophisticated outputs. However, they often struggle to adapt to specific tasks. Reinforcement learning (RL), which allows agents to learn through interaction and feedback, offers a compelling solution. Integrating RL with FMs enables these models to achieve desired outcomes and excel at particular tasks. Additionally, RL can be enhanced by leveraging the reasoning and generalization capabilities of FMs. This synergy is revolutionizing various fields, including robotics. FMs, rich in knowledge and generalization, provide robots with valuable information, while RL facilitates learning and adaptation through real-world interactions. This survey paper comprehensively explores this exciting intersection, examining how these paradigms can be integrated to advance robotic intelligence. We analyze the use of foundation models as action planners, the development of robotics-specific foundation models, and the mutual benefits of combining FMs with RL. Furthermore, we present a taxonomy of integration approaches, including large language models, vision-language models, diffusion models, and transformer-based RL models. We also explore how RL can utilize world representations learned from FMs to enhance robotic task execution. Our survey aims to synthesize current research and highlight key challenges in robotic reasoning and control, particularly in the context of integrating FMs and RL--two rapidly evolving technologies. By doing so, we seek to spark future research and emphasize critical areas that require further investigation to enhance robotics. We provide an updated collection of papers based on our taxonomy, accessible on our open-source project website at: https://github.com/clmoro/Robotics-RL-FMs-Integration.
Enhanced Transformer architecture for in-context learning of dynamical systems
Oct 04, 2024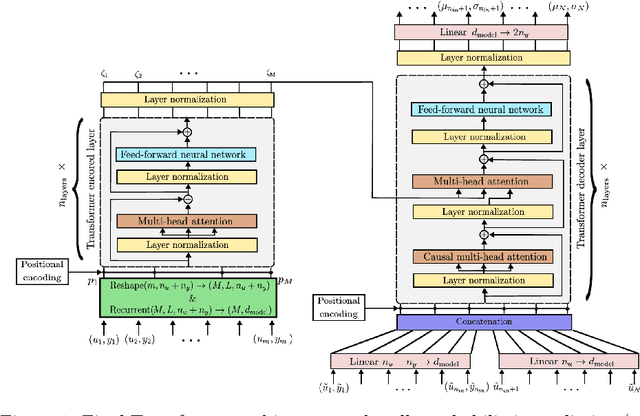

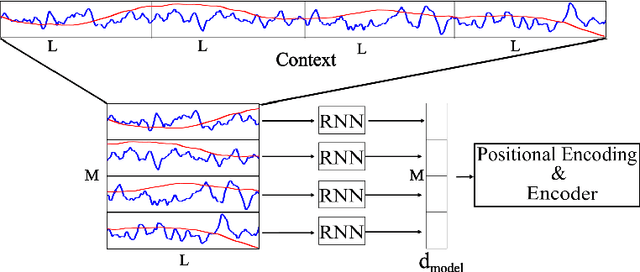

Abstract:Recently introduced by some of the authors, the in-context identification paradigm aims at estimating, offline and based on synthetic data, a meta-model that describes the behavior of a whole class of systems. Once trained, this meta-model is fed with an observed input/output sequence (context) generated by a real system to predict its behavior in a zero-shot learning fashion. In this paper, we enhance the original meta-modeling framework through three key innovations: by formulating the learning task within a probabilistic framework; by managing non-contiguous context and query windows; and by adopting recurrent patching to effectively handle long context sequences. The efficacy of these modifications is demonstrated through a numerical example focusing on the Wiener-Hammerstein system class, highlighting the model's enhanced performance and scalability.
RoboMorph: In-Context Meta-Learning for Robot Dynamics Modeling
Sep 18, 2024



Abstract:The landscape of Deep Learning has experienced a major shift with the pervasive adoption of Transformer-based architectures, particularly in Natural Language Processing (NLP). Novel avenues for physical applications, such as solving Partial Differential Equations and Image Vision, have been explored. However, in challenging domains like robotics, where high non-linearity poses significant challenges, Transformer-based applications are scarce. While Transformers have been used to provide robots with knowledge about high-level tasks, few efforts have been made to perform system identification. This paper proposes a novel methodology to learn a meta-dynamical model of a high-dimensional physical system, such as the Franka robotic arm, using a Transformer-based architecture without prior knowledge of the system's physical parameters. The objective is to predict quantities of interest (end-effector pose and joint positions) given the torque signals for each joint. This prediction can be useful as a component for Deep Model Predictive Control frameworks in robotics. The meta-model establishes the correlation between torques and positions and predicts the output for the complete trajectory. This work provides empirical evidence of the efficacy of the in-context learning paradigm, suggesting future improvements in learning the dynamics of robotic systems without explicit knowledge of physical parameters. Code, videos, and supplementary materials can be found at project website. See https://sites.google.com/view/robomorph/
LightCPPgen: An Explainable Machine Learning Pipeline for Rational Design of Cell Penetrating Peptides
May 31, 2024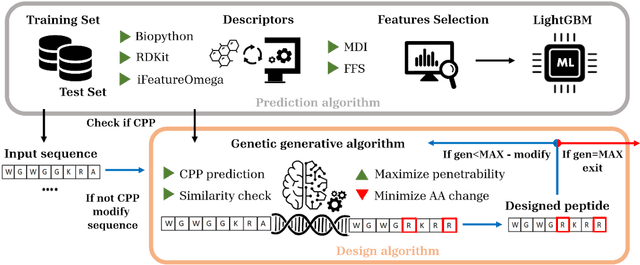
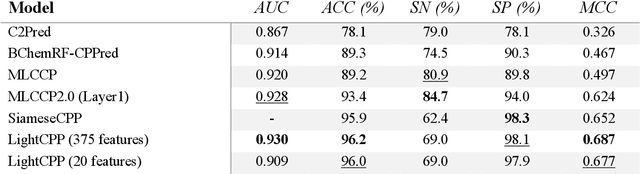
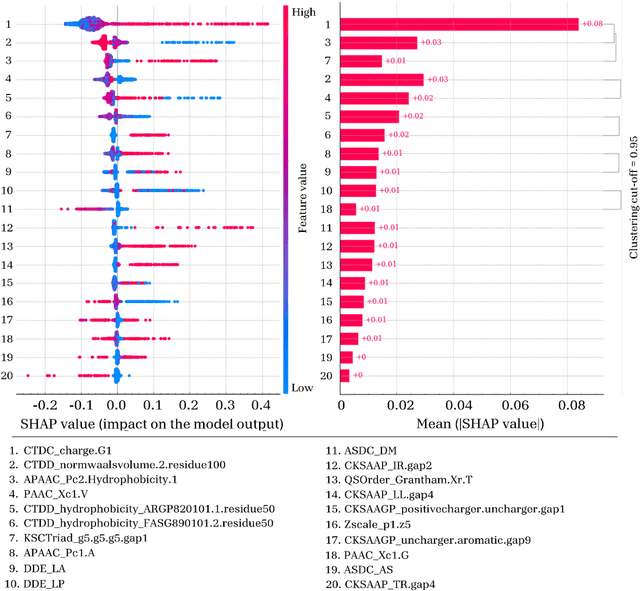
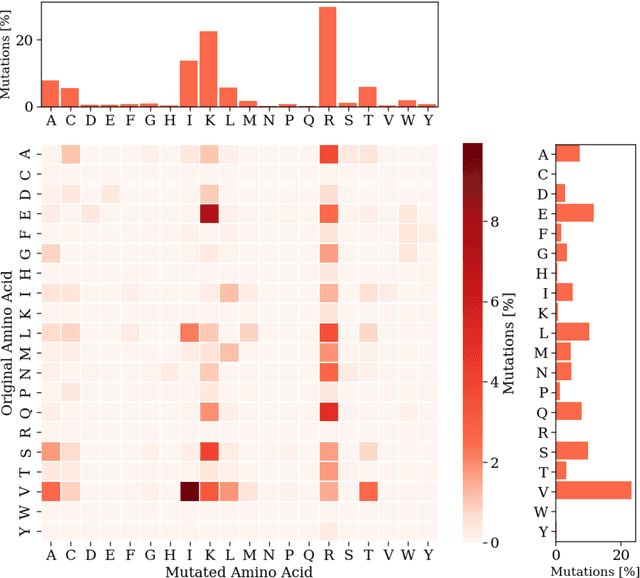
Abstract:Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are powerful vectors for the intracellular delivery of a diverse array of therapeutic molecules. Despite their potential, the rational design of CPPs remains a challenging task that often requires extensive experimental efforts and iterations. In this study, we introduce an innovative approach for the de novo design of CPPs, leveraging the strengths of machine learning (ML) and optimization algorithms. Our strategy, named LightCPPgen, integrates a LightGBM-based predictive model with a genetic algorithm (GA), enabling the systematic generation and optimization of CPP sequences. At the core of our methodology is the development of an accurate, efficient, and interpretable predictive model, which utilizes 20 explainable features to shed light on the critical factors influencing CPP translocation capacity. The CPP predictive model works synergistically with an optimization algorithm, which is tuned to enhance computational efficiency while maintaining optimization performance. The GA solutions specifically target the candidate sequences' penetrability score, while trying to maximize similarity with the original non-penetrating peptide in order to retain its original biological and physicochemical properties. By prioritizing the synthesis of only the most promising CPP candidates, LightCPPgen can drastically reduce the time and cost associated with wet lab experiments. In summary, our research makes a substantial contribution to the field of CPP design, offering a robust framework that combines ML and optimization techniques to facilitate the rational design of penetrating peptides, by enhancing the explainability and interpretability of the design process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge