Daniel S. Marcus
Analysis of the MICCAI Brain Tumor Segmentation -- Metastases (BraTS-METS) 2025 Lighthouse Challenge: Brain Metastasis Segmentation on Pre- and Post-treatment MRI
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Despite continuous advancements in cancer treatment, brain metastatic disease remains a significant complication of primary cancer and is associated with an unfavorable prognosis. One approach for improving diagnosis, management, and outcomes is to implement algorithms based on artificial intelligence for the automated segmentation of both pre- and post-treatment MRI brain images. Such algorithms rely on volumetric criteria for lesion identification and treatment response assessment, which are still not available in clinical practice. Therefore, it is critical to establish tools for rapid volumetric segmentations methods that can be translated to clinical practice and that are trained on high quality annotated data. The BraTS-METS 2025 Lighthouse Challenge aims to address this critical need by establishing inter-rater and intra-rater variability in dataset annotation by generating high quality annotated datasets from four individual instances of segmentation by neuroradiologists while being recorded on video (two instances doing "from scratch" and two instances after AI pre-segmentation). This high-quality annotated dataset will be used for testing phase in 2025 Lighthouse challenge and will be publicly released at the completion of the challenge. The 2025 Lighthouse challenge will also release the 2023 and 2024 segmented datasets that were annotated using an established pipeline of pre-segmentation, student annotation, two neuroradiologists checking, and one neuroradiologist finalizing the process. It builds upon its previous edition by including post-treatment cases in the dataset. Using these high-quality annotated datasets, the 2025 Lighthouse challenge plans to test benchmark algorithms for automated segmentation of pre-and post-treatment brain metastases (BM), trained on diverse and multi-institutional datasets of MRI images obtained from patients with brain metastases.
DMC-Net: Lightweight Dynamic Multi-Scale and Multi-Resolution Convolution Network for Pancreas Segmentation in CT Images
Oct 03, 2024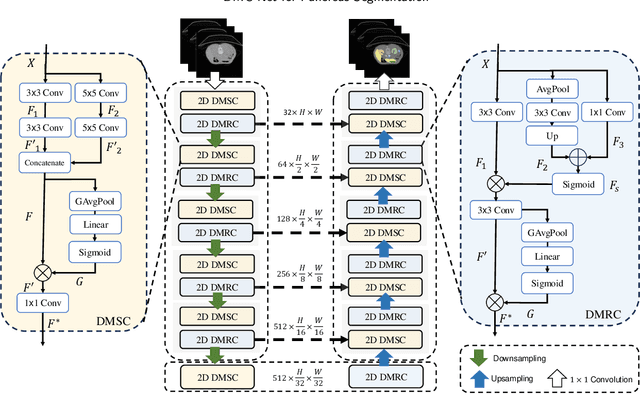
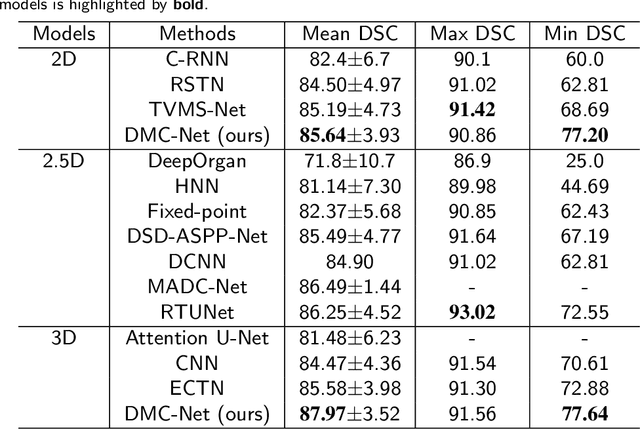
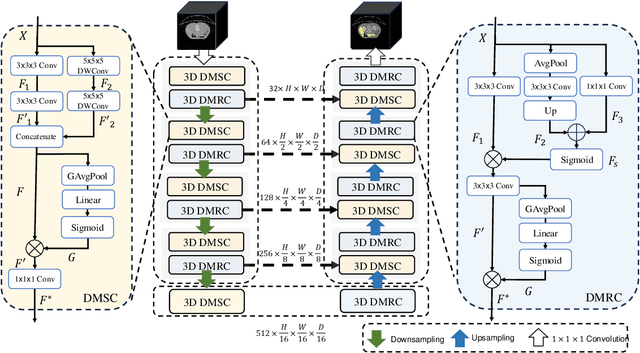
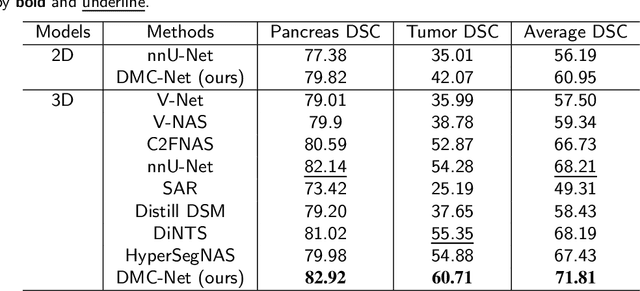
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have shown great effectiveness in medical image segmentation. However, they may be limited in modeling large inter-subject variations in organ shapes and sizes and exploiting global long-range contextual information. This is because CNNs typically employ convolutions with fixed-sized local receptive fields and lack the mechanisms to utilize global information. To address these limitations, we developed Dynamic Multi-Resolution Convolution (DMRC) and Dynamic Multi-Scale Convolution (DMSC) modules. Both modules enhance the representation capabilities of single convolutions to capture varying scaled features and global contextual information. This is achieved in the DMRC module by employing a convolutional filter on images with different resolutions and subsequently utilizing dynamic mechanisms to model global inter-dependencies between features. In contrast, the DMSC module extracts features at different scales by employing convolutions with different kernel sizes and utilizing dynamic mechanisms to extract global contextual information. The utilization of convolutions with different kernel sizes in the DMSC module may increase computational complexity. To lessen this burden, we propose to use a lightweight design for convolution layers with a large kernel size. Thus, DMSC and DMRC modules are designed as lightweight drop-in replacements for single convolutions, and they can be easily integrated into general CNN architectures for end-to-end training. The segmentation network was proposed by incorporating our DMSC and DMRC modules into a standard U-Net architecture, termed Dynamic Multi-scale and Multi-resolution Convolution network (DMC-Net). The results demonstrate that our proposed DMSC and DMRC can enhance the representation capabilities of single convolutions and improve segmentation accuracy.
D-Net: Dynamic Large Kernel with Dynamic Feature Fusion for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Hierarchical transformers have achieved significant success in medical image segmentation due to their large receptive field and capabilities of effectively leveraging global long-range contextual information. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can also deliver a large receptive field by using large kernels, enabling them to achieve competitive performance with fewer model parameters. However, CNNs incorporated with large convolutional kernels remain constrained in adaptively capturing multi-scale features from organs with large variations in shape and size due to the employment of fixed-sized kernels. Additionally, they are unable to utilize global contextual information efficiently. To address these limitations, we propose Dynamic Large Kernel (DLK) and Dynamic Feature Fusion (DFF) modules. The DLK module employs multiple large kernels with varying kernel sizes and dilation rates to capture multi-scale features. Subsequently, a dynamic selection mechanism is utilized to adaptively highlight the most important spatial features based on global information. Additionally, the DFF module is proposed to adaptively fuse multi-scale local feature maps based on their global information. We integrate DLK and DFF in a hierarchical transformer architecture to develop a novel architecture, termed D-Net. D-Net is able to effectively utilize a multi-scale large receptive field and adaptively harness global contextual information. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that D-Net outperforms other state-of-the-art models in the two volumetric segmentation tasks, including abdominal multi-organ segmentation and multi-modality brain tumor segmentation. Our code is available at https://github.com/sotiraslab/DLK.
Dynamic U-Net: Adaptively Calibrate Features for Abdominal Multi-organ Segmentation
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:U-Net has been widely used for segmenting abdominal organs, achieving promising performance. However, when it is used for multi-organ segmentation, first, it may be limited in exploiting global long-range contextual information due to the implementation of standard convolutions. Second, the use of spatial-wise downsampling (e.g., max pooling or strided convolutions) in the encoding path may lead to the loss of deformable or discriminative details. Third, features upsampled from the higher level are concatenated with those that persevered via skip connections. However, repeated downsampling and upsampling operations lead to misalignments between them and their concatenation degrades segmentation performance. To address these limitations, we propose Dynamically Calibrated Convolution (DCC), Dynamically Calibrated Downsampling (DCD), and Dynamically Calibrated Upsampling (DCU) modules, respectively. The DCC module can utilize global inter-dependencies between spatial and channel features to calibrate these features adaptively. The DCD module enables networks to adaptively preserve deformable or discriminative features during downsampling. The DCU module can dynamically align and calibrate upsampled features to eliminate misalignments before concatenations. We integrated the proposed modules into a standard U-Net, resulting in a new architecture, termed Dynamic U-Net. This architectural design enables U-Net to dynamically adjust features for different organs. We evaluated Dynamic U-Net in two abdominal multi-organ segmentation benchmarks. Dynamic U-Net achieved statistically improved segmentation accuracy compared with standard U-Net. Our code is available at https://github.com/sotiraslab/DynamicUNet.
Gene-SGAN: a method for discovering disease subtypes with imaging and genetic signatures via multi-view weakly-supervised deep clustering
Jan 25, 2023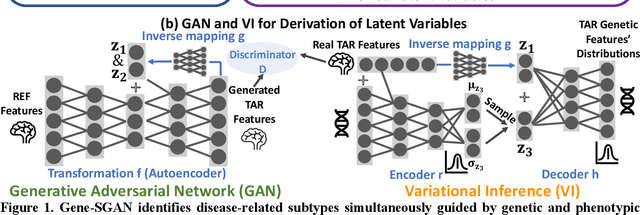
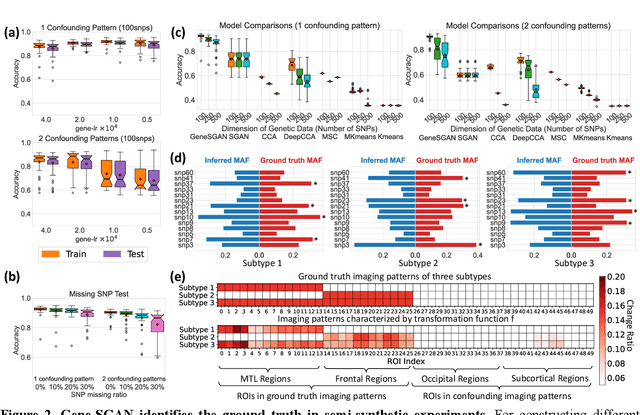
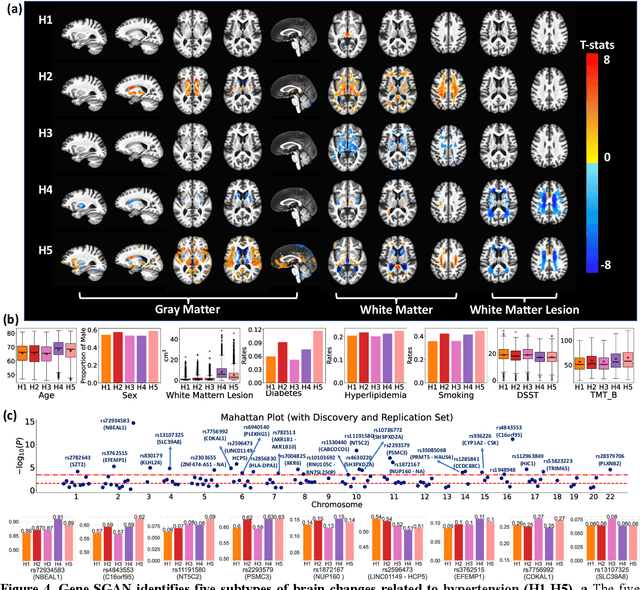
Abstract:Disease heterogeneity has been a critical challenge for precision diagnosis and treatment, especially in neurologic and neuropsychiatric diseases. Many diseases can display multiple distinct brain phenotypes across individuals, potentially reflecting disease subtypes that can be captured using MRI and machine learning methods. However, biological interpretability and treatment relevance are limited if the derived subtypes are not associated with genetic drivers or susceptibility factors. Herein, we describe Gene-SGAN - a multi-view, weakly-supervised deep clustering method - which dissects disease heterogeneity by jointly considering phenotypic and genetic data, thereby conferring genetic correlations to the disease subtypes and associated endophenotypic signatures. We first validate the generalizability, interpretability, and robustness of Gene-SGAN in semi-synthetic experiments. We then demonstrate its application to real multi-site datasets from 28,858 individuals, deriving subtypes of Alzheimer's disease and brain endophenotypes associated with hypertension, from MRI and SNP data. Derived brain phenotypes displayed significant differences in neuroanatomical patterns, genetic determinants, biological and clinical biomarkers, indicating potentially distinct underlying neuropathologic processes, genetic drivers, and susceptibility factors. Overall, Gene-SGAN is broadly applicable to disease subtyping and endophenotype discovery, and is herein tested on disease-related, genetically-driven neuroimaging phenotypes.
MRI-based classification of IDH mutation and 1p/19q codeletion status of gliomas using a 2.5D hybrid multi-task convolutional neural network
Oct 07, 2022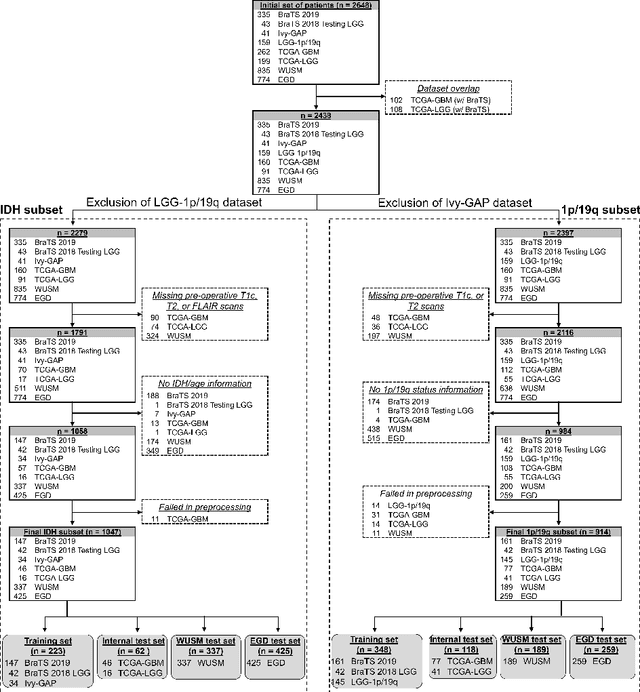
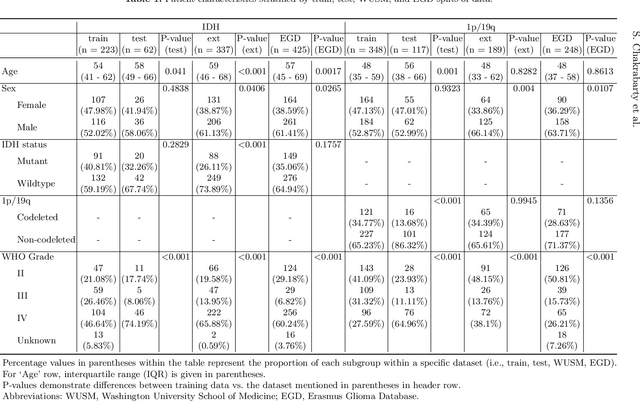
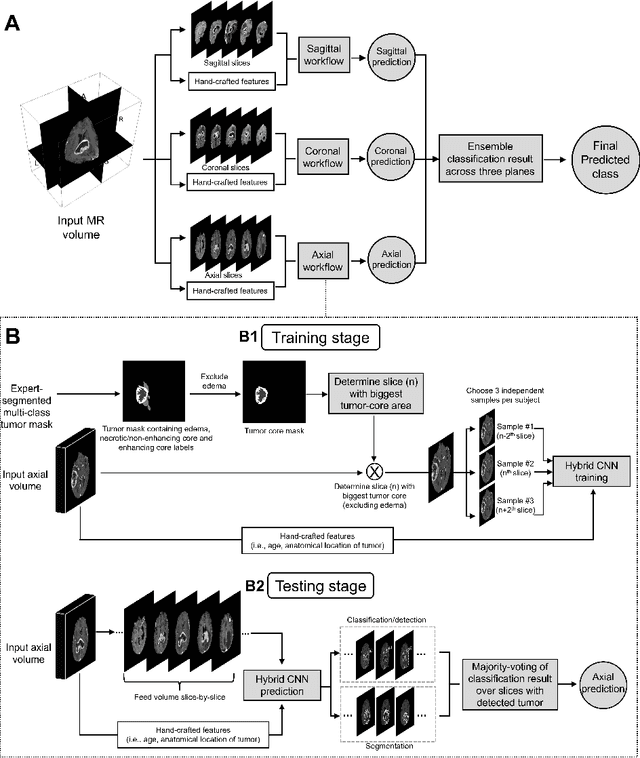
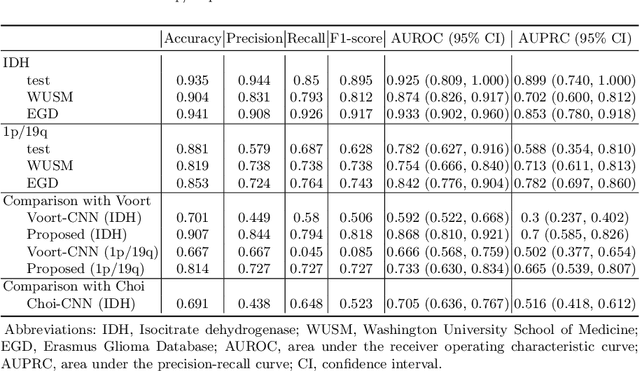
Abstract:Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation and 1p/19q codeletion status are important prognostic markers for glioma. Currently, they are determined using invasive procedures. Our goal was to develop artificial intelligence-based methods to non-invasively determine these molecular alterations from MRI. For this purpose, pre-operative MRI scans of 2648 patients with gliomas (grade II-IV) were collected from Washington University School of Medicine (WUSM; n = 835) and publicly available datasets viz. Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS; n = 378), LGG 1p/19q (n = 159), Ivy Glioblastoma Atlas Project (Ivy GAP; n = 41), The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA; n = 461), and the Erasmus Glioma Database (EGD; n = 774). A 2.5D hybrid convolutional neural network was proposed to simultaneously localize the tumor and classify its molecular status by leveraging imaging features from MR scans and prior knowledge features from clinical records and tumor location. The models were tested on one internal (TCGA) and two external (WUSM and EGD) test sets. For IDH, the best-performing model achieved areas under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) of 0.925, 0.874, 0.933 and areas under the precision-recall curves (AUPRC) of 0.899, 0.702, 0.853 on the internal, WUSM, and EGD test sets, respectively. For 1p/19q, the best model achieved AUROCs of 0.782, 0.754, 0.842, and AUPRCs of 0.588, 0.713, 0.782, on those three data-splits, respectively. The high accuracy of the model on unseen data showcases its generalization capabilities and suggests its potential to perform a 'virtual biopsy' for tailoring treatment planning and overall clinical management of gliomas.
Integrative Imaging Informatics for Cancer Research: Workflow Automation for Neuro-oncology (I3CR-WANO)
Oct 06, 2022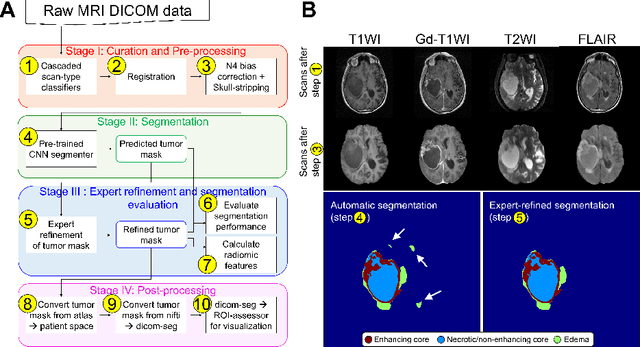
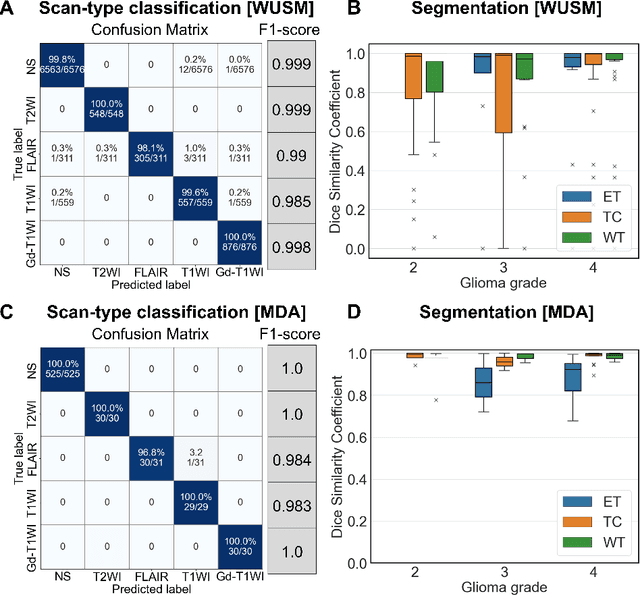
Abstract:Efforts to utilize growing volumes of clinical imaging data to generate tumor evaluations continue to require significant manual data wrangling owing to the data heterogeneity. Here, we propose an artificial intelligence-based solution for the aggregation and processing of multisequence neuro-oncology MRI data to extract quantitative tumor measurements. Our end-to-end framework i) classifies MRI sequences using an ensemble classifier, ii) preprocesses the data in a reproducible manner, iii) delineates tumor tissue subtypes using convolutional neural networks, and iv) extracts diverse radiomic features. Moreover, it is robust to missing sequences and adopts an expert-in-the-loop approach, where the segmentation results may be manually refined by radiologists. Following the implementation of the framework in Docker containers, it was applied to two retrospective glioma datasets collected from the Washington University School of Medicine (WUSM; n = 384) and the M.D. Anderson Cancer Center (MDA; n = 30) comprising preoperative MRI scans from patients with pathologically confirmed gliomas. The scan-type classifier yielded an accuracy of over 99%, correctly identifying sequences from 380/384 and 30/30 sessions from the WUSM and MDA datasets, respectively. Segmentation performance was quantified using the Dice Similarity Coefficient between the predicted and expert-refined tumor masks. Mean Dice scores were 0.882 ($\pm$0.244) and 0.977 ($\pm$0.04) for whole tumor segmentation for WUSM and MDA, respectively. This streamlined framework automatically curated, processed, and segmented raw MRI data of patients with varying grades of gliomas, enabling the curation of large-scale neuro-oncology datasets and demonstrating a high potential for integration as an assistive tool in clinical practice.
The Brain Tumor Sequence Registration Challenge: Establishing Correspondence between Pre-Operative and Follow-up MRI scans of diffuse glioma patients
Dec 13, 2021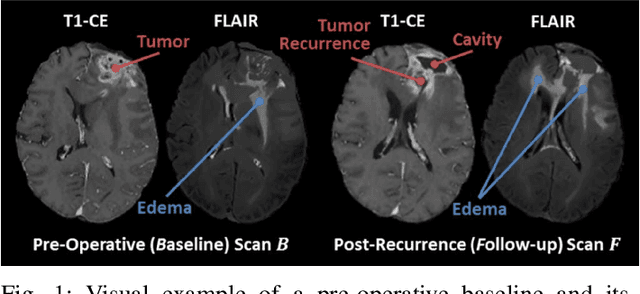
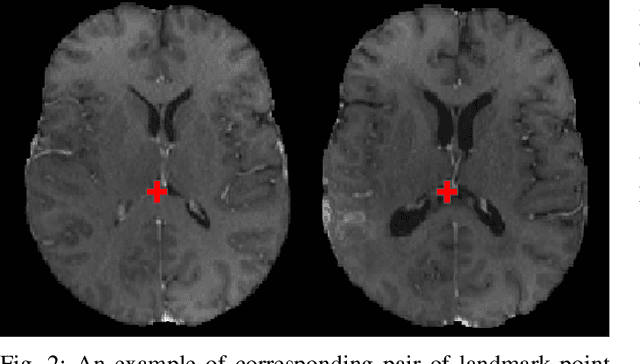
Abstract:Registration of longitudinal brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans containing pathologies is challenging due to tissue appearance changes, and still an unsolved problem. This paper describes the first Brain Tumor Sequence Registration (BraTS-Reg) challenge, focusing on estimating correspondences between pre-operative and follow-up scans of the same patient diagnosed with a brain diffuse glioma. The BraTS-Reg challenge intends to establish a public benchmark environment for deformable registration algorithms. The associated dataset comprises de-identified multi-institutional multi-parametric MRI (mpMRI) data, curated for each scan's size and resolution, according to a common anatomical template. Clinical experts have generated extensive annotations of landmarks points within the scans, descriptive of distinct anatomical locations across the temporal domain. The training data along with these ground truth annotations will be released to participants to design and develop their registration algorithms, whereas the annotations for the validation and the testing data will be withheld by the organizers and used to evaluate the containerized algorithms of the participants. Each submitted algorithm will be quantitatively evaluated using several metrics, such as the Median Absolute Error (MAE), Robustness, and the Jacobian determinant.
Correlation between image quality metrics of magnetic resonance images and the neural network segmentation accuracy
Nov 01, 2021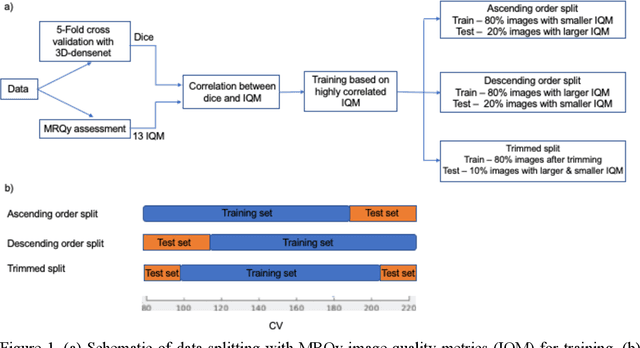
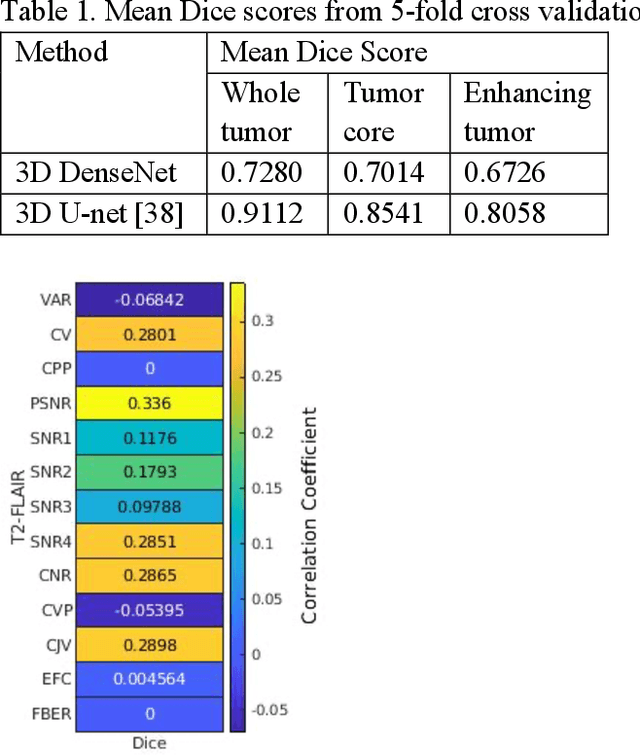
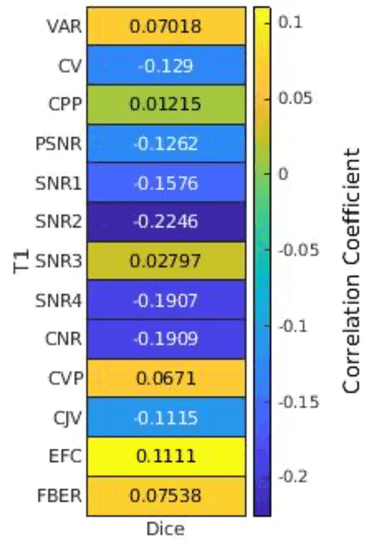
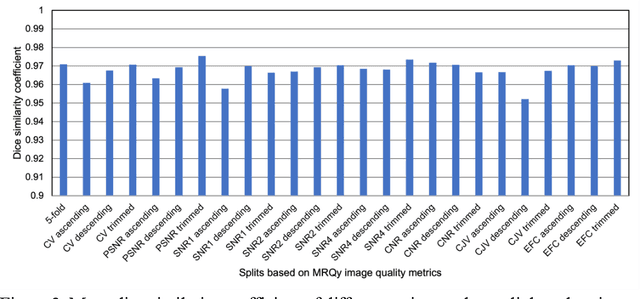
Abstract:Deep neural networks with multilevel connections process input data in complex ways to learn the information.A networks learning efficiency depends not only on the complex neural network architecture but also on the input training images.Medical image segmentation with deep neural networks for skull stripping or tumor segmentation from magnetic resonance images enables learning both global and local features of the images.Though medical images are collected in a controlled environment,there may be artifacts or equipment based variance that cause inherent bias in the input set.In this study, we investigated the correlation between the image quality metrics of MR images with the neural network segmentation accuracy.For that we have used the 3D DenseNet architecture and let the network trained on the same input but applying different methodologies to select the training data set based on the IQM values.The difference in the segmentation accuracy between models based on the random training inputs with IQM based training inputs shed light on the role of image quality metrics on segmentation accuracy.By running the image quality metrics to choose the training inputs,further we may tune the learning efficiency of the network and the segmentation accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge