Alireza Salemi
Improving User Privacy in Personalized Generation: Client-Side Retrieval-Augmented Modification of Server-Side Generated Speculations
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Personalization is crucial for aligning Large Language Model (LLM) outputs with individual user preferences and background knowledge. State-of-the-art solutions are based on retrieval augmentation, where relevant context from a user profile is retrieved for LLM consumption. These methods deal with a trade-off between exposing retrieved private data to cloud providers and relying on less capable local models. We introduce $P^3$, an interactive framework for high-quality personalization without revealing private profiles to server-side LLMs. In $P^3$, a large server-side model generates a sequence of $k$ draft tokens based solely on the user query, while a small client-side model, with retrieval access to the user's private profile, evaluates and modifies these drafts to better reflect user preferences. This process repeats until an end token is generated. Experiments on LaMP-QA, a recent benchmark consisting of three personalized question answering datasets, show that $P^3$ consistently outperforms both non-personalized server-side and personalized client-side baselines, achieving statistically significant improvements of $7.4%$ to $9%$ on average. Importantly, $P^3$ recovers $90.3%$ to $95.7%$ of the utility of a ``leaky'' upper-bound scenario in which the full profile is exposed to the large server-side model. Privacy analyses, including linkability and attribute inference attacks, indicate that $P^3$ preserves the privacy of a non-personalized server-side model, introducing only marginal additional leakage ($1.5%$--$3.5%$) compared to submitting a query without any personal context. Additionally, the framework is efficient for edge deployment, with the client-side model generating only $9.2%$ of the total tokens. These results demonstrate that $P^3$ provides a practical, effective solution for personalized generation with improved privacy.
Beyond a Million Tokens: Benchmarking and Enhancing Long-Term Memory in LLMs
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Evaluating the abilities of large language models (LLMs) for tasks that require long-term memory and thus long-context reasoning, for example in conversational settings, is hampered by the existing benchmarks, which often lack narrative coherence, cover narrow domains, and only test simple recall-oriented tasks. This paper introduces a comprehensive solution to these challenges. First, we present a novel framework for automatically generating long (up to 10M tokens), coherent, and topically diverse conversations, accompanied by probing questions targeting a wide range of memory abilities. From this, we construct BEAM, a new benchmark comprising 100 conversations and 2,000 validated questions. Second, to enhance model performance, we propose LIGHT-a framework inspired by human cognition that equips LLMs with three complementary memory systems: a long-term episodic memory, a short-term working memory, and a scratchpad for accumulating salient facts. Our experiments on BEAM reveal that even LLMs with 1M token context windows (with and without retrieval-augmentation) struggle as dialogues lengthen. In contrast, LIGHT consistently improves performance across various models, achieving an average improvement of 3.5%-12.69% over the strongest baselines, depending on the backbone LLM. An ablation study further confirms the contribution of each memory component.
CIIR@LiveRAG 2025: Optimizing Multi-Agent Retrieval Augmented Generation through Self-Training
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:This paper presents mRAG, a multi-agent retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) framework composed of specialized agents for subtasks such as planning, searching, reasoning, and coordination. Our system uses a self-training paradigm with reward-guided trajectory sampling to optimize inter-agent collaboration and enhance response generation. Evaluated on DataMorgana-derived datasets during the SIGIR 2025 LiveRAG competition, mRAG outperforms conventional RAG baselines. We further analyze competition outcomes and showcase the framework's strengths with case studies, demonstrating its efficacy for complex, real-world RAG tasks.
Plan-and-Refine: Diverse and Comprehensive Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:This paper studies the limitations of (retrieval-augmented) large language models (LLMs) in generating diverse and comprehensive responses, and introduces the Plan-and-Refine (P&R) framework based on a two phase system design. In the global exploration phase, P&R generates a diverse set of plans for the given input, where each plan consists of a list of diverse query aspects with corresponding additional descriptions. This phase is followed by a local exploitation phase that generates a response proposal for the input query conditioned on each plan and iteratively refines the proposal for improving the proposal quality. Finally, a reward model is employed to select the proposal with the highest factuality and coverage. We conduct our experiments based on the ICAT evaluation methodology--a recent approach for answer factuality and comprehensiveness evaluation. Experiments on the two diverse information seeking benchmarks adopted from non-factoid question answering and TREC search result diversification tasks demonstrate that P&R significantly outperforms baselines, achieving up to a 13.1% improvement on the ANTIQUE dataset and a 15.41% improvement on the TREC dataset. Furthermore, a smaller scale user study confirms the substantial efficacy of the P&R framework.
Personalized Generation In Large Model Era: A Survey
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:In the era of large models, content generation is gradually shifting to Personalized Generation (PGen), tailoring content to individual preferences and needs. This paper presents the first comprehensive survey on PGen, investigating existing research in this rapidly growing field. We conceptualize PGen from a unified perspective, systematically formalizing its key components, core objectives, and abstract workflows. Based on this unified perspective, we propose a multi-level taxonomy, offering an in-depth review of technical advancements, commonly used datasets, and evaluation metrics across multiple modalities, personalized contexts, and tasks. Moreover, we envision the potential applications of PGen and highlight open challenges and promising directions for future exploration. By bridging PGen research across multiple modalities, this survey serves as a valuable resource for fostering knowledge sharing and interdisciplinary collaboration, ultimately contributing to a more personalized digital landscape.
ExPerT: Effective and Explainable Evaluation of Personalized Long-Form Text Generation
Jan 24, 2025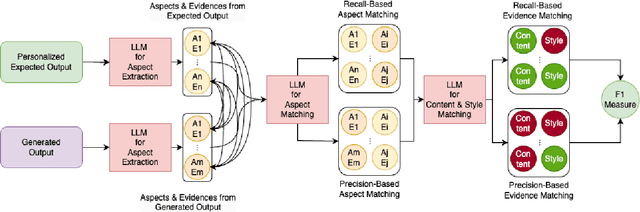
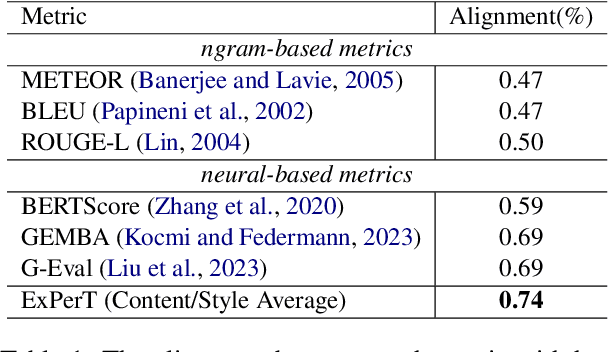
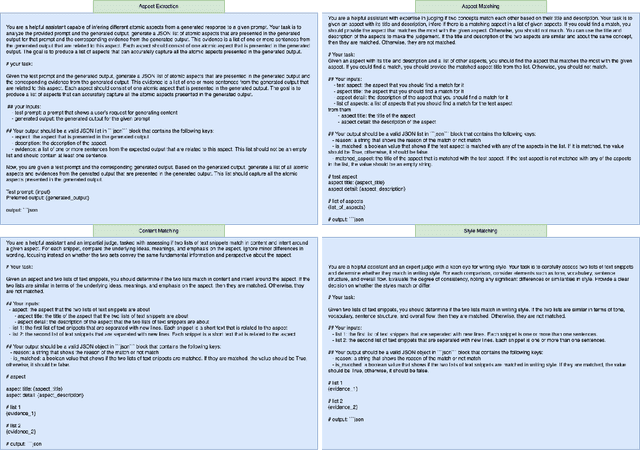
Abstract:Evaluating personalized text generated by large language models (LLMs) is challenging, as only the LLM user, i.e., prompt author, can reliably assess the output, but re-engaging the same individuals across studies is infeasible. This paper addresses the challenge of evaluating personalized text generation by introducing ExPerT, an explainable reference-based evaluation framework. ExPerT leverages an LLM to extract atomic aspects and their evidence from the generated and reference texts, match the aspects, and evaluate their alignment based on content and writing style -- two key attributes in personalized text generation. Additionally, ExPerT generates detailed, fine-grained explanations for every step of the evaluation process, enhancing transparency and interpretability. Our experiments demonstrate that ExPerT achieves a 7.2% relative improvement in alignment with human judgments compared to the state-of-the-art text generation evaluation methods. Furthermore, human evaluators rated the usability of ExPerT's explanations at 4.7 out of 5, highlighting its effectiveness in making evaluation decisions more interpretable.
Beyond Factual Accuracy: Evaluating Coverage of Diverse Factual Information in Long-form Text Generation
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents ICAT, an evaluation framework for measuring coverage of diverse factual information in long-form text generation. ICAT breaks down a long output text into a list of atomic claims and not only verifies each claim through retrieval from a (reliable) knowledge source, but also computes the alignment between the atomic factual claims and various aspects expected to be presented in the output. We study three implementations of the ICAT framework, each with a different assumption on the availability of aspects and alignment method. By adopting data from the diversification task in the TREC Web Track and the ClueWeb corpus, we evaluate the ICAT framework. We demonstrate strong correlation with human judgments and provide comprehensive evaluation across multiple state-of-the-art LLMs. Our framework further offers interpretable and fine-grained analysis of diversity and coverage. Its modular design allows for easy adaptation to different domains and datasets, making it a valuable tool for evaluating the qualitative aspects of long-form responses produced by LLMs.
Reasoning-Enhanced Self-Training for Long-Form Personalized Text Generation
Jan 07, 2025Abstract:Personalized text generation requires a unique ability of large language models (LLMs) to learn from context that they often do not encounter during their standard training. One way to encourage LLMs to better use personalized context for generating outputs that better align with the user's expectations is to instruct them to reason over the user's past preferences, background knowledge, or writing style. To achieve this, we propose Reasoning-Enhanced Self-Training for Personalized Text Generation (REST-PG), a framework that trains LLMs to reason over personal data during response generation. REST-PG first generates reasoning paths to train the LLM's reasoning abilities and then employs Expectation-Maximization Reinforced Self-Training to iteratively train the LLM based on its own high-reward outputs. We evaluate REST-PG on the LongLaMP benchmark, consisting of four diverse personalized long-form text generation tasks. Our experiments demonstrate that REST-PG achieves significant improvements over state-of-the-art baselines, with an average relative performance gain of 14.5% on the benchmark.
Accelerating Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Dec 14, 2024Abstract:An evolving solution to address hallucination and enhance accuracy in large language models (LLMs) is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which involves augmenting LLMs with information retrieved from an external knowledge source, such as the web. This paper profiles several RAG execution pipelines and demystifies the complex interplay between their retrieval and generation phases. We demonstrate that while exact retrieval schemes are expensive, they can reduce inference time compared to approximate retrieval variants because an exact retrieval model can send a smaller but more accurate list of documents to the generative model while maintaining the same end-to-end accuracy. This observation motivates the acceleration of the exact nearest neighbor search for RAG. In this work, we design Intelligent Knowledge Store (IKS), a type-2 CXL device that implements a scale-out near-memory acceleration architecture with a novel cache-coherent interface between the host CPU and near-memory accelerators. IKS offers 13.4-27.9x faster exact nearest neighbor search over a 512GB vector database compared with executing the search on Intel Sapphire Rapids CPUs. This higher search performance translates to 1.7-26.3x lower end-to-end inference time for representative RAG applications. IKS is inherently a memory expander; its internal DRAM can be disaggregated and used for other applications running on the server to prevent DRAM, which is the most expensive component in today's servers, from being stranded.
Learning to Rank for Multiple Retrieval-Augmented Models through Iterative Utility Maximization
Oct 13, 2024Abstract:This paper investigates the design of a unified search engine to serve multiple retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) agents, each with a distinct task, backbone large language model (LLM), and retrieval-augmentation strategy. We introduce an iterative approach where the search engine generates retrieval results for these RAG agents and gathers feedback on the quality of the retrieved documents during an offline phase. This feedback is then used to iteratively optimize the search engine using a novel expectation-maximization algorithm, with the goal of maximizing each agent's utility function. Additionally, we adapt this approach to an online setting, allowing the search engine to refine its behavior based on real-time individual agents feedback to better serve the results for each of them. Experiments on diverse datasets from the Knowledge-Intensive Language Tasks (KILT) benchmark demonstrates that our approach significantly on average outperforms competitive baselines across 18 RAG models. We also demonstrate that our method effectively ``personalizes'' the retrieval process for each RAG agent based on the collected feedback. Finally, we provide a comprehensive ablation study to explore various aspects of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge