Alan Hanjalic
Delft University of Technology
Towards Carbon Footprint-Aware Recommender Systems for Greener Item Recommendation
Mar 21, 2025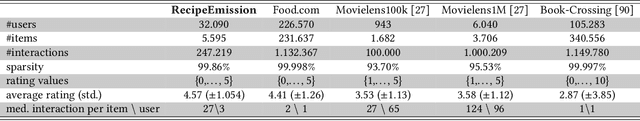
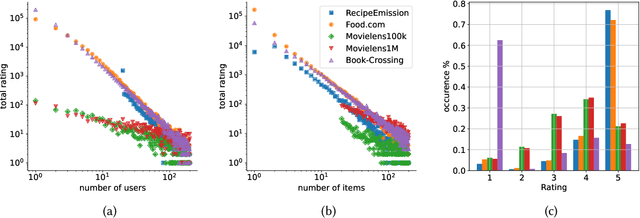
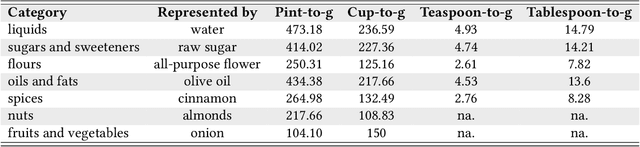
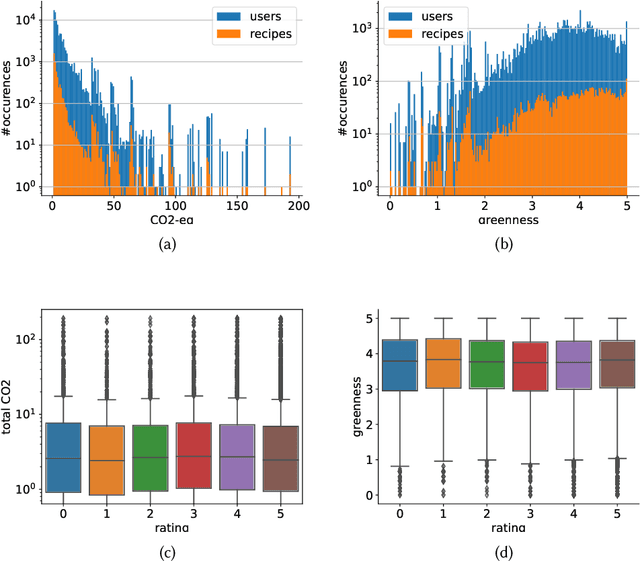
Abstract:The commodity and widespread use of online shopping are having an unprecedented impact on climate, with emission figures from key actors that are easily comparable to those of a large-scale metropolis. Despite online shopping being fueled by recommender systems (RecSys) algorithms, the role and potential of the latter in promoting more sustainable choices is little studied. One of the main reasons for this could be attributed to the lack of a dataset containing carbon footprint emissions for the items. While building such a dataset is a rather challenging task, its presence is pivotal for opening the doors to novel perspectives, evaluations, and methods for RecSys research. In this paper, we target this bottleneck and study the environmental role of RecSys algorithms. First, we mine a dataset that includes carbon footprint emissions for its items. Then, we benchmark conventional RecSys algorithms in terms of accuracy and sustainability as two faces of the same coin. We find that RecSys algorithms optimized for accuracy overlook greenness and that longer recommendation lists are greener but less accurate. Then, we show that a simple reranking approach that accounts for the item's carbon footprint can establish a better trade-off between accuracy and greenness. This reranking approach is modular, ready to use, and can be applied to any RecSys algorithm without the need to alter the underlying mechanisms or retrain models. Our results show that a small sacrifice of accuracy can lead to significant improvements of recommendation greenness across all algorithms and list lengths. Arguably, this accuracy-greenness trade-off could even be seen as an enhancement of user satisfaction, particularly for purpose-driven users who prioritize the environmental impact of their choices. We anticipate this work will serve as the starting point for studying RecSys for more sustainable recommendations.
A data-centric approach for assessing progress of Graph Neural Networks
Jun 18, 2024


Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have achieved state-of-the-art results in node classification tasks. However, most improvements are in multi-class classification, with less focus on the cases where each node could have multiple labels. The first challenge in studying multi-label node classification is the scarcity of publicly available datasets. To address this, we collected and released three real-world biological datasets and developed a multi-label graph generator with tunable properties. We also argue that traditional notions of homophily and heterophily do not apply well to multi-label scenarios. Therefore, we define homophily and Cross-Class Neighborhood Similarity for multi-label classification and investigate $9$ collected multi-label datasets. Lastly, we conducted a large-scale comparative study with $8$ methods across nine datasets to evaluate current progress in multi-label node classification. We release our code at \url{https://github.com/Tianqi-py/MLGNC}.
Mitigating Mainstream Bias in Recommendation via Cost-sensitive Learning
Jul 25, 2023



Abstract:Mainstream bias, where some users receive poor recommendations because their preferences are uncommon or simply because they are less active, is an important aspect to consider regarding fairness in recommender systems. Existing methods to mitigate mainstream bias do not explicitly model the importance of these non-mainstream users or, when they do, it is in a way that is not necessarily compatible with the data and recommendation model at hand. In contrast, we use the recommendation utility as a more generic and implicit proxy to quantify mainstreamness, and propose a simple user-weighting approach to incorporate it into the training process while taking the cost of potential recommendation errors into account. We provide extensive experimental results showing that quantifying mainstreamness via utility is better able at identifying non-mainstream users, and that they are indeed better served when training the model in a cost-sensitive way. This is achieved with negligible or no loss in overall recommendation accuracy, meaning that the models learn a better balance across users. In addition, we show that research of this kind, which evaluates recommendation quality at the individual user level, may not be reliable if not using enough interactions when assessing model performance.
Multi-label Node Classification On Graph-Structured Data
Apr 20, 2023Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have shown state-of-the-art improvements in node classification tasks on graphs. While these improvements have been largely demonstrated in a multi-class classification scenario, a more general and realistic scenario in which each node could have multiple labels has so far received little attention. The first challenge in conducting focused studies on multi-label node classification is the limited number of publicly available multi-label graph datasets. Therefore, as our first contribution, we collect and release three real-world biological datasets and develop a multi-label graph generator to generate datasets with tunable properties. While high label similarity (high homophily) is usually attributed to the success of GNNs, we argue that a multi-label scenario does not follow the usual semantics of homophily and heterophily so far defined for a multi-class scenario. As our second contribution, besides defining homophily for the multi-label scenario, we develop a new approach that dynamically fuses the feature and label correlation information to learn label-informed representations. Finally, we perform a large-scale comparative study with $10$ methods and $9$ datasets which also showcase the effectiveness of our approach. We release our benchmark at \url{https://anonymous.4open.science/r/LFLF-5D8C/}.
New Insights into Metric Optimization for Ranking-based Recommendation
Jun 04, 2021



Abstract:Direct optimization of IR metrics has often been adopted as an approach to devise and develop ranking-based recommender systems. Most methods following this approach aim at optimizing the same metric being used for evaluation, under the assumption that this will lead to the best performance. A number of studies of this practice bring this assumption, however, into question. In this paper, we dig deeper into this issue in order to learn more about the effects of the choice of the metric to optimize on the performance of a ranking-based recommender system. We present an extensive experimental study conducted on different datasets in both pairwise and listwise learning-to-rank scenarios, to compare the relative merit of four popular IR metrics, namely RR, AP, nDCG and RBP, when used for optimization and assessment of recommender systems in various combinations. For the first three, we follow the practice of loss function formulation available in literature. For the fourth one, we propose novel loss functions inspired by RBP for both the pairwise and listwise scenario. Our results confirm that the best performance is indeed not necessarily achieved when optimizing the same metric being used for evaluation. In fact, we find that RBP-inspired losses perform at least as well as other metrics in a consistent way, and offer clear benefits in several cases. Interesting to see is that RBP-inspired losses, while improving the recommendation performance for all uses, may lead to an individual performance gain that is correlated with the activity level of a user in interacting with items. The more active the users, the more they benefit. Overall, our results challenge the assumption behind the current research practice of optimizing and evaluating the same metric, and point to RBP-based optimization instead as a promising alternative when learning to rank in the recommendation context.
Leave No User Behind: Towards Improving the Utility of Recommender Systems for Non-mainstream Users
Feb 02, 2021



Abstract:In a collaborative-filtering recommendation scenario, biases in the data will likely propagate in the learned recommendations. In this paper we focus on the so-called mainstream bias: the tendency of a recommender system to provide better recommendations to users who have a mainstream taste, as opposed to non-mainstream users. We propose NAECF, a conceptually simple but effective idea to address this bias. The idea consists of adding an autoencoder (AE) layer when learning user and item representations with text-based Convolutional Neural Networks. The AEs, one for the users and one for the items, serve as adversaries to the process of minimizing the rating prediction error when learning how to recommend. They enforce that the specific unique properties of all users and items are sufficiently well incorporated and preserved in the learned representations. These representations, extracted as the bottlenecks of the corresponding AEs, are expected to be less biased towards mainstream users, and to provide more balanced recommendation utility across all users. Our experimental results confirm these expectations, significantly improving the recommendations for non-mainstream users while maintaining the recommendation quality for mainstream users. Our results emphasize the importance of deploying extensive content-based features, such as online reviews, in order to better represent users and items to maximize the de-biasing effect.
S2IGAN: Speech-to-Image Generation via Adversarial Learning
May 14, 2020



Abstract:An estimated half of the world's languages do not have a written form, making it impossible for these languages to benefit from any existing text-based technologies. In this paper, a speech-to-image generation (S2IG) framework is proposed which translates speech descriptions to photo-realistic images without using any text information, thus allowing unwritten languages to potentially benefit from this technology. The proposed S2IG framework, named S2IGAN, consists of a speech embedding network (SEN) and a relation-supervised densely-stacked generative model (RDG). SEN learns the speech embedding with the supervision of the corresponding visual information. Conditioned on the speech embedding produced by SEN, the proposed RDG synthesizes images that are semantically consistent with the corresponding speech descriptions. Extensive experiments on two public benchmark datasets CUB and Oxford-102 demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed S2IGAN on synthesizing high-quality and semantically-consistent images from the speech signal, yielding a good performance and a solid baseline for the S2IG task.
Matching Images and Text with Multi-modal Tensor Fusion and Re-ranking
Aug 12, 2019



Abstract:A major challenge in matching images and text is that they have intrinsically different data distributions and feature representations. Most existing approaches are based either on embedding or classification, the first one mapping image and text instances into a common embedding space for distance measuring, and the second one regarding image-text matching as a binary classification problem. Neither of these approaches can, however, balance the matching accuracy and model complexity well. We propose a novel framework that achieves remarkable matching performance with acceptable model complexity. Specifically, in the training stage, we propose a novel Multi-modal Tensor Fusion Network (MTFN) to explicitly learn an accurate image-text similarity function with rank-based tensor fusion rather than seeking a common embedding space for each image-text instance. Then, during testing, we deploy a generic Cross-modal Re-ranking (RR) scheme for refinement without requiring additional training procedure. Extensive experiments on two datasets demonstrate that our MTFN-RR consistently achieves the state-of-the-art matching performance with much less time complexity. The implementation code is available at https://github.com/Wangt-CN/MTFN-RR-PyTorch-Code.
Statistical Significance Testing in Information Retrieval: An Empirical Analysis of Type I, Type II and Type III Errors
Jun 05, 2019



Abstract:Statistical significance testing is widely accepted as a means to assess how well a difference in effectiveness reflects an actual difference between systems, as opposed to random noise because of the selection of topics. According to recent surveys on SIGIR, CIKM, ECIR and TOIS papers, the t-test is the most popular choice among IR researchers. However, previous work has suggested computer intensive tests like the bootstrap or the permutation test, based mainly on theoretical arguments. On empirical grounds, others have suggested non-parametric alternatives such as the Wilcoxon test. Indeed, the question of which tests we should use has accompanied IR and related fields for decades now. Previous theoretical studies on this matter were limited in that we know that test assumptions are not met in IR experiments, and empirical studies were limited in that we do not have the necessary control over the null hypotheses to compute actual Type I and Type II error rates under realistic conditions. Therefore, not only is it unclear which test to use, but also how much trust we should put in them. In contrast to past studies, in this paper we employ a recent simulation methodology from TREC data to go around these limitations. Our study comprises over 500 million p-values computed for a range of tests, systems, effectiveness measures, topic set sizes and effect sizes, and for both the 2-tail and 1-tail cases. Having such a large supply of IR evaluation data with full knowledge of the null hypotheses, we are finally in a position to evaluate how well statistical significance tests really behave with IR data, and make sound recommendations for practitioners.
Are Nearby Neighbors Relatives?: Diagnosing Deep Music Embedding Spaces
Apr 15, 2019



Abstract:Deep neural networks have frequently been used to directly learn representations useful for a given task from raw input data. In terms of overall performance metrics, machine learning solutions employing deep representations frequently have been reported to greatly outperform those using hand-crafted feature representations. At the same time, they may pick up on aspects that are predominant in the data, yet not actually meaningful or interpretable. In this paper, we therefore propose a systematic way to diagnose the trustworthiness of deep music representations, considering musical semantics. The underlying assumption is that in case a deep representation is to be trusted, distance consistency between known related points should be maintained both in the input audio space and corresponding latent deep space. We generate known related points through semantically meaningful transformations, both considering imperceptible and graver transformations. Then, we examine within- and between-space distance consistencies, both considering audio space and latent embedded space, the latter either being a result of a conventional feature extractor or a deep encoder. We illustrate how our method, as a complement to task-specific performance, provides interpretable insight into what a network may have captured from training data signals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge