To Eun Kim
Towards Reducible Uncertainty Modeling for Reliable Large Language Model Agents
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Uncertainty quantification (UQ) for large language models (LLMs) is a key building block for safety guardrails of daily LLM applications. Yet, even as LLM agents are increasingly deployed in highly complex tasks, most UQ research still centers on single-turn question-answering. We argue that UQ research must shift to realistic settings with interactive agents, and that a new principled framework for agent UQ is needed. This paper presents the first general formulation of agent UQ that subsumes broad classes of existing UQ setups. Under this formulation, we show that prior works implicitly treat LLM UQ as an uncertainty accumulation process, a viewpoint that breaks down for interactive agents in an open world. In contrast, we propose a novel perspective, a conditional uncertainty reduction process, that explicitly models reducible uncertainty over an agent's trajectory by highlighting "interactivity" of actions. From this perspective, we outline a conceptual framework to provide actionable guidance for designing UQ in LLM agent setups. Finally, we conclude with practical implications of the agent UQ in frontier LLM development and domain-specific applications, as well as open remaining problems.
Overview of the TREC 2025 Tip-of-the-Tongue track
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Tip-of-the-tongue (ToT) known-item retrieval involves re-finding an item for which the searcher does not reliably recall an identifier. ToT information requests (or queries) are verbose and tend to include several complex phenomena, making them especially difficult for existing information retrieval systems. The TREC 2025 ToT track focused on a single ad-hoc retrieval task. This year, we extended the track to general domain and incorporated different sets of test queries from diverse sources, namely from the MS-ToT dataset, manual topic development, and LLM-based synthetic query generation. This year, 9 groups (including the track coordinators) submitted 32 runs.
LTRR: Learning To Rank Retrievers for LLMs
Jun 16, 2025



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems typically rely on a single fixed retriever, despite growing evidence that no single retriever performs optimally across all query types. In this paper, we explore a query routing approach that dynamically selects from a pool of retrievers based on the query, using both train-free heuristics and learned routing models. We frame routing as a learning-to-rank (LTR) problem and introduce LTRR, a framework that learns to rank retrievers by their expected utility gain to downstream LLM performance. Our experiments, conducted on synthetic QA data with controlled query type variations, show that routing-based RAG systems can outperform the best single-retriever-based systems. Performance gains are especially pronounced in models trained with the Answer Correctness (AC) metric and with pairwise learning approaches, especially with XGBoost. We also observe improvements in generalization to out-of-distribution queries. As part of the SIGIR 2025 LiveRAG challenge, our submitted system demonstrated the practical viability of our approach, achieving competitive performance in both answer correctness and faithfulness. These findings highlight the importance of both training methodology and metric selection in query routing for RAG systems.
Tip of the Tongue Query Elicitation for Simulated Evaluation
Feb 25, 2025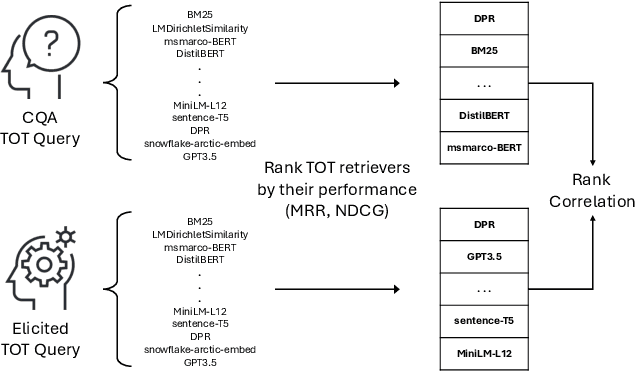
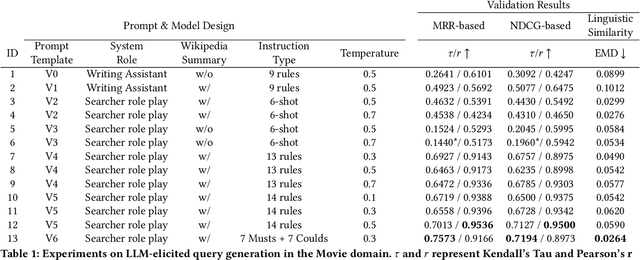
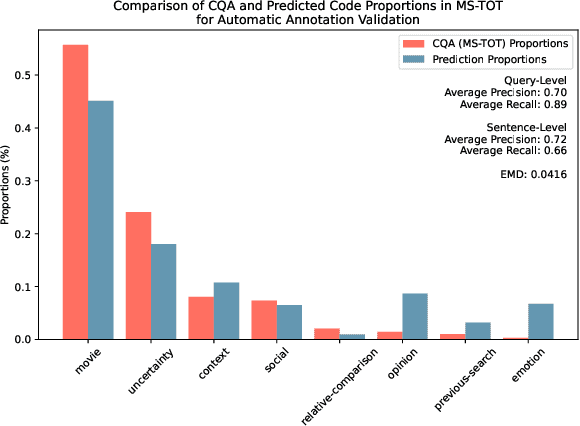

Abstract:Tip-of-the-tongue (TOT) search occurs when a user struggles to recall a specific identifier, such as a document title. While common, existing search systems often fail to effectively support TOT scenarios. Research on TOT retrieval is further constrained by the challenge of collecting queries, as current approaches rely heavily on community question-answering (CQA) websites, leading to labor-intensive evaluation and domain bias. To overcome these limitations, we introduce two methods for eliciting TOT queries - leveraging large language models (LLMs) and human participants - to facilitate simulated evaluations of TOT retrieval systems. Our LLM-based TOT user simulator generates synthetic TOT queries at scale, achieving high correlations with how CQA-based TOT queries rank TOT retrieval systems when tested in the Movie domain. Additionally, these synthetic queries exhibit high linguistic similarity to CQA-derived queries. For human-elicited queries, we developed an interface that uses visual stimuli to place participants in a TOT state, enabling the collection of natural queries. In the Movie domain, system rank correlation and linguistic similarity analyses confirm that human-elicited queries are both effective and closely resemble CQA-based queries. These approaches reduce reliance on CQA-based data collection while expanding coverage to underrepresented domains, such as Landmark and Person. LLM-elicited queries for the Movie, Landmark, and Person domains have been released as test queries in the TREC 2024 TOT track, with human-elicited queries scheduled for inclusion in the TREC 2025 TOT track. Additionally, we provide source code for synthetic query generation and the human query collection interface, along with curated visual stimuli used for eliciting TOT queries.
Towards Fair RAG: On the Impact of Fair Ranking in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Sep 17, 2024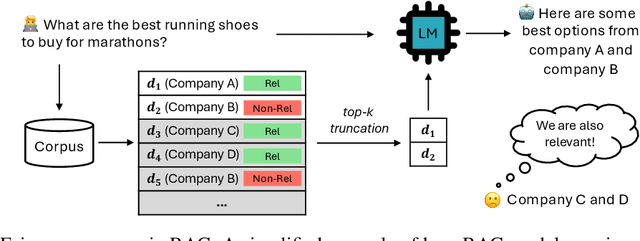
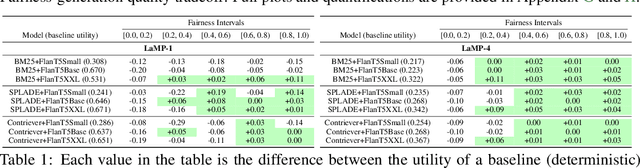

Abstract:Many language models now enhance their responses with retrieval capabilities, leading to the widespread adoption of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems. However, despite retrieval being a core component of RAG, much of the research in this area overlooks the extensive body of work on fair ranking, neglecting the importance of considering all stakeholders involved. This paper presents the first systematic evaluation of RAG systems integrated with fair rankings. We focus specifically on measuring the fair exposure of each relevant item across the rankings utilized by RAG systems (i.e., item-side fairness), aiming to promote equitable growth for relevant item providers. To gain a deep understanding of the relationship between item-fairness, ranking quality, and generation quality in the context of RAG, we analyze nine different RAG systems that incorporate fair rankings across seven distinct datasets. Our findings indicate that RAG systems with fair rankings can maintain a high level of generation quality and, in many cases, even outperform traditional RAG systems, despite the general trend of a tradeoff between ensuring fairness and maintaining system-effectiveness. We believe our insights lay the groundwork for responsible and equitable RAG systems and open new avenues for future research. We publicly release our codebase and dataset at https://github.com/kimdanny/Fair-RAG.
Retrieval-Enhanced Machine Learning: Synthesis and Opportunities
Jul 17, 2024


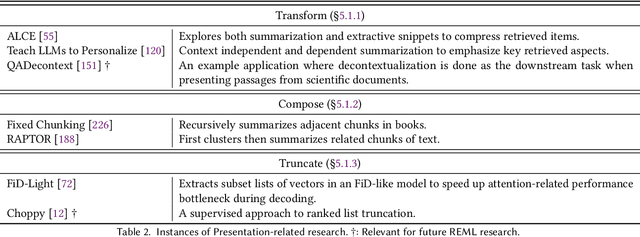
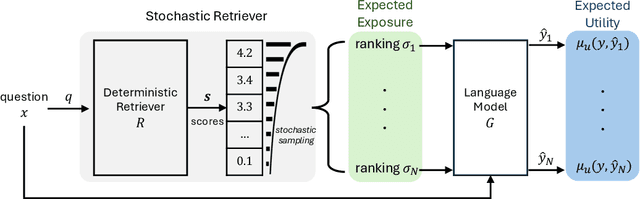
Abstract:In the field of language modeling, models augmented with retrieval components have emerged as a promising solution to address several challenges faced in the natural language processing (NLP) field, including knowledge grounding, interpretability, and scalability. Despite the primary focus on NLP, we posit that the paradigm of retrieval-enhancement can be extended to a broader spectrum of machine learning (ML) such as computer vision, time series prediction, and computational biology. Therefore, this work introduces a formal framework of this paradigm, Retrieval-Enhanced Machine Learning (REML), by synthesizing the literature in various domains in ML with consistent notations which is missing from the current literature. Also, we found that while a number of studies employ retrieval components to augment their models, there is a lack of integration with foundational Information Retrieval (IR) research. We bridge this gap between the seminal IR research and contemporary REML studies by investigating each component that comprises the REML framework. Ultimately, the goal of this work is to equip researchers across various disciplines with a comprehensive, formally structured framework of retrieval-enhanced models, thereby fostering interdisciplinary future research.
When and What to Ask Through World States and Text Instructions: IGLU NLP Challenge Solution
May 09, 2023Abstract:In collaborative tasks, effective communication is crucial for achieving joint goals. One such task is collaborative building where builders must communicate with each other to construct desired structures in a simulated environment such as Minecraft. We aim to develop an intelligent builder agent to build structures based on user input through dialogue. However, in collaborative building, builders may encounter situations that are difficult to interpret based on the available information and instructions, leading to ambiguity. In the NeurIPS 2022 Competition NLP Task, we address two key research questions, with the goal of filling this gap: when should the agent ask for clarification, and what clarification questions should it ask? We move towards this target with two sub-tasks, a classification task and a ranking task. For the classification task, the goal is to determine whether the agent should ask for clarification based on the current world state and dialogue history. For the ranking task, the goal is to rank the relevant clarification questions from a pool of candidates. In this report, we briefly introduce our methods for the classification and ranking task. For the classification task, our model achieves an F1 score of 0.757, which placed the 3rd on the leaderboard. For the ranking task, our model achieves about 0.38 for Mean Reciprocal Rank by extending the traditional ranking model. Lastly, we discuss various neural approaches for the ranking task and future direction.
Attention-based Ingredient Phrase Parser
Oct 05, 2022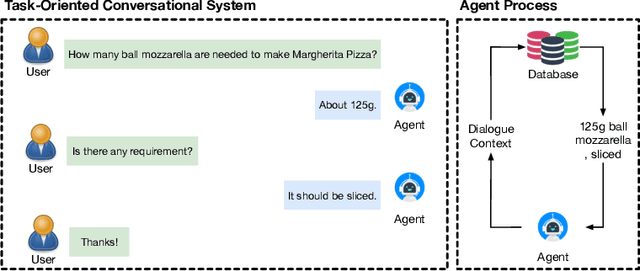
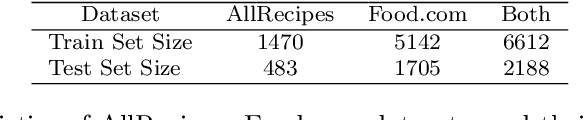
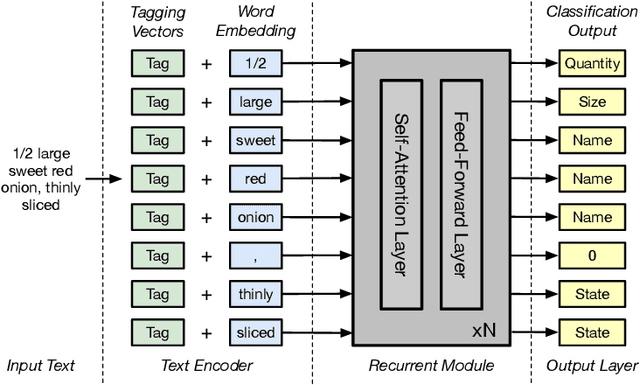
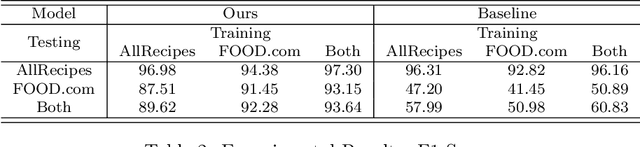
Abstract:As virtual personal assistants have now penetrated the consumer market, with products such as Siri and Alexa, the research community has produced several works on task-oriented dialogue tasks such as hotel booking, restaurant booking, and movie recommendation. Assisting users to cook is one of these tasks that are expected to be solved by intelligent assistants, where ingredients and their corresponding attributes, such as name, unit, and quantity, should be provided to users precisely and promptly. However, existing ingredient information scraped from the cooking website is in the unstructured form with huge variation in the lexical structure, for example, '1 garlic clove, crushed', and '1 (8 ounce) package cream cheese, softened', making it difficult to extract information exactly. To provide an engaged and successful conversational service to users for cooking tasks, we propose a new ingredient parsing model that can parse an ingredient phrase of recipes into the structure form with its corresponding attributes with over 0.93 F1-score. Experimental results show that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on AllRecipes and Food.com datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge