Bastian Leibe
Faster VGGT with Block-Sparse Global Attention
Sep 08, 2025Abstract:Efficient and accurate feed-forward multi-view reconstruction has long been an important task in computer vision. Recent transformer-based models like VGGT and $\pi^3$ have achieved impressive results with simple architectures, yet they face an inherent runtime bottleneck, due to the quadratic complexity of the global attention layers, that limits the scalability to large image sets. In this paper, we empirically analyze the global attention matrix of these models and observe that probability mass concentrates on a small subset of patch-patch interactions that correspond to cross-view geometric matches. Motivated by the structured attention and inspired by recent advancement in large language models, we propose a replacement for the dense global attention operation based on highly optimized block-sparse kernels, yielding up to $4\times$ faster inference with comparable task performance. Our retrofit requires no retraining of the backbone, extends to both VGGT and $\pi^3$, and supports large image collections. Evaluations on a comprehensive suite of multi-view benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
How do Foundation Models Compare to Skeleton-Based Approaches for Gesture Recognition in Human-Robot Interaction?
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:Gestures enable non-verbal human-robot communication, especially in noisy environments like agile production. Traditional deep learning-based gesture recognition relies on task-specific architectures using images, videos, or skeletal pose estimates as input. Meanwhile, Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) and Vision Language Models (VLMs) with their strong generalization abilities offer potential to reduce system complexity by replacing dedicated task-specific modules. This study investigates adapting such models for dynamic, full-body gesture recognition, comparing V-JEPA (a state-of-the-art VFM), Gemini Flash 2.0 (a multimodal VLM), and HD-GCN (a top-performing skeleton-based approach). We introduce NUGGET, a dataset tailored for human-robot communication in intralogistics environments, to evaluate the different gesture recognition approaches. In our experiments, HD-GCN achieves best performance, but V-JEPA comes close with a simple, task-specific classification head - thus paving a possible way towards reducing system complexity, by using it as a shared multi-task model. In contrast, Gemini struggles to differentiate gestures based solely on textual descriptions in the zero-shot setting, highlighting the need of further research on suitable input representations for gestures.
Systematic Comparison of Projection Methods for Monocular 3D Human Pose Estimation on Fisheye Images
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Fisheye cameras offer robots the ability to capture human movements across a wider field of view (FOV) than standard pinhole cameras, making them particularly useful for applications in human-robot interaction and automotive contexts. However, accurately detecting human poses in fisheye images is challenging due to the curved distortions inherent to fisheye optics. While various methods for undistorting fisheye images have been proposed, their effectiveness and limitations for poses that cover a wide FOV has not been systematically evaluated in the context of absolute human pose estimation from monocular fisheye images. To address this gap, we evaluate the impact of pinhole, equidistant and double sphere camera models, as well as cylindrical projection methods, on 3D human pose estimation accuracy. We find that in close-up scenarios, pinhole projection is inadequate, and the optimal projection method varies with the FOV covered by the human pose. The usage of advanced fisheye models like the double sphere model significantly enhances 3D human pose estimation accuracy. We propose a heuristic for selecting the appropriate projection model based on the detection bounding box to enhance prediction quality. Additionally, we introduce and evaluate on our novel dataset FISHnCHIPS, which features 3D human skeleton annotations in fisheye images, including images from unconventional angles, such as extreme close-ups, ground-mounted cameras, and wide-FOV poses, available at: https://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/fishnchips
OpenSplat3D: Open-Vocabulary 3D Instance Segmentation using Gaussian Splatting
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful representation for neural scene reconstruction, offering high-quality novel view synthesis while maintaining computational efficiency. In this paper, we extend the capabilities of 3DGS beyond pure scene representation by introducing an approach for open-vocabulary 3D instance segmentation without requiring manual labeling, termed OpenSplat3D. Our method leverages feature-splatting techniques to associate semantic information with individual Gaussians, enabling fine-grained scene understanding. We incorporate Segment Anything Model instance masks with a contrastive loss formulation as guidance for the instance features to achieve accurate instance-level segmentation. Furthermore, we utilize language embeddings of a vision-language model, allowing for flexible, text-driven instance identification. This combination enables our system to identify and segment arbitrary objects in 3D scenes based on natural language descriptions. We show results on LERF-mask and LERF-OVS as well as the full ScanNet++ validation set, demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach.
How Important are Videos for Training Video LLMs?
Jun 07, 2025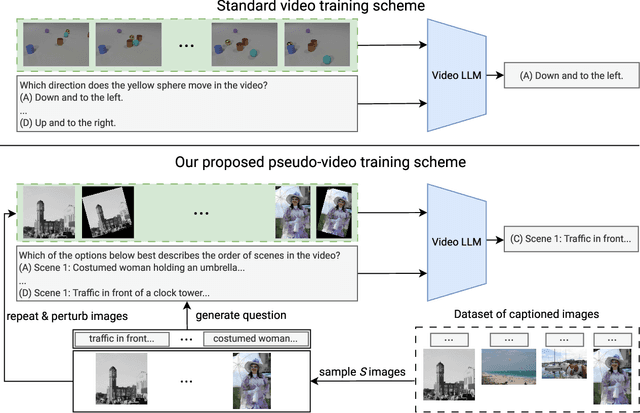

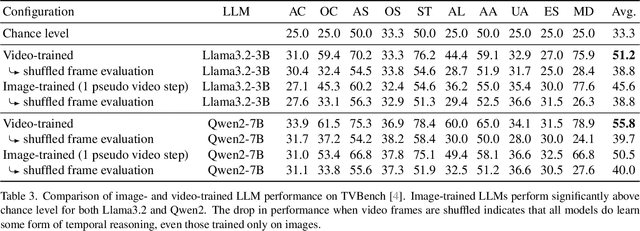
Abstract:Research into Video Large Language Models (LLMs) has progressed rapidly, with numerous models and benchmarks emerging in just a few years. Typically, these models are initialized with a pretrained text-only LLM and finetuned on both image- and video-caption datasets. In this paper, we present findings indicating that Video LLMs are more capable of temporal reasoning after image-only training than one would assume, and that improvements from video-specific training are surprisingly small. Specifically, we show that image-trained versions of two LLMs trained with the recent LongVU algorithm perform significantly above chance level on TVBench, a temporal reasoning benchmark. Additionally, we introduce a simple finetuning scheme involving sequences of annotated images and questions targeting temporal capabilities. This baseline results in temporal reasoning performance close to, and occasionally higher than, what is achieved by video-trained LLMs. This suggests suboptimal utilization of rich temporal features found in real video by current models. Our analysis motivates further research into the mechanisms that allow image-trained LLMs to perform temporal reasoning, as well as into the bottlenecks that render current video training schemes inefficient.
DONUT: A Decoder-Only Model for Trajectory Prediction
Jun 07, 2025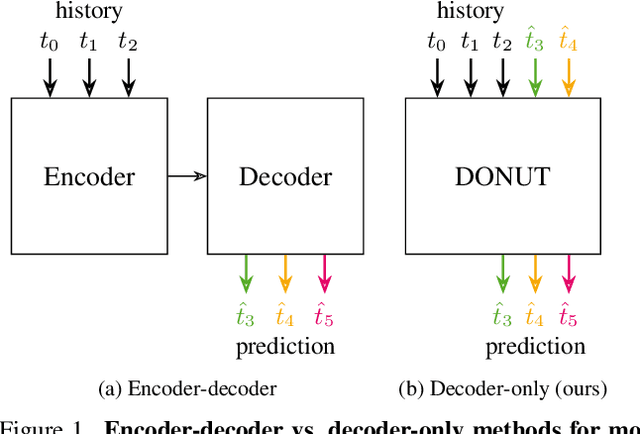
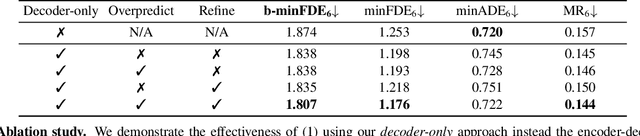
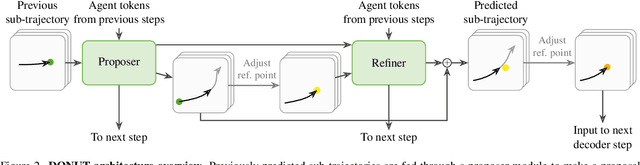
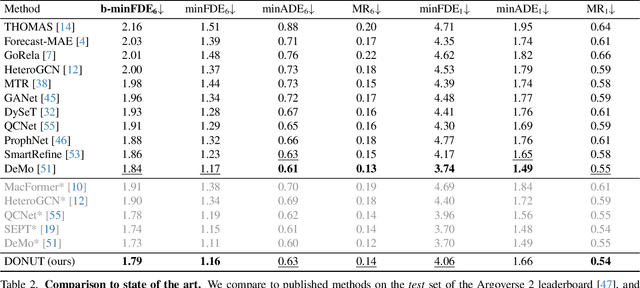
Abstract:Predicting the motion of other agents in a scene is highly relevant for autonomous driving, as it allows a self-driving car to anticipate. Inspired by the success of decoder-only models for language modeling, we propose DONUT, a Decoder-Only Network for Unrolling Trajectories. Different from existing encoder-decoder forecasting models, we encode historical trajectories and predict future trajectories with a single autoregressive model. This allows the model to make iterative predictions in a consistent manner, and ensures that the model is always provided with up-to-date information, enhancing the performance. Furthermore, inspired by multi-token prediction for language modeling, we introduce an 'overprediction' strategy that gives the network the auxiliary task of predicting trajectories at longer temporal horizons. This allows the model to better anticipate the future, and further improves the performance. With experiments, we demonstrate that our decoder-only approach outperforms the encoder-decoder baseline, and achieves new state-of-the-art results on the Argoverse 2 single-agent motion forecasting benchmark.
Spotting the Unexpected (STU): A 3D LiDAR Dataset for Anomaly Segmentation in Autonomous Driving
May 04, 2025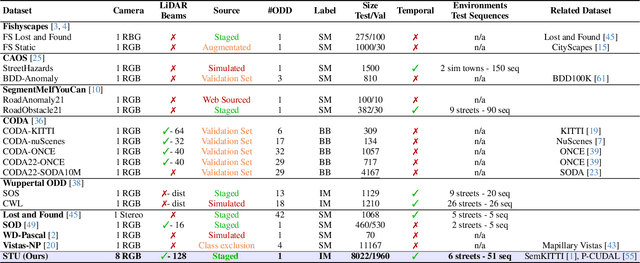
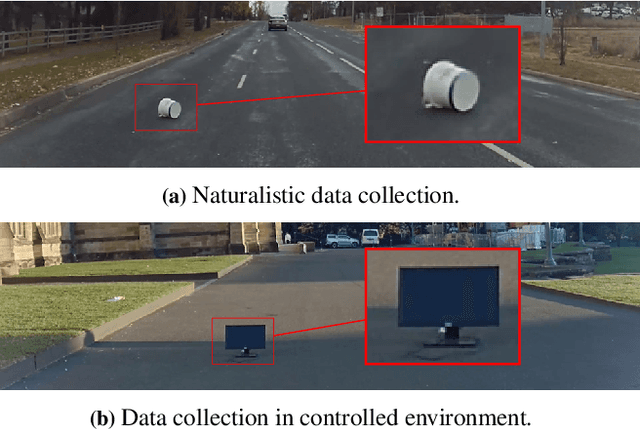
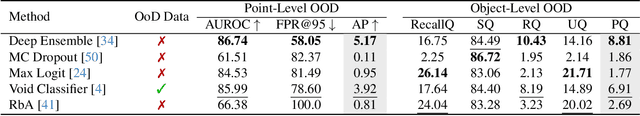

Abstract:To operate safely, autonomous vehicles (AVs) need to detect and handle unexpected objects or anomalies on the road. While significant research exists for anomaly detection and segmentation in 2D, research progress in 3D is underexplored. Existing datasets lack high-quality multimodal data that are typically found in AVs. This paper presents a novel dataset for anomaly segmentation in driving scenarios. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first publicly available dataset focused on road anomaly segmentation with dense 3D semantic labeling, incorporating both LiDAR and camera data, as well as sequential information to enable anomaly detection across various ranges. This capability is critical for the safe navigation of autonomous vehicles. We adapted and evaluated several baseline models for 3D segmentation, highlighting the challenges of 3D anomaly detection in driving environments. Our dataset and evaluation code will be openly available, facilitating the testing and performance comparison of different approaches.
Acquisition of high-quality images for camera calibration in robotics applications via speech prompts
Apr 15, 2025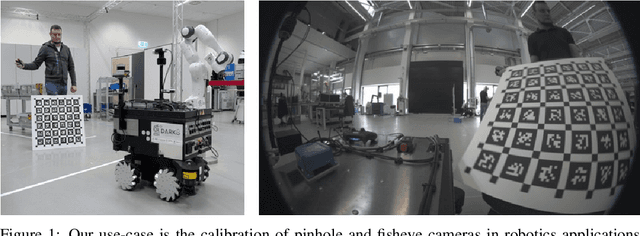


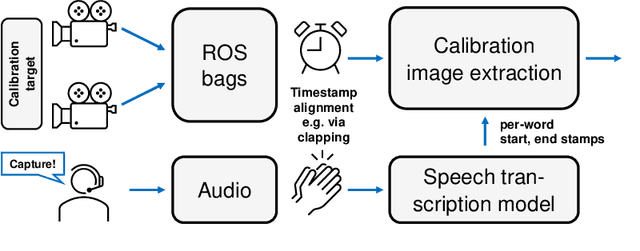
Abstract:Accurate intrinsic and extrinsic camera calibration can be an important prerequisite for robotic applications that rely on vision as input. While there is ongoing research on enabling camera calibration using natural images, many systems in practice still rely on using designated calibration targets with e.g. checkerboard patterns or April tag grids. Once calibration images from different perspectives have been acquired and feature descriptors detected, those are typically used in an optimization process to minimize the geometric reprojection error. For this optimization to converge, input images need to be of sufficient quality and particularly sharpness; they should neither contain motion blur nor rolling-shutter artifacts that can arise when the calibration board was not static during image capture. In this work, we present a novel calibration image acquisition technique controlled via voice commands recorded with a clip-on microphone, that can be more robust and user-friendly than e.g. triggering capture with a remote control, or filtering out blurry frames from a video sequence in postprocessing. To achieve this, we use a state-of-the-art speech-to-text transcription model with accurate per-word timestamping to capture trigger words with precise temporal alignment. Our experiments show that the proposed method improves user experience by being fast and efficient, allowing us to successfully calibrate complex multi-camera setups.
DINO in the Room: Leveraging 2D Foundation Models for 3D Segmentation
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Vision foundation models (VFMs) trained on large-scale image datasets provide high-quality features that have significantly advanced 2D visual recognition. However, their potential in 3D vision remains largely untapped, despite the common availability of 2D images alongside 3D point cloud datasets. While significant research has been dedicated to 2D-3D fusion, recent state-of-the-art 3D methods predominantly focus on 3D data, leaving the integration of VFMs into 3D models underexplored. In this work, we challenge this trend by introducing DITR, a simple yet effective approach that extracts 2D foundation model features, projects them to 3D, and finally injects them into a 3D point cloud segmentation model. DITR achieves state-of-the-art results on both indoor and outdoor 3D semantic segmentation benchmarks. To enable the use of VFMs even when images are unavailable during inference, we further propose to distill 2D foundation models into a 3D backbone as a pretraining task. By initializing the 3D backbone with knowledge distilled from 2D VFMs, we create a strong basis for downstream 3D segmentation tasks, ultimately boosting performance across various datasets.
Your ViT is Secretly an Image Segmentation Model
Mar 24, 2025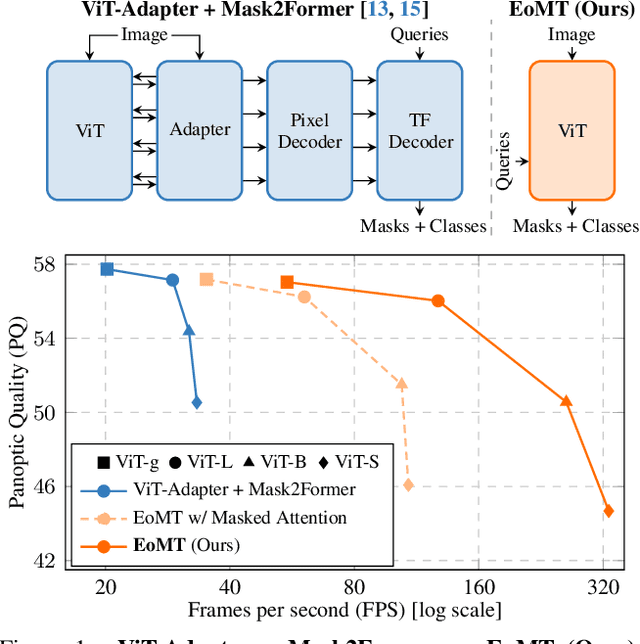
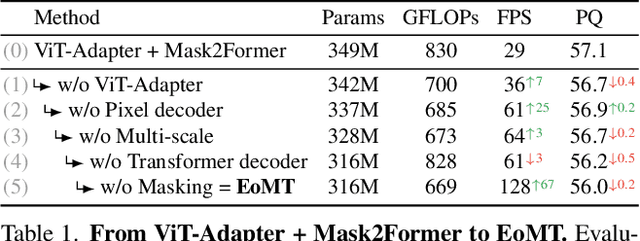
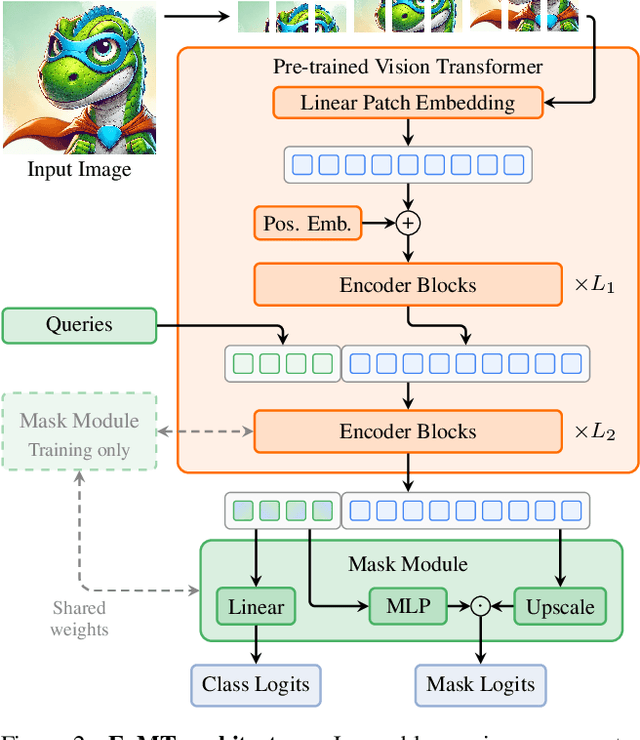
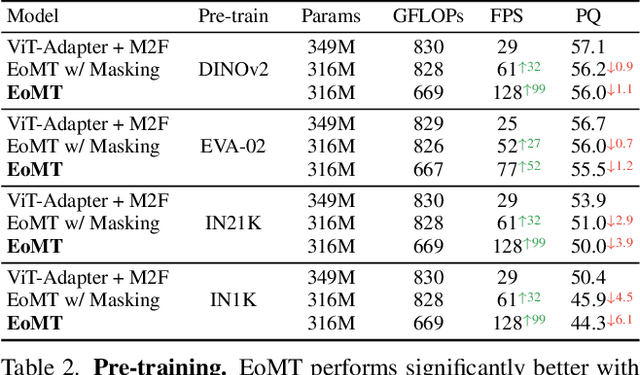
Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown remarkable performance and scalability across various computer vision tasks. To apply single-scale ViTs to image segmentation, existing methods adopt a convolutional adapter to generate multi-scale features, a pixel decoder to fuse these features, and a Transformer decoder that uses the fused features to make predictions. In this paper, we show that the inductive biases introduced by these task-specific components can instead be learned by the ViT itself, given sufficiently large models and extensive pre-training. Based on these findings, we introduce the Encoder-only Mask Transformer (EoMT), which repurposes the plain ViT architecture to conduct image segmentation. With large-scale models and pre-training, EoMT obtains a segmentation accuracy similar to state-of-the-art models that use task-specific components. At the same time, EoMT is significantly faster than these methods due to its architectural simplicity, e.g., up to 4x faster with ViT-L. Across a range of model sizes, EoMT demonstrates an optimal balance between segmentation accuracy and prediction speed, suggesting that compute resources are better spent on scaling the ViT itself rather than adding architectural complexity. Code: https://www.tue-mps.org/eomt/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge