Simon Jégou
Expected Attention: KV Cache Compression by Estimating Attention from Future Queries Distribution
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Memory consumption of the Key-Value (KV) cache represents a major bottleneck for efficient large language model inference. While attention-score-based KV cache pruning shows promise, it faces critical practical limitations: attention scores from future tokens are unavailable during compression, and modern implementations like Flash Attention do not materialize the full attention matrix, making past scores inaccessible. To overcome these challenges, we introduce $\textbf{Expected Attention, a training-free compression method}$ that estimates KV pairs importance by predicting how future queries will attend to them. Our approach leverages the distributional properties of LLM activations to compute expected attention scores in closed form for each KV pair. These scores enable principled ranking and pruning of KV pairs with minimal impact on the residual stream, achieving effective compression without performance degradation. Importantly, our method operates seamlessly across both prefilling and decoding phases, consistently outperforming state-of-the-art baselines in both scenarios. Finally, $\textbf{we release KVPress, a comprehensive library to enable researchers to implement and benchmark KV cache compression methods, already including more than 20 techniques}$.
Using StyleGAN for Visual Interpretability of Deep Learning Models on Medical Images
Jan 19, 2021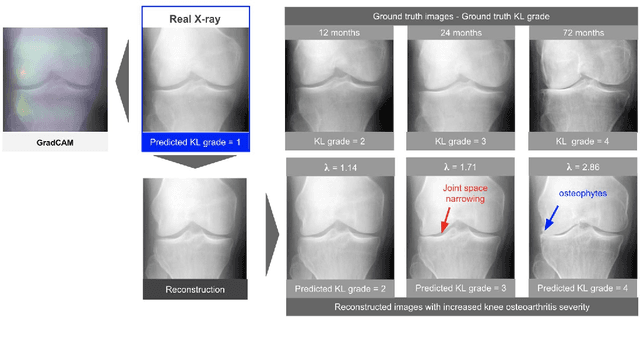
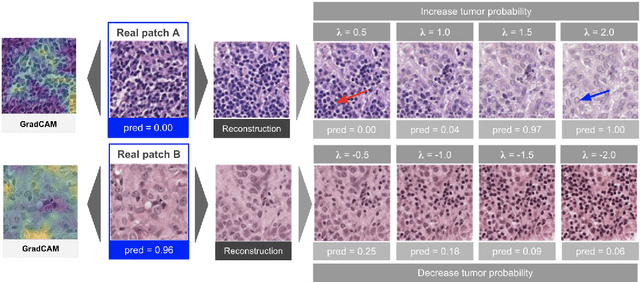
Abstract:As AI-based medical devices are becoming more common in imaging fields like radiology and histology, interpretability of the underlying predictive models is crucial to expand their use in clinical practice. Existing heatmap-based interpretability methods such as GradCAM only highlight the location of predictive features but do not explain how they contribute to the prediction. In this paper, we propose a new interpretability method that can be used to understand the predictions of any black-box model on images, by showing how the input image would be modified in order to produce different predictions. A StyleGAN is trained on medical images to provide a mapping between latent vectors and images. Our method identifies the optimal direction in the latent space to create a change in the model prediction. By shifting the latent representation of an input image along this direction, we can produce a series of new synthetic images with changed predictions. We validate our approach on histology and radiology images, and demonstrate its ability to provide meaningful explanations that are more informative than GradCAM heatmaps. Our method reveals the patterns learned by the model, which allows clinicians to build trust in the model's predictions, discover new biomarkers and eventually reveal potential biases.
ToxicBlend: Virtual Screening of Toxic Compounds with Ensemble Predictors
Jun 12, 2018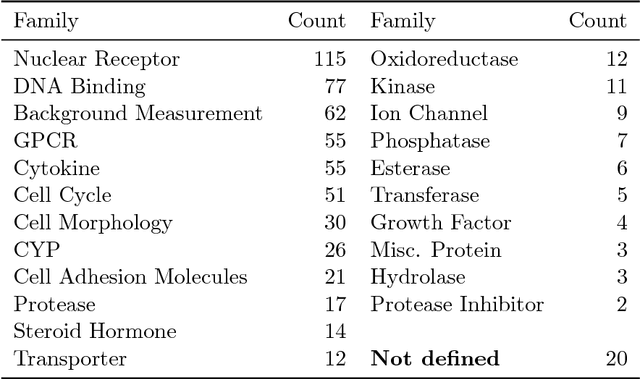
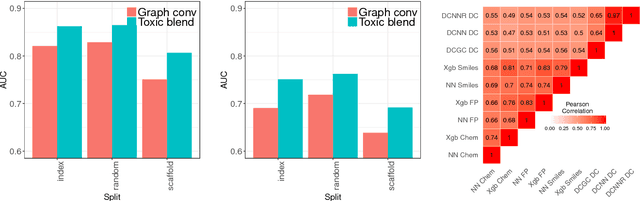
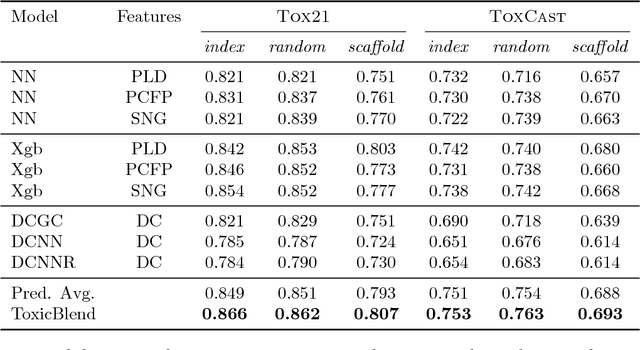
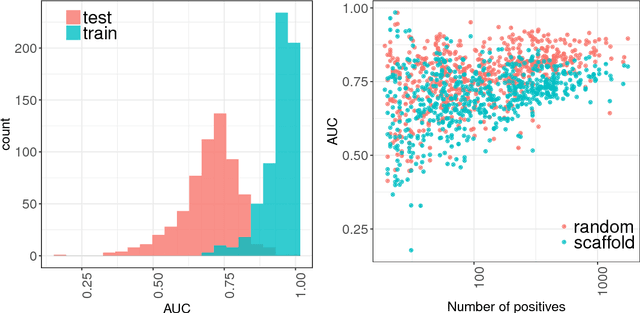
Abstract:Timely assessment of compound toxicity is one of the biggest challenges facing the pharmaceutical industry today. A significant proportion of compounds identified as potential leads are ultimately discarded due to the toxicity they induce. In this paper, we propose a novel machine learning approach for the prediction of molecular activity on ToxCast targets. We combine extreme gradient boosting with fully-connected and graph-convolutional neural network architectures trained on QSAR physical molecular property descriptors, PubChem molecular fingerprints, and SMILES sequences. Our ensemble predictor leverages the strengths of each individual technique, significantly outperforming existing state-of-the art models on the ToxCast and Tox21 toxicity-prediction datasets. We provide free access to molecule toxicity prediction using our model at http://www.owkin.com/toxicblend.
The One Hundred Layers Tiramisu: Fully Convolutional DenseNets for Semantic Segmentation
Oct 31, 2017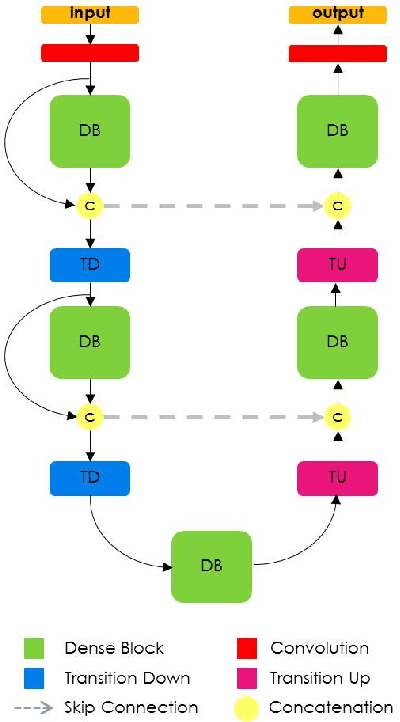
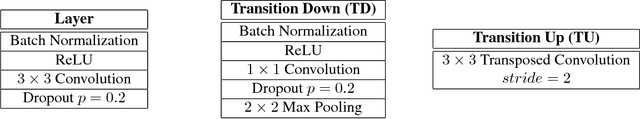
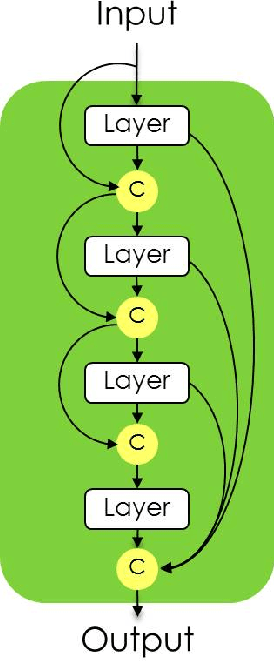
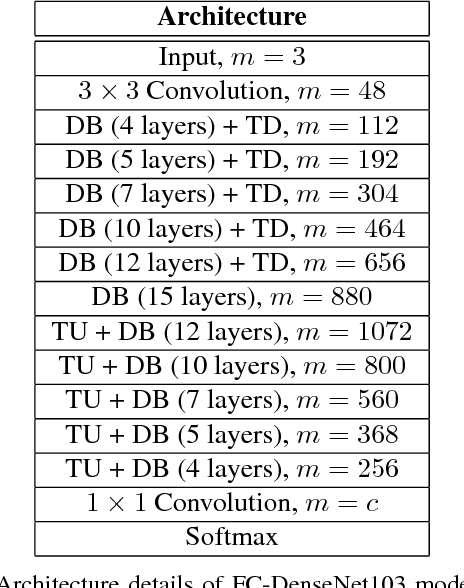
Abstract:State-of-the-art approaches for semantic image segmentation are built on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). The typical segmentation architecture is composed of (a) a downsampling path responsible for extracting coarse semantic features, followed by (b) an upsampling path trained to recover the input image resolution at the output of the model and, optionally, (c) a post-processing module (e.g. Conditional Random Fields) to refine the model predictions. Recently, a new CNN architecture, Densely Connected Convolutional Networks (DenseNets), has shown excellent results on image classification tasks. The idea of DenseNets is based on the observation that if each layer is directly connected to every other layer in a feed-forward fashion then the network will be more accurate and easier to train. In this paper, we extend DenseNets to deal with the problem of semantic segmentation. We achieve state-of-the-art results on urban scene benchmark datasets such as CamVid and Gatech, without any further post-processing module nor pretraining. Moreover, due to smart construction of the model, our approach has much less parameters than currently published best entries for these datasets. Code to reproduce the experiments is available here : https://github.com/SimJeg/FC-DenseNet/blob/master/train.py
Image Segmentation by Iterative Inference from Conditional Score Estimation
Aug 18, 2017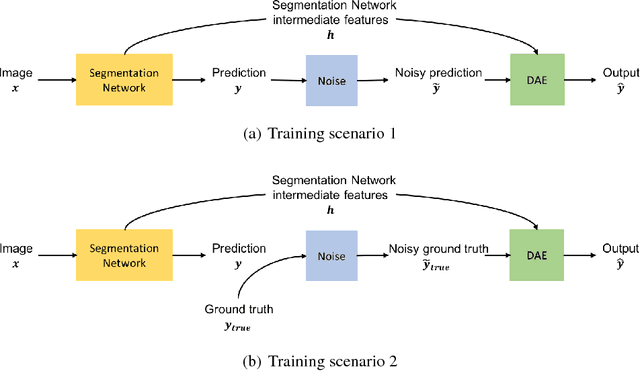
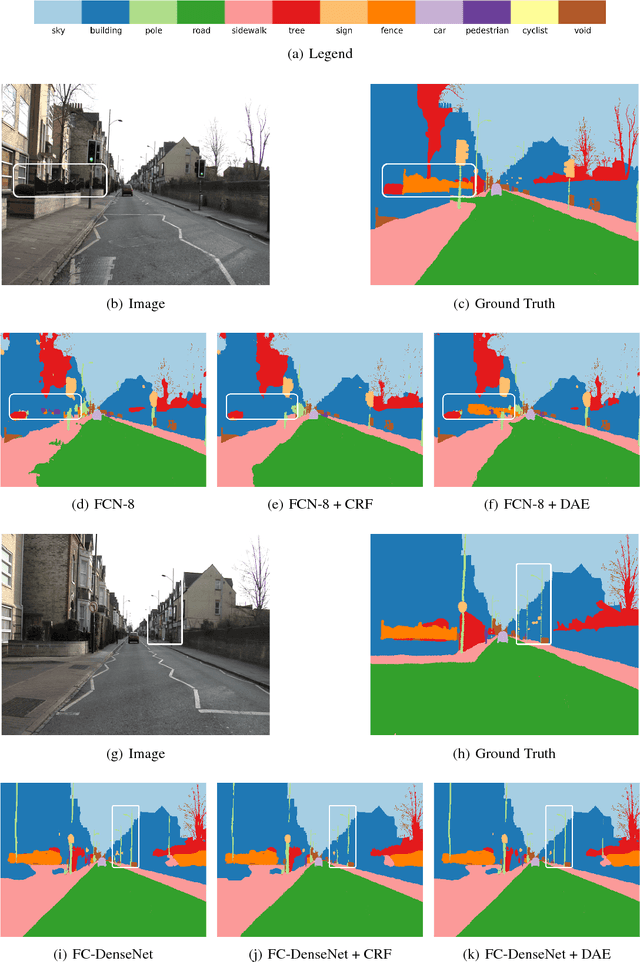
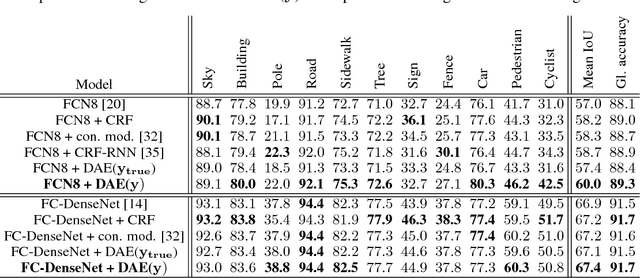
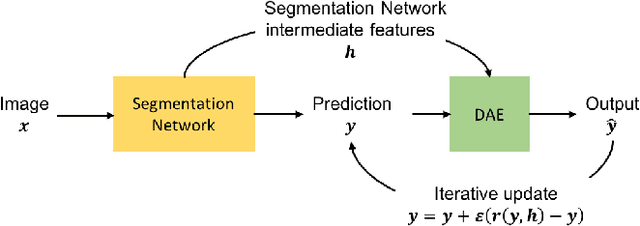

Abstract:Inspired by the combination of feedforward and iterative computations in the virtual cortex, and taking advantage of the ability of denoising autoencoders to estimate the score of a joint distribution, we propose a novel approach to iterative inference for capturing and exploiting the complex joint distribution of output variables conditioned on some input variables. This approach is applied to image pixel-wise segmentation, with the estimated conditional score used to perform gradient ascent towards a mode of the estimated conditional distribution. This extends previous work on score estimation by denoising autoencoders to the case of a conditional distribution, with a novel use of a corrupted feedforward predictor replacing Gaussian corruption. An advantage of this approach over more classical ways to perform iterative inference for structured outputs, like conditional random fields (CRFs), is that it is not any more necessary to define an explicit energy function linking the output variables. To keep computations tractable, such energy function parametrizations are typically fairly constrained, involving only a few neighbors of each of the output variables in each clique. We experimentally find that the proposed iterative inference from conditional score estimation by conditional denoising autoencoders performs better than comparable models based on CRFs or those not using any explicit modeling of the conditional joint distribution of outputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge