Chih-wei Hsu
DynaMITE-RL: A Dynamic Model for Improved Temporal Meta-Reinforcement Learning
Feb 25, 2024



Abstract:We introduce DynaMITE-RL, a meta-reinforcement learning (meta-RL) approach to approximate inference in environments where the latent state evolves at varying rates. We model episode sessions - parts of the episode where the latent state is fixed - and propose three key modifications to existing meta-RL methods: consistency of latent information within sessions, session masking, and prior latent conditioning. We demonstrate the importance of these modifications in various domains, ranging from discrete Gridworld environments to continuous-control and simulated robot assistive tasks, demonstrating that DynaMITE-RL significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in sample efficiency and inference returns.
Preference Elicitation with Soft Attributes in Interactive Recommendation
Oct 22, 2023



Abstract:Preference elicitation plays a central role in interactive recommender systems. Most preference elicitation approaches use either item queries that ask users to select preferred items from a slate, or attribute queries that ask them to express their preferences for item characteristics. Unfortunately, users often wish to describe their preferences using soft attributes for which no ground-truth semantics is given. Leveraging concept activation vectors for soft attribute semantics, we develop novel preference elicitation methods that can accommodate soft attributes and bring together both item and attribute-based preference elicitation. Our techniques query users using both items and soft attributes to update the recommender system's belief about their preferences to improve recommendation quality. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods vis-a-vis competing approaches on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
Discovering Personalized Semantics for Soft Attributes in Recommender Systems using Concept Activation Vectors
Feb 06, 2022



Abstract:Interactive recommender systems (RSs) allow users to express intent, preferences and contexts in a rich fashion, often using natural language. One challenge in using such feedback is inferring a user's semantic intent from the open-ended terms used to describe an item, and using it to refine recommendation results. Leveraging concept activation vectors (CAVs) [21], we develop a framework to learn a representation that captures the semantics of such attributes and connects them to user preferences and behaviors in RSs. A novel feature of our approach is its ability to distinguish objective and subjective attributes and associate different senses with different users. Using synthetic and real-world datasets, we show that our CAV representation accurately interprets users' subjective semantics, and can improve recommendations via interactive critiquing
Meta-Thompson Sampling
Feb 11, 2021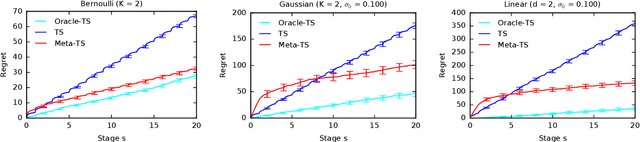
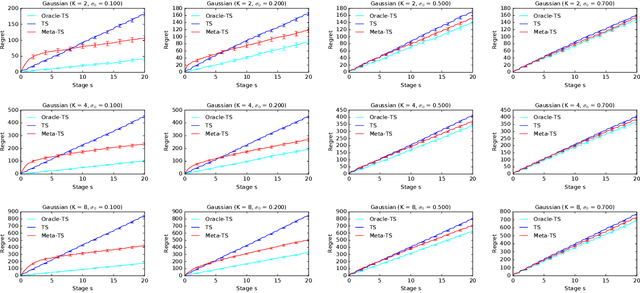
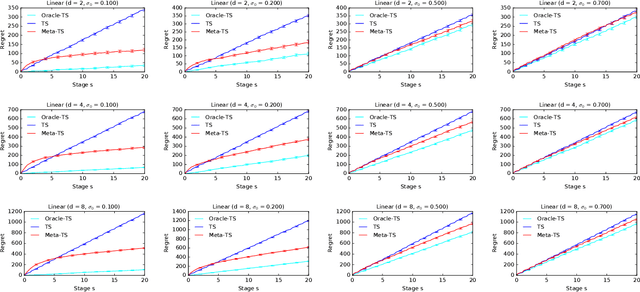
Abstract:Efficient exploration in multi-armed bandits is a fundamental online learning problem. In this work, we propose a variant of Thompson sampling that learns to explore better as it interacts with problem instances drawn from an unknown prior distribution. Our algorithm meta-learns the prior and thus we call it Meta-TS. We propose efficient implementations of Meta-TS and analyze it in Gaussian bandits. Our analysis shows the benefit of meta-learning the prior and is of a broader interest, because we derive the first prior-dependent upper bound on the Bayes regret of Thompson sampling. This result is complemented by empirical evaluation, which shows that Meta-TS quickly adapts to the unknown prior.
RecSim: A Configurable Simulation Platform for Recommender Systems
Sep 26, 2019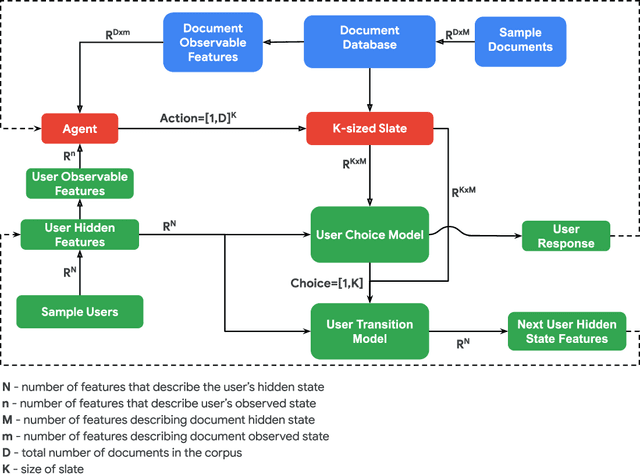
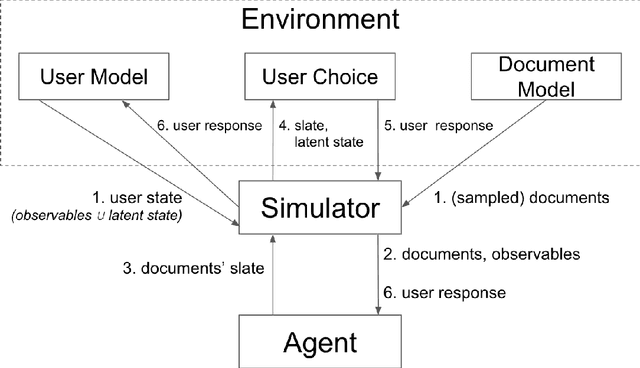
Abstract:We propose RecSim, a configurable platform for authoring simulation environments for recommender systems (RSs) that naturally supports sequential interaction with users. RecSim allows the creation of new environments that reflect particular aspects of user behavior and item structure at a level of abstraction well-suited to pushing the limits of current reinforcement learning (RL) and RS techniques in sequential interactive recommendation problems. Environments can be easily configured that vary assumptions about: user preferences and item familiarity; user latent state and its dynamics; and choice models and other user response behavior. We outline how RecSim offers value to RL and RS researchers and practitioners, and how it can serve as a vehicle for academic-industrial collaboration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge