Eric W. Tramel
Digital Twin Generators for Disease Modeling
May 02, 2024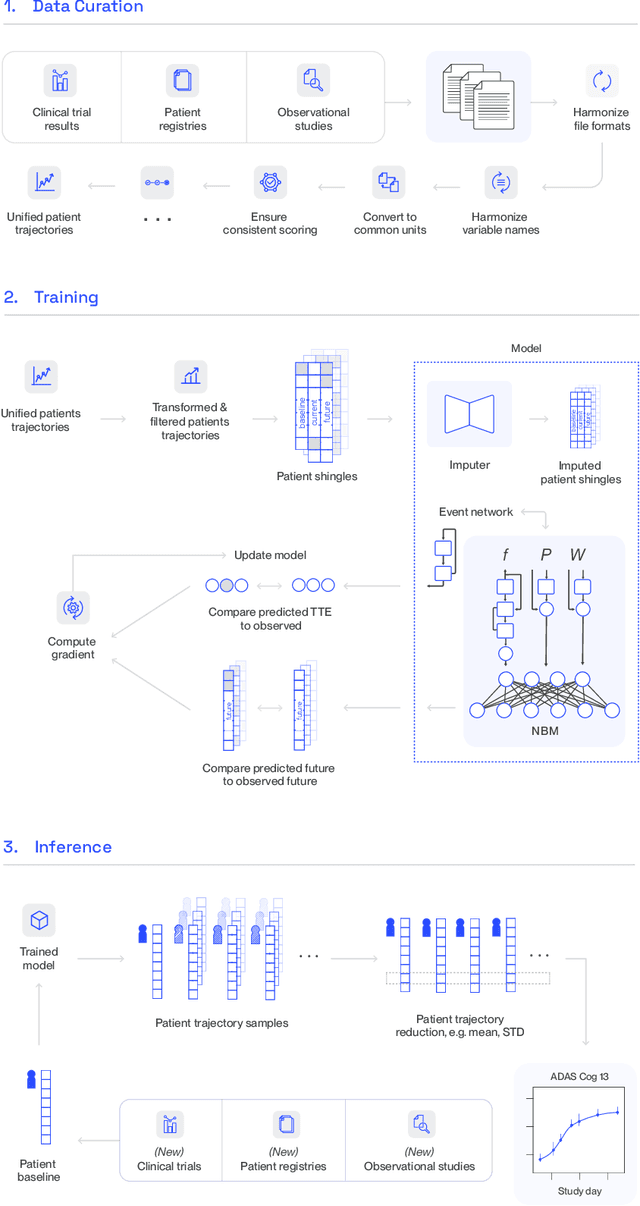
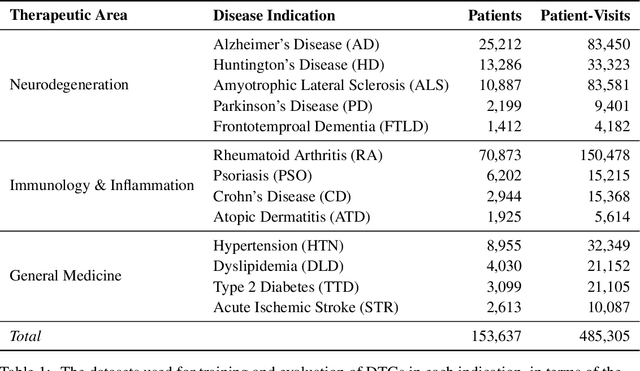
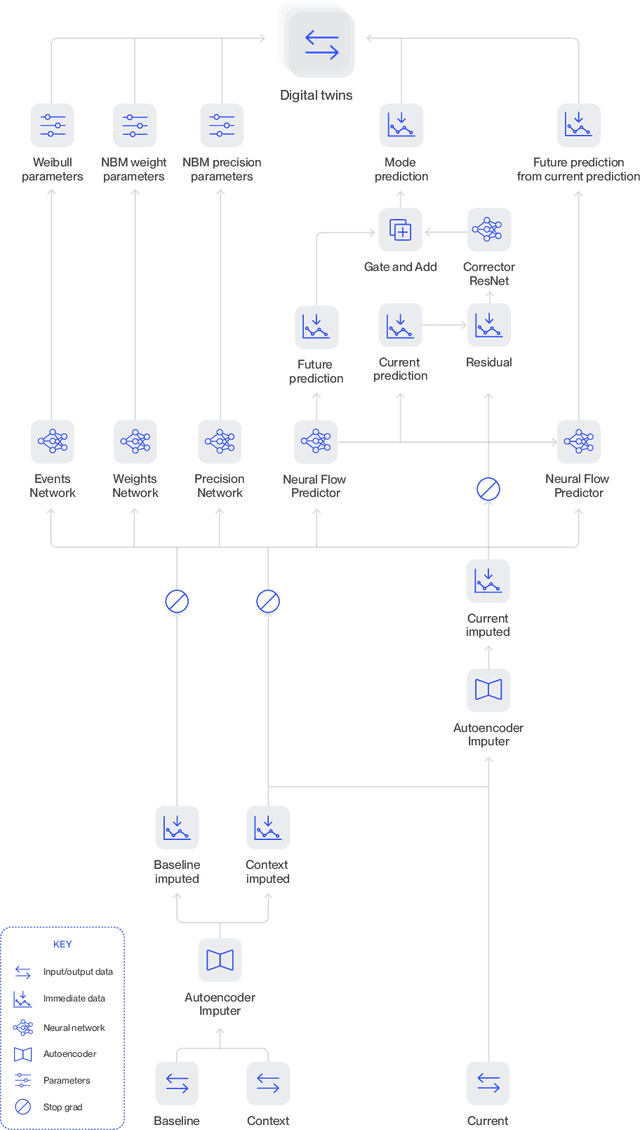
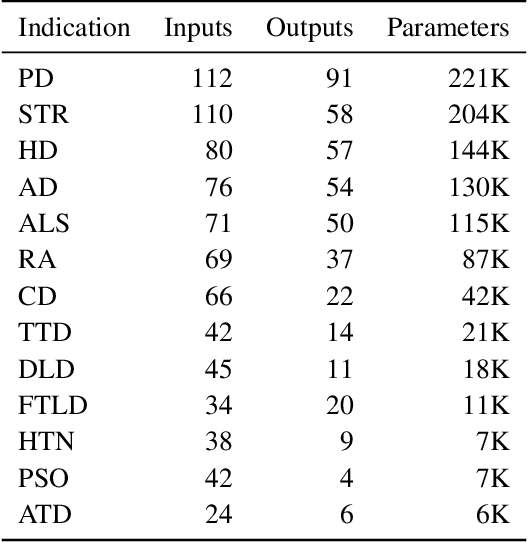
Abstract:A patient's digital twin is a computational model that describes the evolution of their health over time. Digital twins have the potential to revolutionize medicine by enabling individual-level computer simulations of human health, which can be used to conduct more efficient clinical trials or to recommend personalized treatment options. Due to the overwhelming complexity of human biology, machine learning approaches that leverage large datasets of historical patients' longitudinal health records to generate patients' digital twins are more tractable than potential mechanistic models. In this manuscript, we describe a neural network architecture that can learn conditional generative models of clinical trajectories, which we call Digital Twin Generators (DTGs), that can create digital twins of individual patients. We show that the same neural network architecture can be trained to generate accurate digital twins for patients across 13 different indications simply by changing the training set and tuning hyperparameters. By introducing a general purpose architecture, we aim to unlock the ability to scale machine learning approaches to larger datasets and across more indications so that a digital twin could be created for any patient in the world.
Semi-Supervised Federated Learning for Keyword Spotting
May 09, 2023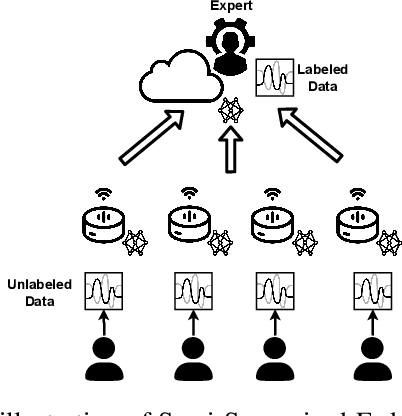
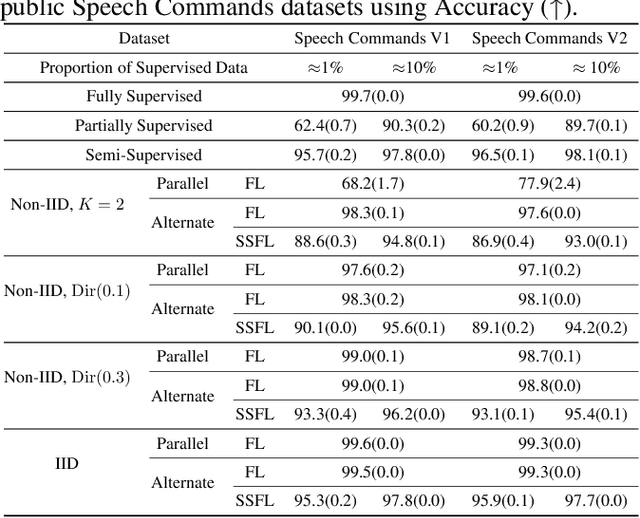
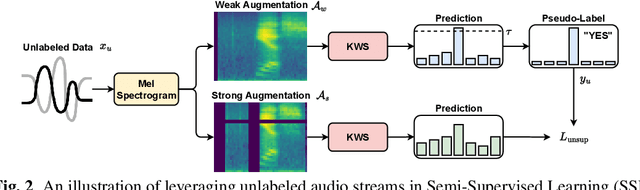
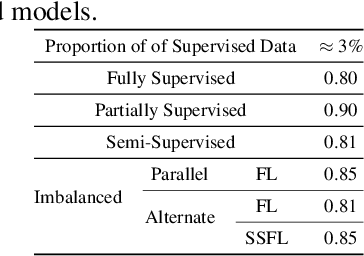
Abstract:Keyword Spotting (KWS) is a critical aspect of audio-based applications on mobile devices and virtual assistants. Recent developments in Federated Learning (FL) have significantly expanded the ability to train machine learning models by utilizing the computational and private data resources of numerous distributed devices. However, existing FL methods typically require that devices possess accurate ground-truth labels, which can be both expensive and impractical when dealing with local audio data. In this study, we first demonstrate the effectiveness of Semi-Supervised Federated Learning (SSL) and FL for KWS. We then extend our investigation to Semi-Supervised Federated Learning (SSFL) for KWS, where devices possess completely unlabeled data, while the server has access to a small amount of labeled data. We perform numerical analyses using state-of-the-art SSL, FL, and SSFL techniques to demonstrate that the performance of KWS models can be significantly improved by leveraging the abundant unlabeled heterogeneous data available on devices.
Differentially Private Federated Learning for Cancer Prediction
Jan 08, 2021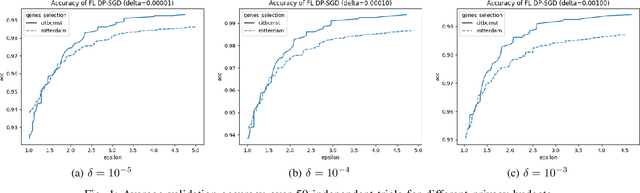
Abstract:Since 2014, the NIH funded iDASH (integrating Data for Analysis, Anonymization, SHaring) National Center for Biomedical Computing has hosted yearly competitions on the topic of private computing for genomic data. For one track of the 2020 iteration of this competition, participants were challenged to produce an approach to federated learning (FL) training of genomic cancer prediction models using differential privacy (DP), with submissions ranked according to held-out test accuracy for a given set of DP budgets. More precisely, in this track, we are tasked with training a supervised model for the prediction of breast cancer occurrence from genomic data split between two virtual centers while ensuring data privacy with respect to model transfer via DP. In this article, we present our 3rd place submission to this competition. During the competition, we encountered two main challenges discussed in this article: i) ensuring correctness of the privacy budget evaluation and ii) achieving an acceptable trade-off between prediction performance and privacy budget.
Siloed Federated Learning for Multi-Centric Histopathology Datasets
Aug 17, 2020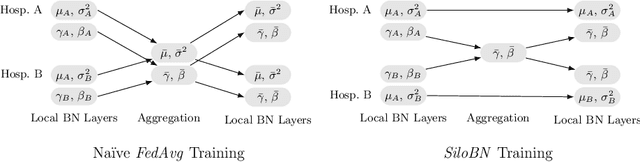
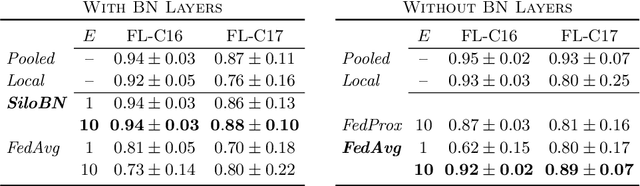
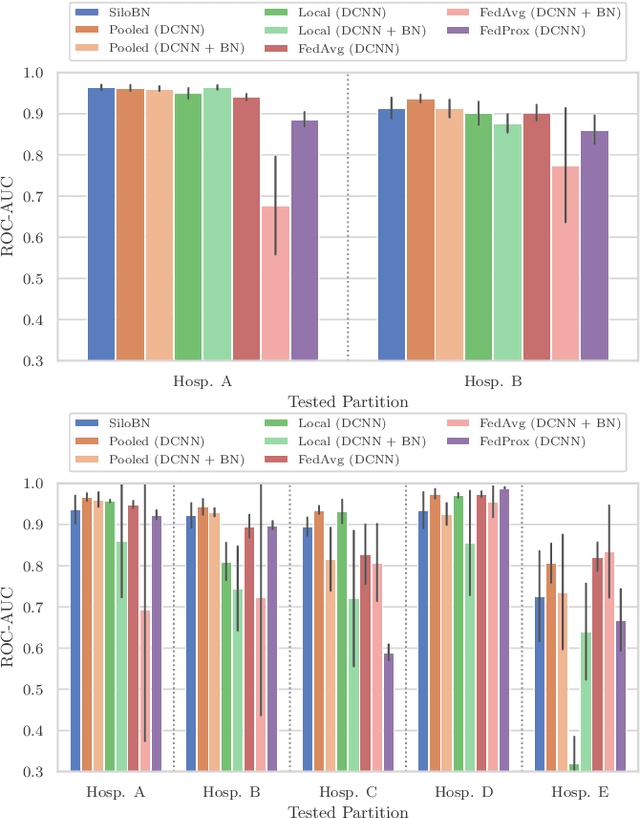

Abstract:While federated learning is a promising approach for training deep learning models over distributed sensitive datasets, it presents new challenges for machine learning, especially when applied in the medical domain where multi-centric data heterogeneity is common. Building on previous domain adaptation works, this paper proposes a novel federated learning approach for deep learning architectures via the introduction of local-statistic batch normalization (BN) layers, resulting in collaboratively-trained, yet center-specific models. This strategy improves robustness to data heterogeneity while also reducing the potential for information leaks by not sharing the center-specific layer activation statistics. We benchmark the proposed method on the classification of tumorous histopathology image patches extracted from the Camelyon16 and Camelyon17 datasets. We show that our approach compares favorably to previous state-of-the-art methods, especially for transfer learning across datasets.
SAFER: Sparse secure Aggregation for FEderated leaRning
Jul 29, 2020

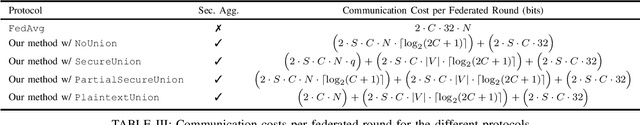
Abstract:Federated learning enables one to train a common machine learning model across separate, privately-held datasets via distributed model training. During federated model training, only intermediate model parameters are transmitted to a central server which aggregates these models to create a new common model, thus exposing only intermediate model parameters rather than the training data itself. However, some attacks (e.g. membership inference) are able to infer properties of private data from these intermediate model parameters. Hence, performing the aggregation of these client-specific model parameters in a secure way is required. Additionally, the communication cost is often the bottleneck of the federated systems, especially for large neural networks. So, limiting the number and the size of communications is necessary to efficiently train large neural architectures. In this article, we present an efficient and secure protocol for performing secure aggregations over compressed model updates in the context of collaborative, few-party federated learning, a context common in the medical, healthcare, and biotechnical use-cases of federated systems. By making compression-based federated techniques amenable to secure computation, we develop a secure aggregation protocol between multiple servers with very low communication and computation costs and without preprocessing overhead. Our experiments demonstrate the efficiency of this new approach for secure federated training of deep convolutional neural networks.
Efficient Per-Example Gradient Computations in Convolutional Neural Networks
Dec 12, 2019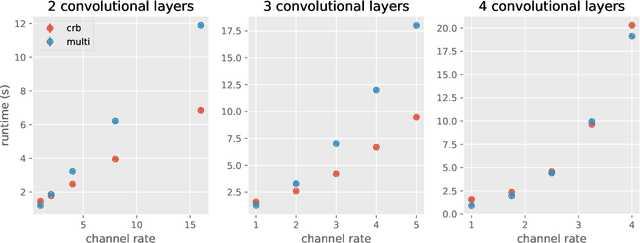
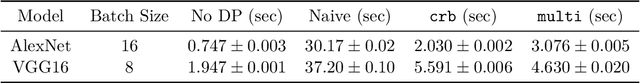
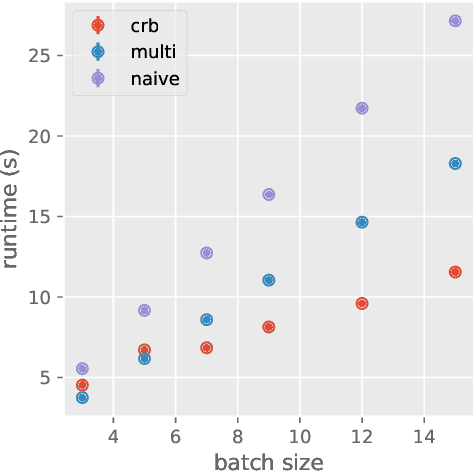
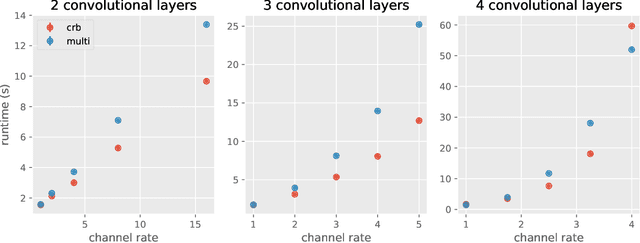
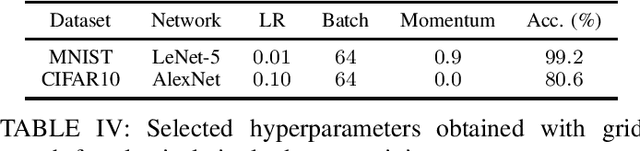
Abstract:Deep learning frameworks leverage GPUs to perform massively-parallel computations over batches of many training examples efficiently. However, for certain tasks, one may be interested in performing per-example computations, for instance using per-example gradients to evaluate a quantity of interest unique to each example. One notable application comes from the field of differential privacy, where per-example gradients must be norm-bounded in order to limit the impact of each example on the aggregated batch gradient. In this work, we discuss how per-example gradients can be efficiently computed in convolutional neural networks (CNNs). We compare existing strategies by performing a few steps of differentially-private training on CNNs of varying sizes. We also introduce a new strategy for per-example gradient calculation, which is shown to be advantageous depending on the model architecture and how the model is trained. This is a first step in making differentially-private training of CNNs practical.
ToxicBlend: Virtual Screening of Toxic Compounds with Ensemble Predictors
Jun 12, 2018
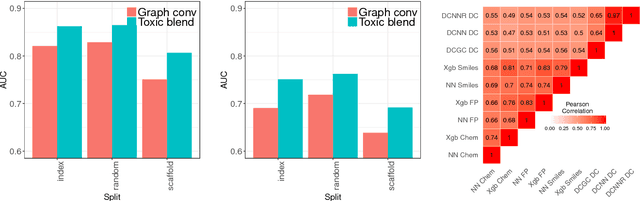
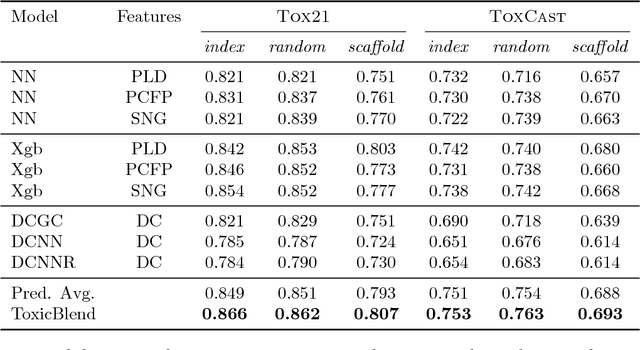
Abstract:Timely assessment of compound toxicity is one of the biggest challenges facing the pharmaceutical industry today. A significant proportion of compounds identified as potential leads are ultimately discarded due to the toxicity they induce. In this paper, we propose a novel machine learning approach for the prediction of molecular activity on ToxCast targets. We combine extreme gradient boosting with fully-connected and graph-convolutional neural network architectures trained on QSAR physical molecular property descriptors, PubChem molecular fingerprints, and SMILES sequences. Our ensemble predictor leverages the strengths of each individual technique, significantly outperforming existing state-of-the art models on the ToxCast and Tox21 toxicity-prediction datasets. We provide free access to molecule toxicity prediction using our model at http://www.owkin.com/toxicblend.
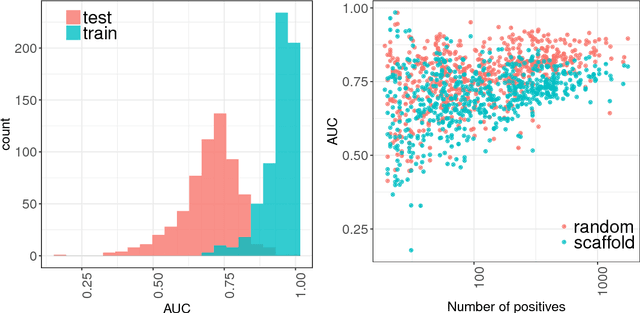
Classification and Disease Localization in Histopathology Using Only Global Labels: A Weakly-Supervised Approach
Feb 01, 2018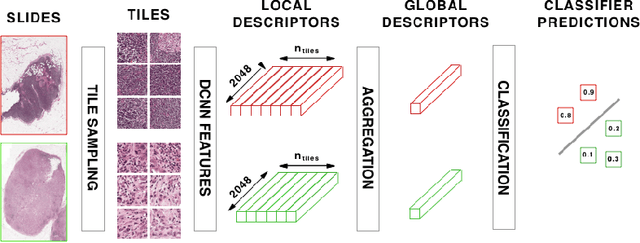
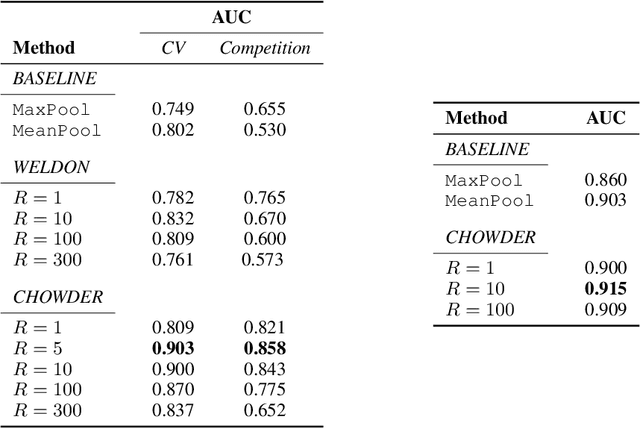
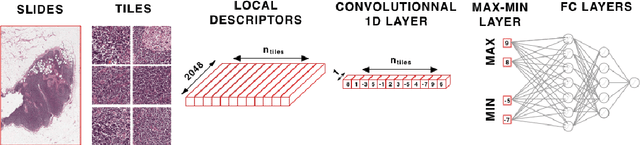
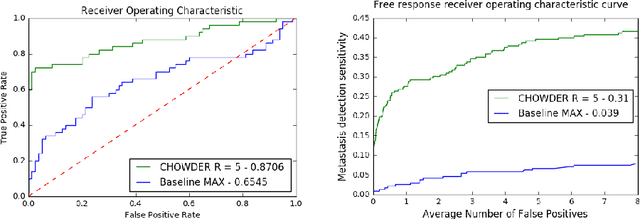
Abstract:Analysis of histopathology slides is a critical step for many diagnoses, and in particular in oncology where it defines the gold standard. In the case of digital histopathological analysis, highly trained pathologists must review vast whole-slide-images of extreme digital resolution ($100,000^2$ pixels) across multiple zoom levels in order to locate abnormal regions of cells, or in some cases single cells, out of millions. The application of deep learning to this problem is hampered not only by small sample sizes, as typical datasets contain only a few hundred samples, but also by the generation of ground-truth localized annotations for training interpretable classification and segmentation models. We propose a method for disease localization in the context of weakly supervised learning, where only image-level labels are available during training. Even without pixel-level annotations, we are able to demonstrate performance comparable with models trained with strong annotations on the Camelyon-16 lymph node metastases detection challenge. We accomplish this through the use of pre-trained deep convolutional networks, feature embedding, as well as learning via top instances and negative evidence, a multiple instance learning technique from the field of semantic segmentation and object detection.
Robust Detection of Covariate-Treatment Interactions in Clinical Trials
Dec 21, 2017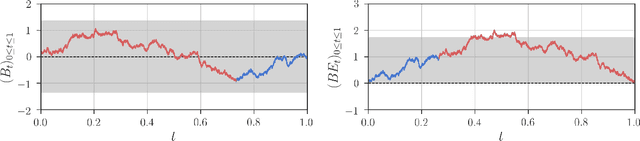

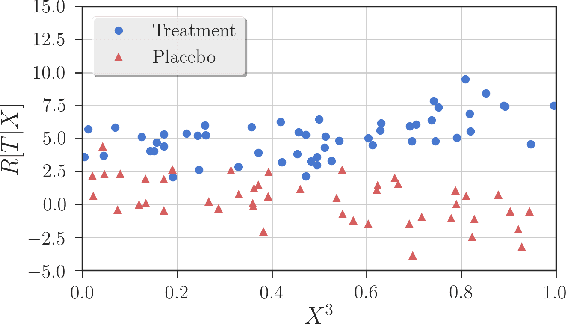
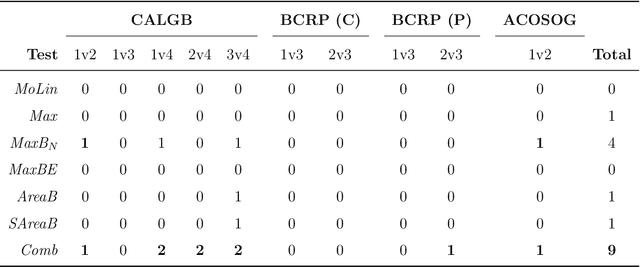
Abstract:Detection of interactions between treatment effects and patient descriptors in clinical trials is critical for optimizing the drug development process. The increasing volume of data accumulated in clinical trials provides a unique opportunity to discover new biomarkers and further the goal of personalized medicine, but it also requires innovative robust biomarker detection methods capable of detecting non-linear, and sometimes weak, signals. We propose a set of novel univariate statistical tests, based on the theory of random walks, which are able to capture non-linear and non-monotonic covariate-treatment interactions. We also propose a novel combined test, which leverages the power of all of our proposed univariate tests into a single general-case tool. We present results for both synthetic trials as well as real-world clinical trials, where we compare our method with state-of-the-art techniques and demonstrate the utility and robustness of our approach.
Streaming Bayesian inference: theoretical limits and mini-batch approximate message-passing
Jun 02, 2017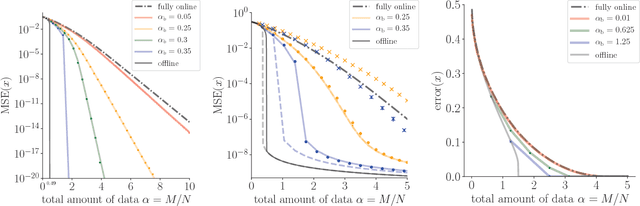
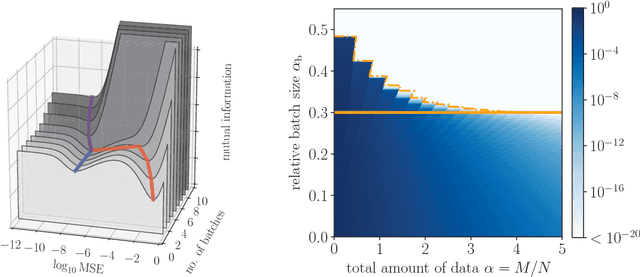
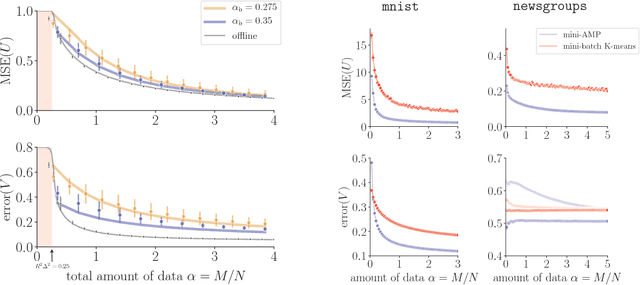
Abstract:In statistical learning for real-world large-scale data problems, one must often resort to "streaming" algorithms which operate sequentially on small batches of data. In this work, we present an analysis of the information-theoretic limits of mini-batch inference in the context of generalized linear models and low-rank matrix factorization. In a controlled Bayes-optimal setting, we characterize the optimal performance and phase transitions as a function of mini-batch size. We base part of our results on a detailed analysis of a mini-batch version of the approximate message-passing algorithm (Mini-AMP), which we introduce. Additionally, we show that this theoretical optimality carries over into real-data problems by illustrating that Mini-AMP is competitive with standard streaming algorithms for clustering.
* 19 pages, 4 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge