Kadir Yilmaz
Acquisition of high-quality images for camera calibration in robotics applications via speech prompts
Apr 15, 2025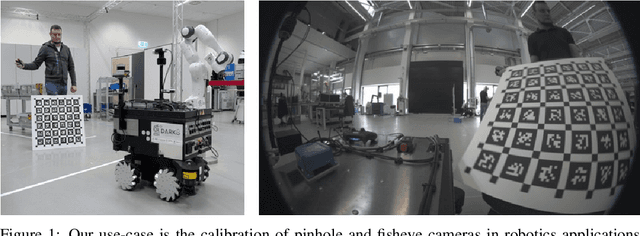


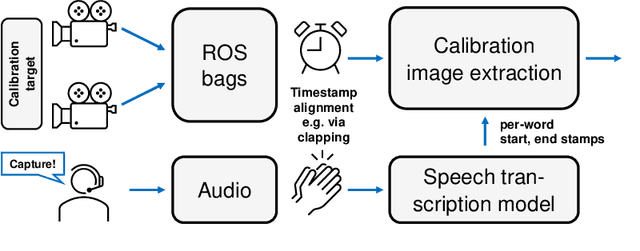
Abstract:Accurate intrinsic and extrinsic camera calibration can be an important prerequisite for robotic applications that rely on vision as input. While there is ongoing research on enabling camera calibration using natural images, many systems in practice still rely on using designated calibration targets with e.g. checkerboard patterns or April tag grids. Once calibration images from different perspectives have been acquired and feature descriptors detected, those are typically used in an optimization process to minimize the geometric reprojection error. For this optimization to converge, input images need to be of sufficient quality and particularly sharpness; they should neither contain motion blur nor rolling-shutter artifacts that can arise when the calibration board was not static during image capture. In this work, we present a novel calibration image acquisition technique controlled via voice commands recorded with a clip-on microphone, that can be more robust and user-friendly than e.g. triggering capture with a remote control, or filtering out blurry frames from a video sequence in postprocessing. To achieve this, we use a state-of-the-art speech-to-text transcription model with accurate per-word timestamping to capture trigger words with precise temporal alignment. Our experiments show that the proposed method improves user experience by being fast and efficient, allowing us to successfully calibrate complex multi-camera setups.
DINO in the Room: Leveraging 2D Foundation Models for 3D Segmentation
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Vision foundation models (VFMs) trained on large-scale image datasets provide high-quality features that have significantly advanced 2D visual recognition. However, their potential in 3D vision remains largely untapped, despite the common availability of 2D images alongside 3D point cloud datasets. While significant research has been dedicated to 2D-3D fusion, recent state-of-the-art 3D methods predominantly focus on 3D data, leaving the integration of VFMs into 3D models underexplored. In this work, we challenge this trend by introducing DITR, a simple yet effective approach that extracts 2D foundation model features, projects them to 3D, and finally injects them into a 3D point cloud segmentation model. DITR achieves state-of-the-art results on both indoor and outdoor 3D semantic segmentation benchmarks. To enable the use of VFMs even when images are unavailable during inference, we further propose to distill 2D foundation models into a 3D backbone as a pretraining task. By initializing the 3D backbone with knowledge distilled from 2D VFMs, we create a strong basis for downstream 3D segmentation tasks, ultimately boosting performance across various datasets.
Interactive4D: Interactive 4D LiDAR Segmentation
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Interactive segmentation has an important role in facilitating the annotation process of future LiDAR datasets. Existing approaches sequentially segment individual objects at each LiDAR scan, repeating the process throughout the entire sequence, which is redundant and ineffective. In this work, we propose interactive 4D segmentation, a new paradigm that allows segmenting multiple objects on multiple LiDAR scans simultaneously, and Interactive4D, the first interactive 4D segmentation model that segments multiple objects on superimposed consecutive LiDAR scans in a single iteration by utilizing the sequential nature of LiDAR data. While performing interactive segmentation, our model leverages the entire space-time volume, leading to more efficient segmentation. Operating on the 4D volume, it directly provides consistent instance IDs over time and also simplifies tracking annotations. Moreover, we show that click simulations are crucial for successful model training on LiDAR point clouds. To this end, we design a click simulation strategy that is better suited for the characteristics of LiDAR data. To demonstrate its accuracy and effectiveness, we evaluate Interactive4D on multiple LiDAR datasets, where Interactive4D achieves a new state-of-the-art by a large margin. Upon acceptance, we will publicly release the code and models at https://vision.rwth-aachen.de/Interactive4D.
Loss Functions in the Era of Semantic Segmentation: A Survey and Outlook
Dec 08, 2023



Abstract:Semantic image segmentation, the process of classifying each pixel in an image into a particular class, plays an important role in many visual understanding systems. As the predominant criterion for evaluating the performance of statistical models, loss functions are crucial for shaping the development of deep learning-based segmentation algorithms and improving their overall performance. To aid researchers in identifying the optimal loss function for their particular application, this survey provides a comprehensive and unified review of $25$ loss functions utilized in image segmentation. We provide a novel taxonomy and thorough review of how these loss functions are customized and leveraged in image segmentation, with a systematic categorization emphasizing their significant features and applications. Furthermore, to evaluate the efficacy of these methods in real-world scenarios, we propose unbiased evaluations of some distinct and renowned loss functions on established medical and natural image datasets. We conclude this review by identifying current challenges and unveiling future research opportunities. Finally, we have compiled the reviewed studies that have open-source implementations on our GitHub page.
MASK4D: Mask Transformer for 4D Panoptic Segmentation
Sep 28, 2023



Abstract:Accurately perceiving and tracking instances over time is essential for the decision-making processes of autonomous agents interacting safely in dynamic environments. With this intention, we propose Mask4D for the challenging task of 4D panoptic segmentation of LiDAR point clouds. Mask4D is the first transformer-based approach unifying semantic instance segmentation and tracking of sparse and irregular sequences of 3D point clouds into a single joint model. Our model directly predicts semantic instances and their temporal associations without relying on any hand-crafted non-learned association strategies such as probabilistic clustering or voting-based center prediction. Instead, Mask4D introduces spatio-temporal instance queries which encode the semantic and geometric properties of each semantic tracklet in the sequence. In an in-depth study, we find that it is critical to promote spatially compact instance predictions as spatio-temporal instance queries tend to merge multiple semantically similar instances, even if they are spatially distant. To this end, we regress 6-DOF bounding box parameters from spatio-temporal instance queries, which is used as an auxiliary task to foster spatially compact predictions. Mask4D achieves a new state-of-the-art on the SemanticKITTI test set with a score of 68.4 LSTQ, improving upon published top-performing methods by at least +4.5%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge