Jean-Baptiste Schiratti
Using StyleGAN for Visual Interpretability of Deep Learning Models on Medical Images
Jan 19, 2021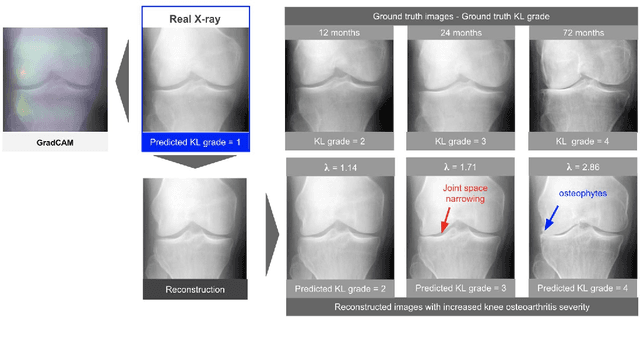
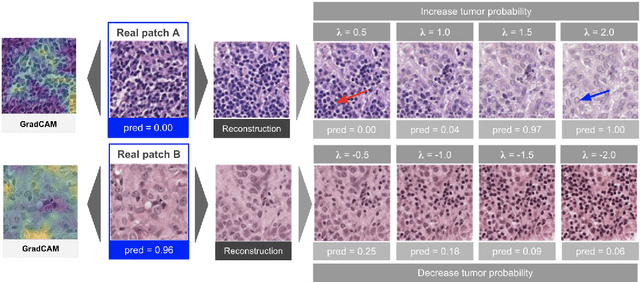
Abstract:As AI-based medical devices are becoming more common in imaging fields like radiology and histology, interpretability of the underlying predictive models is crucial to expand their use in clinical practice. Existing heatmap-based interpretability methods such as GradCAM only highlight the location of predictive features but do not explain how they contribute to the prediction. In this paper, we propose a new interpretability method that can be used to understand the predictions of any black-box model on images, by showing how the input image would be modified in order to produce different predictions. A StyleGAN is trained on medical images to provide a mapping between latent vectors and images. Our method identifies the optimal direction in the latent space to create a change in the model prediction. By shifting the latent representation of an input image along this direction, we can produce a series of new synthetic images with changed predictions. We validate our approach on histology and radiology images, and demonstrate its ability to provide meaningful explanations that are more informative than GradCAM heatmaps. Our method reveals the patterns learned by the model, which allows clinicians to build trust in the model's predictions, discover new biomarkers and eventually reveal potential biases.
Statistical learning of spatiotemporal patterns from longitudinal manifold-valued networks
Sep 25, 2017


Abstract:We introduce a mixed-effects model to learn spatiotempo-ral patterns on a network by considering longitudinal measures distributed on a fixed graph. The data come from repeated observations of subjects at different time points which take the form of measurement maps distributed on a graph such as an image or a mesh. The model learns a typical group-average trajectory characterizing the propagation of measurement changes across the graph nodes. The subject-specific trajectories are defined via spatial and temporal transformations of the group-average scenario, thus estimating the variability of spatiotemporal patterns within the group. To estimate population and individual model parameters, we adapted a stochastic version of the Expectation-Maximization algorithm, the MCMC-SAEM. The model is used to describe the propagation of cortical atrophy during the course of Alzheimer's Disease. Model parameters show the variability of this average pattern of atrophy in terms of trajectories across brain regions, age at disease onset and pace of propagation. We show that the personalization of this model yields accurate prediction of maps of cortical thickness in patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge