Akram Erraqabi
Controlled Sparsity via Constrained Optimization or: How I Learned to Stop Tuning Penalties and Love Constraints
Aug 08, 2022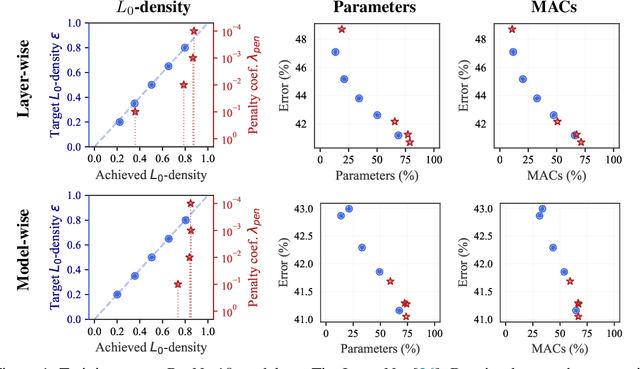

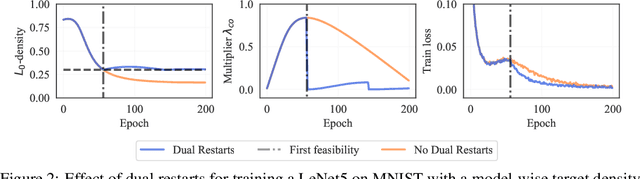

Abstract:The performance of trained neural networks is robust to harsh levels of pruning. Coupled with the ever-growing size of deep learning models, this observation has motivated extensive research on learning sparse models. In this work, we focus on the task of controlling the level of sparsity when performing sparse learning. Existing methods based on sparsity-inducing penalties involve expensive trial-and-error tuning of the penalty factor, thus lacking direct control of the resulting model sparsity. In response, we adopt a constrained formulation: using the gate mechanism proposed by Louizos et al. (2018), we formulate a constrained optimization problem where sparsification is guided by the training objective and the desired sparsity target in an end-to-end fashion. Experiments on CIFAR-10/100, TinyImageNet, and ImageNet using WideResNet and ResNet{18, 50} models validate the effectiveness of our proposal and demonstrate that we can reliably achieve pre-determined sparsity targets without compromising on predictive performance.
Temporal Abstractions-Augmented Temporally Contrastive Learning: An Alternative to the Laplacian in RL
Mar 21, 2022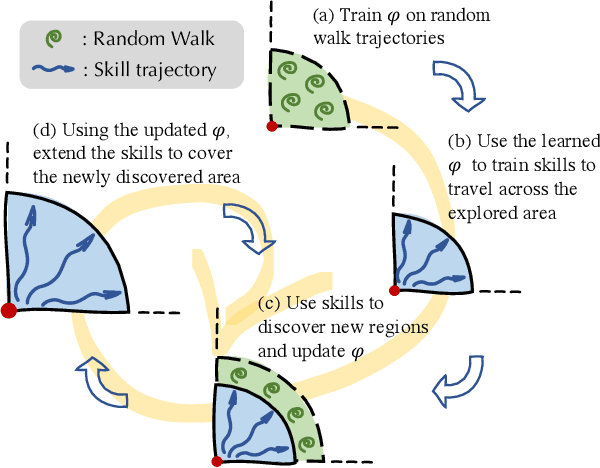
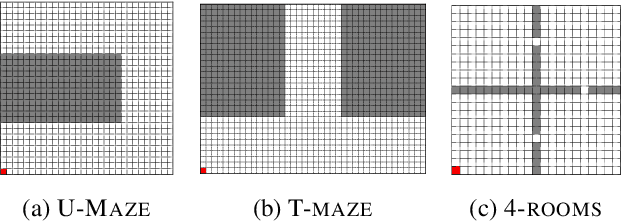
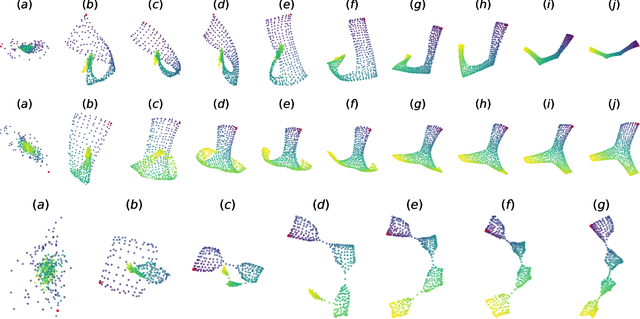
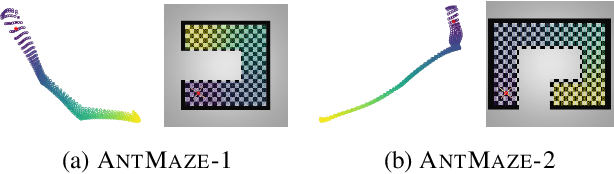
Abstract:In reinforcement learning, the graph Laplacian has proved to be a valuable tool in the task-agnostic setting, with applications ranging from skill discovery to reward shaping. Recently, learning the Laplacian representation has been framed as the optimization of a temporally-contrastive objective to overcome its computational limitations in large (or continuous) state spaces. However, this approach requires uniform access to all states in the state space, overlooking the exploration problem that emerges during the representation learning process. In this work, we propose an alternative method that is able to recover, in a non-uniform-prior setting, the expressiveness and the desired properties of the Laplacian representation. We do so by combining the representation learning with a skill-based covering policy, which provides a better training distribution to extend and refine the representation. We also show that a simple augmentation of the representation objective with the learned temporal abstractions improves dynamics-awareness and helps exploration. We find that our method succeeds as an alternative to the Laplacian in the non-uniform setting and scales to challenging continuous control environments. Finally, even if our method is not optimized for skill discovery, the learned skills can successfully solve difficult continuous navigation tasks with sparse rewards, where standard skill discovery approaches are no so effective.
A3T: Adversarially Augmented Adversarial Training
Jan 12, 2018


Abstract:Recent research showed that deep neural networks are highly sensitive to so-called adversarial perturbations, which are tiny perturbations of the input data purposely designed to fool a machine learning classifier. Most classification models, including deep learning models, are highly vulnerable to adversarial attacks. In this work, we investigate a procedure to improve adversarial robustness of deep neural networks through enforcing representation invariance. The idea is to train the classifier jointly with a discriminator attached to one of its hidden layer and trained to filter the adversarial noise. We perform preliminary experiments to test the viability of the approach and to compare it to other standard adversarial training methods.
Image Segmentation by Iterative Inference from Conditional Score Estimation
Aug 18, 2017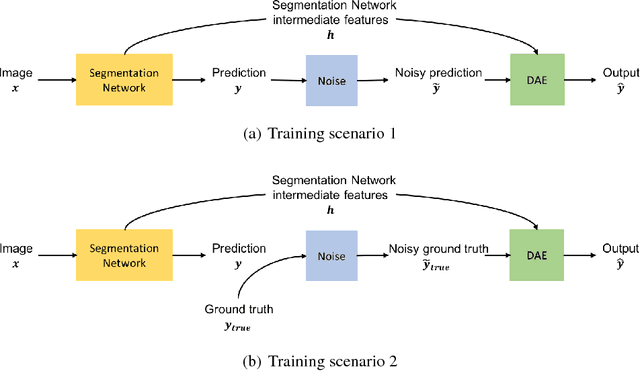
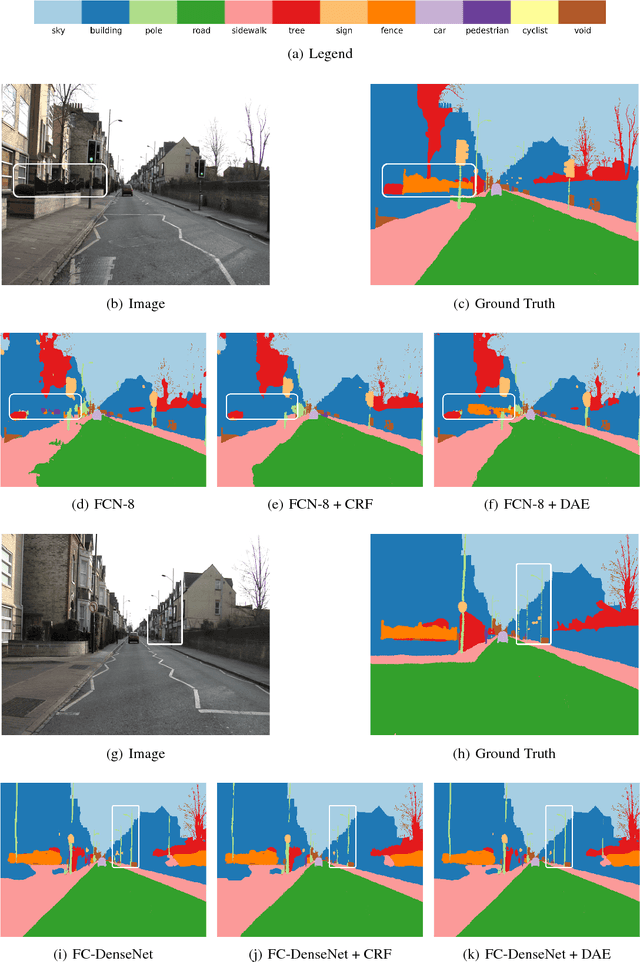
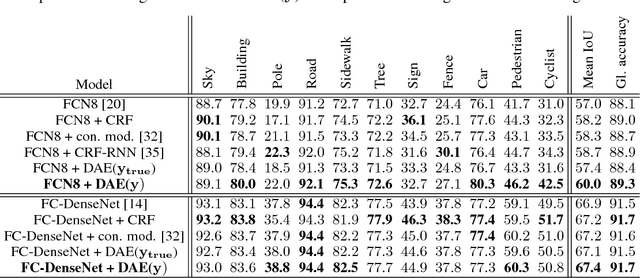
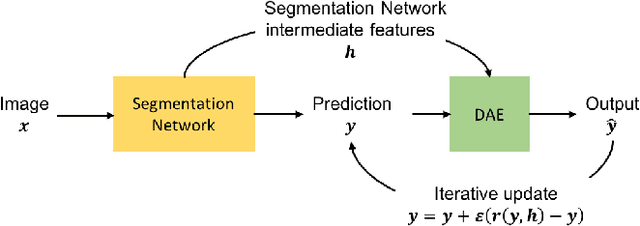

Abstract:Inspired by the combination of feedforward and iterative computations in the virtual cortex, and taking advantage of the ability of denoising autoencoders to estimate the score of a joint distribution, we propose a novel approach to iterative inference for capturing and exploiting the complex joint distribution of output variables conditioned on some input variables. This approach is applied to image pixel-wise segmentation, with the estimated conditional score used to perform gradient ascent towards a mode of the estimated conditional distribution. This extends previous work on score estimation by denoising autoencoders to the case of a conditional distribution, with a novel use of a corrupted feedforward predictor replacing Gaussian corruption. An advantage of this approach over more classical ways to perform iterative inference for structured outputs, like conditional random fields (CRFs), is that it is not any more necessary to define an explicit energy function linking the output variables. To keep computations tractable, such energy function parametrizations are typically fairly constrained, involving only a few neighbors of each of the output variables in each clique. We experimentally find that the proposed iterative inference from conditional score estimation by conditional denoising autoencoders performs better than comparable models based on CRFs or those not using any explicit modeling of the conditional joint distribution of outputs.
Diet Networks: Thin Parameters for Fat Genomics
Mar 16, 2017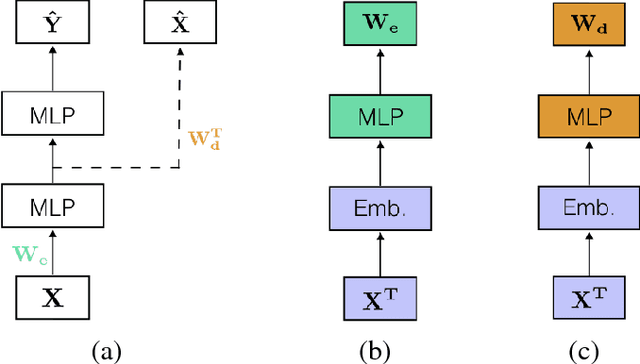
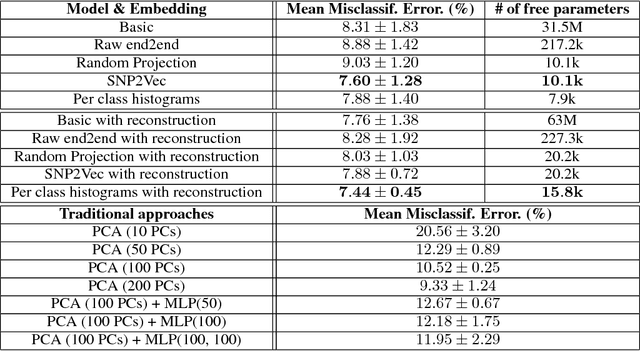
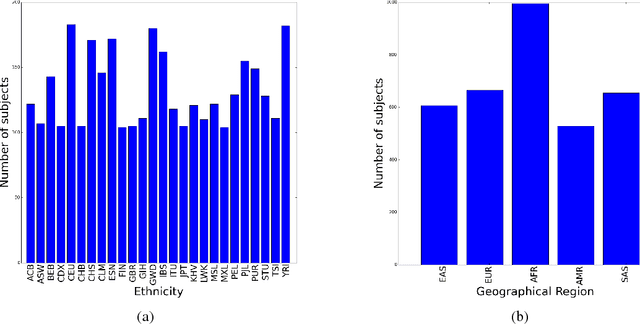
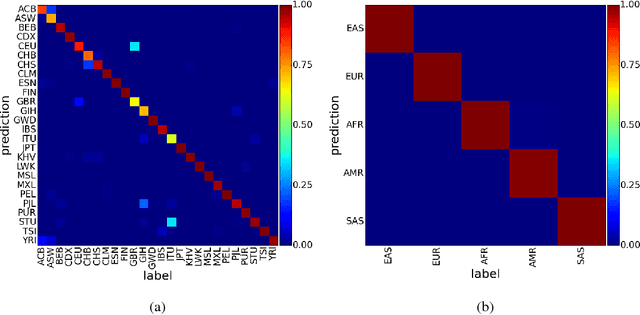
Abstract:Learning tasks such as those involving genomic data often poses a serious challenge: the number of input features can be orders of magnitude larger than the number of training examples, making it difficult to avoid overfitting, even when using the known regularization techniques. We focus here on tasks in which the input is a description of the genetic variation specific to a patient, the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), yielding millions of ternary inputs. Improving the ability of deep learning to handle such datasets could have an important impact in precision medicine, where high-dimensional data regarding a particular patient is used to make predictions of interest. Even though the amount of data for such tasks is increasing, this mismatch between the number of examples and the number of inputs remains a concern. Naive implementations of classifier neural networks involve a huge number of free parameters in their first layer: each input feature is associated with as many parameters as there are hidden units. We propose a novel neural network parametrization which considerably reduces the number of free parameters. It is based on the idea that we can first learn or provide a distributed representation for each input feature (e.g. for each position in the genome where variations are observed), and then learn (with another neural network called the parameter prediction network) how to map a feature's distributed representation to the vector of parameters specific to that feature in the classifier neural network (the weights which link the value of the feature to each of the hidden units). We show experimentally on a population stratification task of interest to medical studies that the proposed approach can significantly reduce both the number of parameters and the error rate of the classifier.
On Random Weights for Texture Generation in One Layer Neural Networks
Dec 19, 2016
Abstract:Recent work in the literature has shown experimentally that one can use the lower layers of a trained convolutional neural network (CNN) to model natural textures. More interestingly, it has also been experimentally shown that only one layer with random filters can also model textures although with less variability. In this paper we ask the question as to why one layer CNNs with random filters are so effective in generating textures? We theoretically show that one layer convolutional architectures (without a non-linearity) paired with the an energy function used in previous literature, can in fact preserve and modulate frequency coefficients in a manner so that random weights and pretrained weights will generate the same type of images. Based on the results of this analysis we question whether similar properties hold in the case where one uses one convolution layer with a non-linearity. We show that in the case of ReLu non-linearity there are situations where only one input will give the minimum possible energy whereas in the case of no nonlinearity, there are always infinite solutions that will give the minimum possible energy. Thus we can show that in certain situations adding a ReLu non-linearity generates less variable images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge