Chunxiao Fan
MIND: A Multi-agent Framework for Zero-shot Harmful Meme Detection
Jul 09, 2025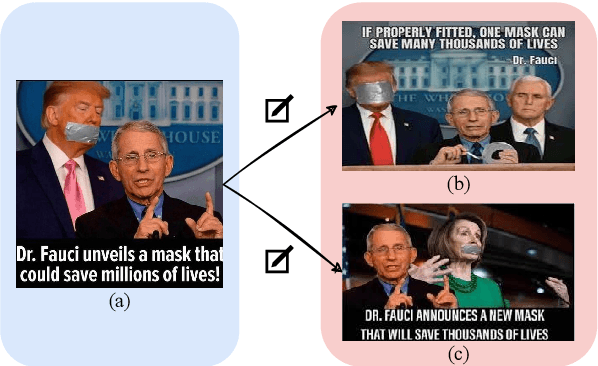
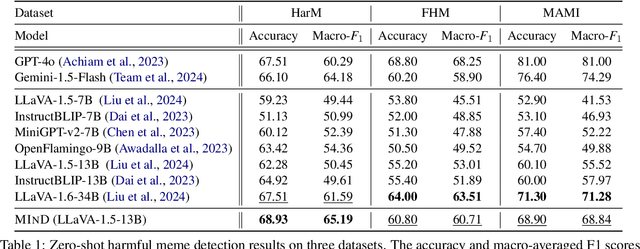
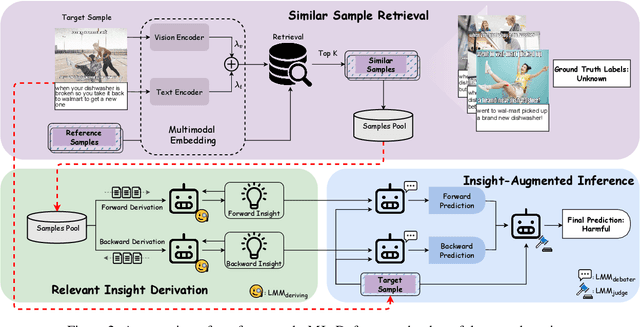
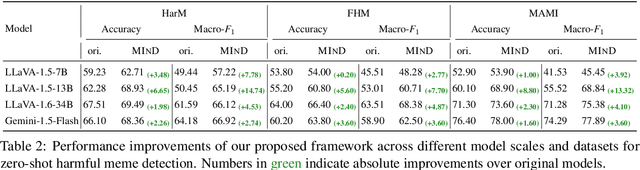
Abstract:The rapid expansion of memes on social media has highlighted the urgent need for effective approaches to detect harmful content. However, traditional data-driven approaches struggle to detect new memes due to their evolving nature and the lack of up-to-date annotated data. To address this issue, we propose MIND, a multi-agent framework for zero-shot harmful meme detection that does not rely on annotated data. MIND implements three key strategies: 1) We retrieve similar memes from an unannotated reference set to provide contextual information. 2) We propose a bi-directional insight derivation mechanism to extract a comprehensive understanding of similar memes. 3) We then employ a multi-agent debate mechanism to ensure robust decision-making through reasoned arbitration. Extensive experiments on three meme datasets demonstrate that our proposed framework not only outperforms existing zero-shot approaches but also shows strong generalization across different model architectures and parameter scales, providing a scalable solution for harmful meme detection. The code is available at https://github.com/destroy-lonely/MIND.
Prototypical Calibrating Ambiguous Samples for Micro-Action Recognition
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Micro-Action Recognition (MAR) has gained increasing attention due to its crucial role as a form of non-verbal communication in social interactions, with promising potential for applications in human communication and emotion analysis. However, current approaches often overlook the inherent ambiguity in micro-actions, which arises from the wide category range and subtle visual differences between categories. This oversight hampers the accuracy of micro-action recognition. In this paper, we propose a novel Prototypical Calibrating Ambiguous Network (\textbf{PCAN}) to unleash and mitigate the ambiguity of MAR. \textbf{Firstly}, we employ a hierarchical action-tree to identify the ambiguous sample, categorizing them into distinct sets of ambiguous samples of false negatives and false positives, considering both body- and action-level categories. \textbf{Secondly}, we implement an ambiguous contrastive refinement module to calibrate these ambiguous samples by regulating the distance between ambiguous samples and their corresponding prototypes. This calibration process aims to pull false negative ($\mathbb{FN}$) samples closer to their respective prototypes and push false positive ($\mathbb{FP}$) samples apart from their affiliated prototypes. In addition, we propose a new prototypical diversity amplification loss to strengthen the model's capacity by amplifying the differences between different prototypes. \textbf{Finally}, we propose a prototype-guided rectification to rectify prediction by incorporating the representability of prototypes. Extensive experiments conducted on the benchmark dataset demonstrate the superior performance of our method compared to existing approaches. The code is available at https://github.com/kunli-cs/PCAN.
Hybrid Multimodal Feature Extraction, Mining and Fusion for Sentiment Analysis
Aug 12, 2022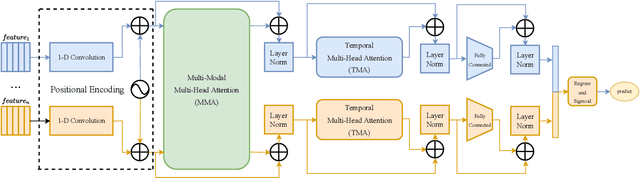
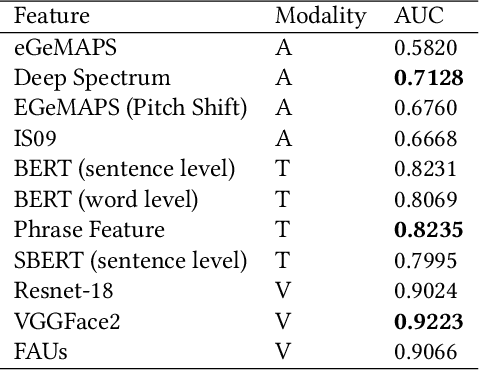
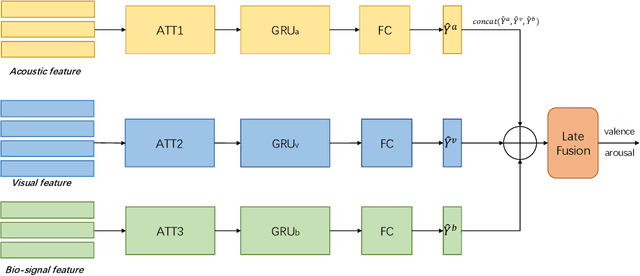
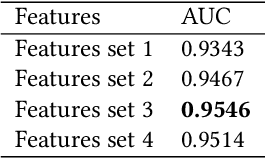
Abstract:In this paper, we present our solutions for the Multimodal Sentiment Analysis Challenge (MuSe) 2022, which includes MuSe-Humor, MuSe-Reaction and MuSe-Stress Sub-challenges. The MuSe 2022 focuses on humor detection, emotional reactions and multimodal emotional stress utilizing different modalities and data sets. In our work, different kinds of multimodal features are extracted, including acoustic, visual, text and biological features. These features are fused by TEMMA and GRU with self-attention mechanism frameworks. In this paper, 1) several new audio features, facial expression features and paragraph-level text embeddings are extracted for accuracy improvement. 2) we substantially improve the accuracy and reliability of multimodal sentiment prediction by mining and blending the multimodal features. 3) effective data augmentation strategies are applied in model training to alleviate the problem of sample imbalance and prevent the model from learning biased subject characters. For the MuSe-Humor sub-challenge, our model obtains the AUC score of 0.8932. For the MuSe-Reaction sub-challenge, the Pearson's Correlations Coefficient of our approach on the test set is 0.3879, which outperforms all other participants. For the MuSe-Stress sub-challenge, our approach outperforms the baseline in both arousal and valence on the test dataset, reaching a final combined result of 0.5151.
PCANet-II: When PCANet Meets the Second Order Pooling
Sep 30, 2017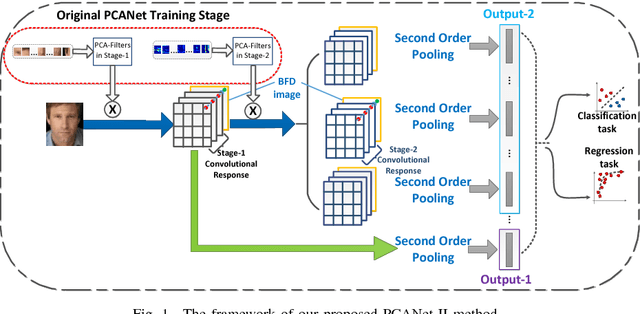

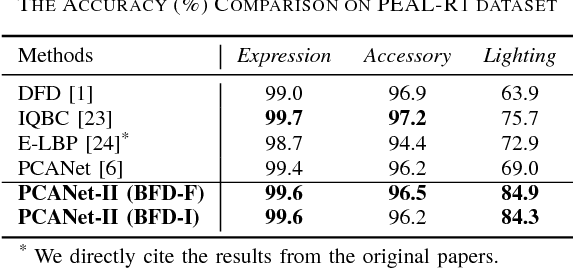
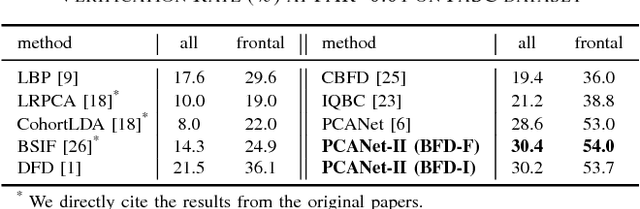
Abstract:PCANet, as one noticeable shallow network, employs the histogram representation for feature pooling. However, there are three main problems about this kind of pooling method. First, the histogram-based pooling method binarizes the feature maps and leads to inevitable discriminative information loss. Second, it is difficult to effectively combine other visual cues into a compact representation, because the simple concatenation of various visual cues leads to feature representation inefficiency. Third, the dimensionality of histogram-based output grows exponentially with the number of feature maps used. In order to overcome these problems, we propose a novel shallow network model, named as PCANet-II. Compared with the histogram-based output, the second order pooling not only provides more discriminative information by preserving both the magnitude and sign of convolutional responses, but also dramatically reduces the size of output features. Thus we combine the second order statistical pooling method with the shallow network, i.e., PCANet. Moreover, it is easy to combine other discriminative and robust cues by using the second order pooling. So we introduce the binary feature difference encoding scheme into our PCANet-II to further improve robustness. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed PCANet-II method.
Improving Deep Neural Network with Multiple Parametric Exponential Linear Units
Jan 17, 2017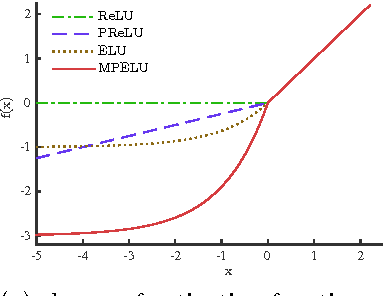
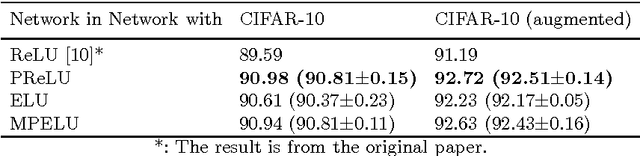

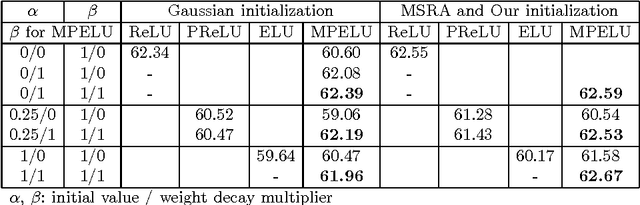
Abstract:Activation function is crucial to the recent successes of deep neural networks. In this paper, we first propose a new activation function, Multiple Parametric Exponential Linear Units (MPELU), aiming to generalize and unify the rectified and exponential linear units. As the generalized form, MPELU shares the advantages of Parametric Rectified Linear Unit (PReLU) and Exponential Linear Unit (ELU), leading to better classification performance and convergence property. In addition, weight initialization is very important to train very deep networks. The existing methods laid a solid foundation for networks using rectified linear units but not for exponential linear units. This paper complements the current theory and extends it to the wider range. Specifically, we put forward a way of initialization, enabling training of very deep networks using exponential linear units. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed initialization not only helps the training process but leads to better generalization performance. Finally, utilizing the proposed activation function and initialization, we present a deep MPELU residual architecture that achieves state-of-the-art performance on the CIFAR-10/100 datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/Coldmooon/Code-for-MPELU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge