Abhishek Thakur
AutoTrain: No-code training for state-of-the-art models
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:With the advancements in open-source models, training (or finetuning) models on custom datasets has become a crucial part of developing solutions which are tailored to specific industrial or open-source applications. Yet, there is no single tool which simplifies the process of training across different types of modalities or tasks. We introduce AutoTrain (aka AutoTrain Advanced) -- an open-source, no code tool/library which can be used to train (or finetune) models for different kinds of tasks such as: large language model (LLM) finetuning, text classification/regression, token classification, sequence-to-sequence task, finetuning of sentence transformers, visual language model (VLM) finetuning, image classification/regression and even classification and regression tasks on tabular data. AutoTrain Advanced is an open-source library providing best practices for training models on custom datasets. The library is available at https://github.com/huggingface/autotrain-advanced. AutoTrain can be used in fully local mode or on cloud machines and works with tens of thousands of models shared on Hugging Face Hub and their variations.
Evaluate & Evaluation on the Hub: Better Best Practices for Data and Model Measurements
Oct 06, 2022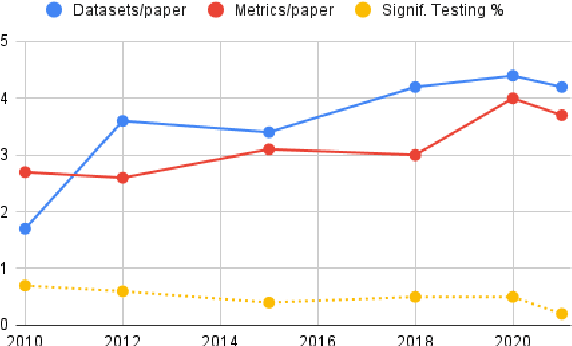
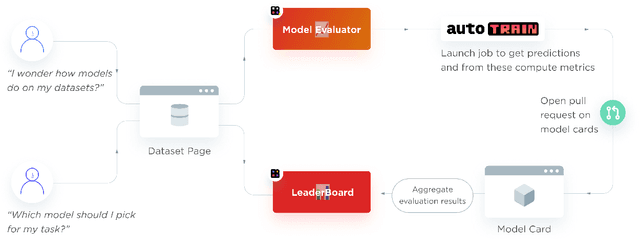
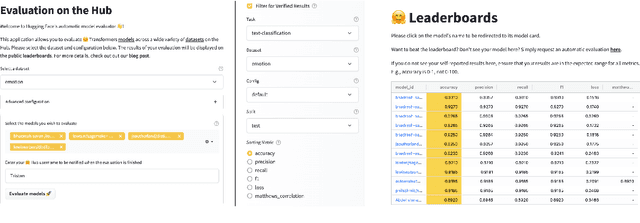
Abstract:Evaluation is a key part of machine learning (ML), yet there is a lack of support and tooling to enable its informed and systematic practice. We introduce Evaluate and Evaluation on the Hub --a set of tools to facilitate the evaluation of models and datasets in ML. Evaluate is a library to support best practices for measurements, metrics, and comparisons of data and models. Its goal is to support reproducibility of evaluation, centralize and document the evaluation process, and broaden evaluation to cover more facets of model performance. It includes over 50 efficient canonical implementations for a variety of domains and scenarios, interactive documentation, and the ability to easily share implementations and outcomes. The library is available at https://github.com/huggingface/evaluate. In addition, we introduce Evaluation on the Hub, a platform that enables the large-scale evaluation of over 75,000 models and 11,000 datasets on the Hugging Face Hub, for free, at the click of a button. Evaluation on the Hub is available at https://huggingface.co/autoevaluate.
UltraMNIST Classification: A Benchmark to Train CNNs for Very Large Images
Jun 25, 2022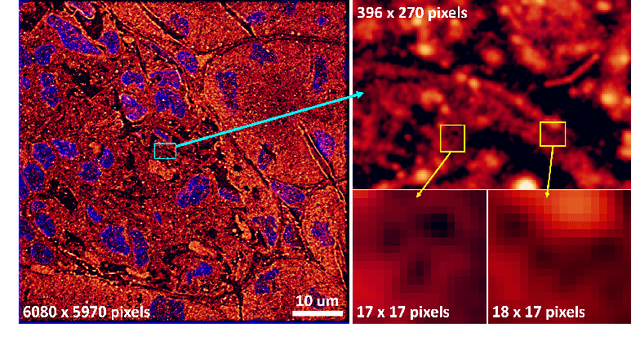
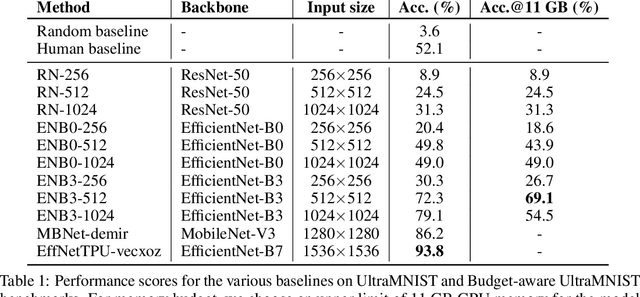
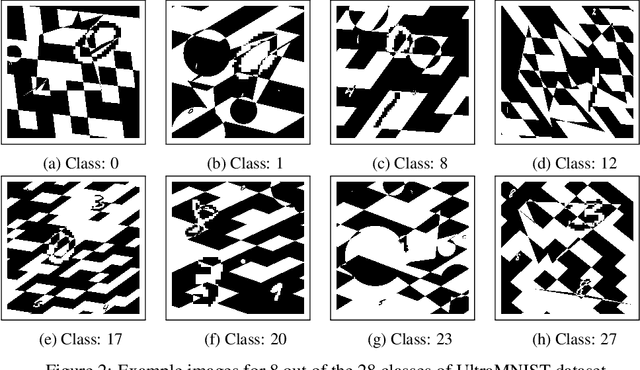
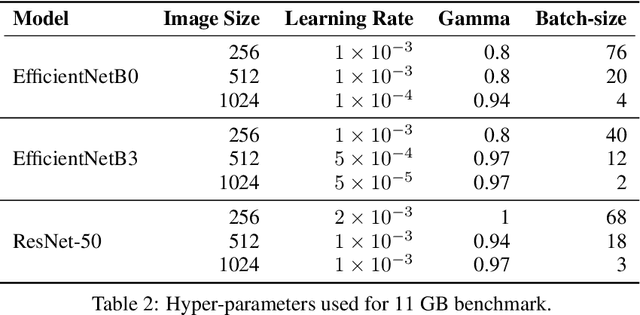
Abstract:Convolutional neural network (CNN) approaches available in the current literature are designed to work primarily with low-resolution images. When applied on very large images, challenges related to GPU memory, smaller receptive field than needed for semantic correspondence and the need to incorporate multi-scale features arise. The resolution of input images can be reduced, however, with significant loss of critical information. Based on the outlined issues, we introduce a novel research problem of training CNN models for very large images, and present 'UltraMNIST dataset', a simple yet representative benchmark dataset for this task. UltraMNIST has been designed using the popular MNIST digits with additional levels of complexity added to replicate well the challenges of real-world problems. We present two variants of the problem: 'UltraMNIST classification' and 'Budget-aware UltraMNIST classification'. The standard UltraMNIST classification benchmark is intended to facilitate the development of novel CNN training methods that make the effective use of the best available GPU resources. The budget-aware variant is intended to promote development of methods that work under constrained GPU memory. For the development of competitive solutions, we present several baseline models for the standard benchmark and its budget-aware variant. We study the effect of reducing resolution on the performance and present results for baseline models involving pretrained backbones from among the popular state-of-the-art models. Finally, with the presented benchmark dataset and the baselines, we hope to pave the ground for a new generation of CNN methods suitable for handling large images in an efficient and resource-light manner.
RAFT: A Real-World Few-Shot Text Classification Benchmark
Sep 28, 2021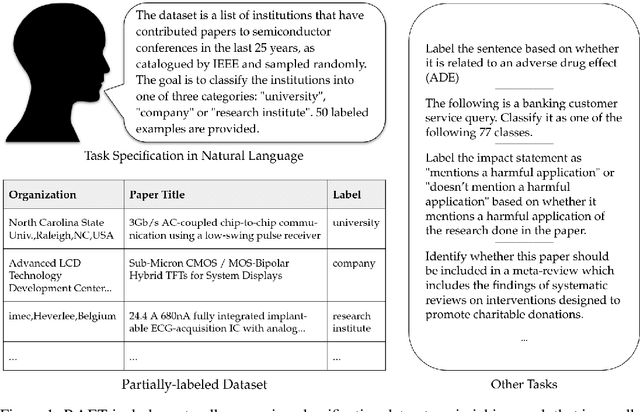
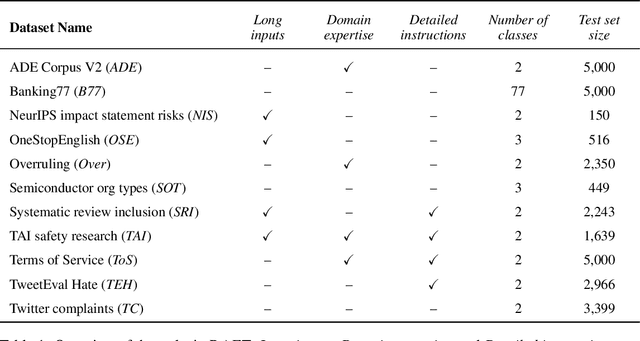
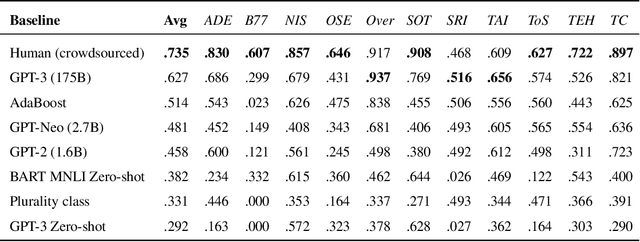
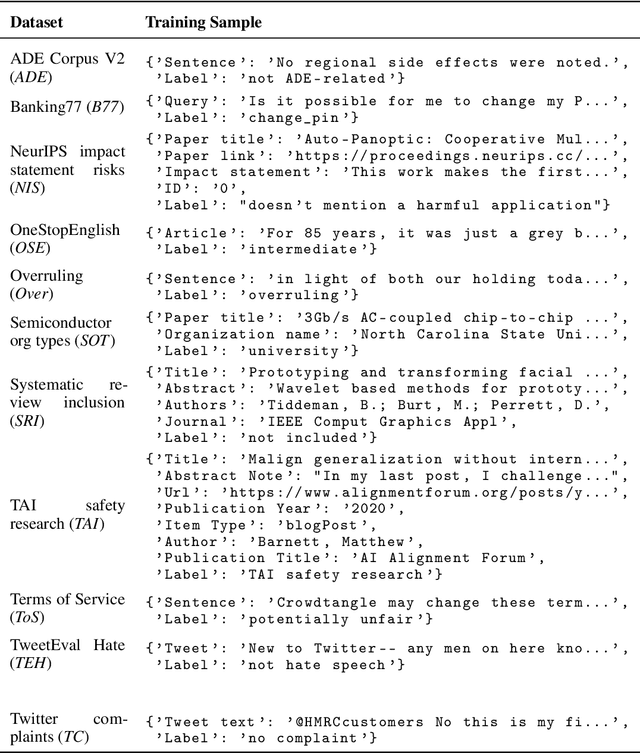
Abstract:Large pre-trained language models have shown promise for few-shot learning, completing text-based tasks given only a few task-specific examples. Will models soon solve classification tasks that have so far been reserved for human research assistants? Existing benchmarks are not designed to measure progress in applied settings, and so don't directly answer this question. The RAFT benchmark (Real-world Annotated Few-shot Tasks) focuses on naturally occurring tasks and uses an evaluation setup that mirrors deployment. Baseline evaluations on RAFT reveal areas current techniques struggle with: reasoning over long texts and tasks with many classes. Human baselines show that some classification tasks are difficult for non-expert humans, reflecting that real-world value sometimes depends on domain expertise. Yet even non-expert human baseline F1 scores exceed GPT-3 by an average of 0.11. The RAFT datasets and leaderboard will track which model improvements translate into real-world benefits at https://raft.elicit.org .
Datasets: A Community Library for Natural Language Processing
Sep 07, 2021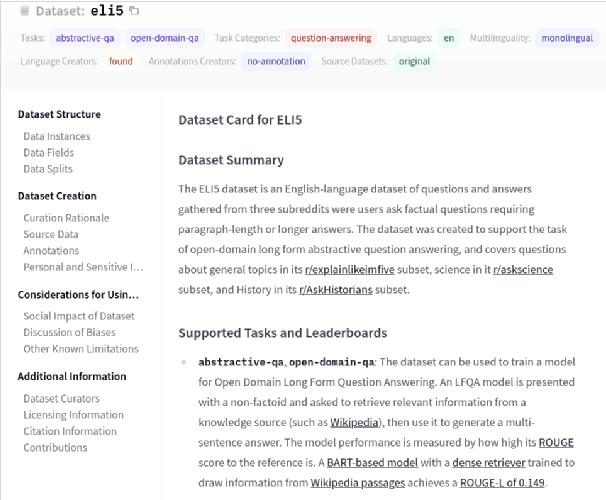
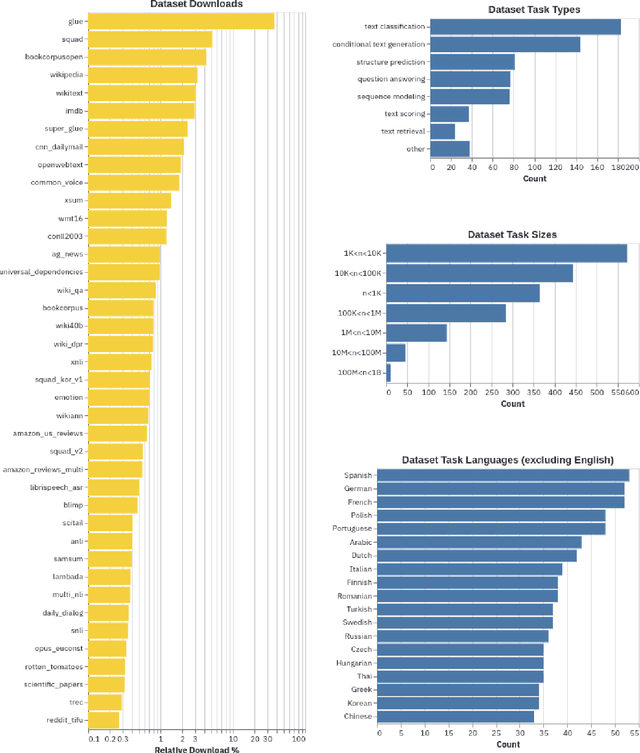
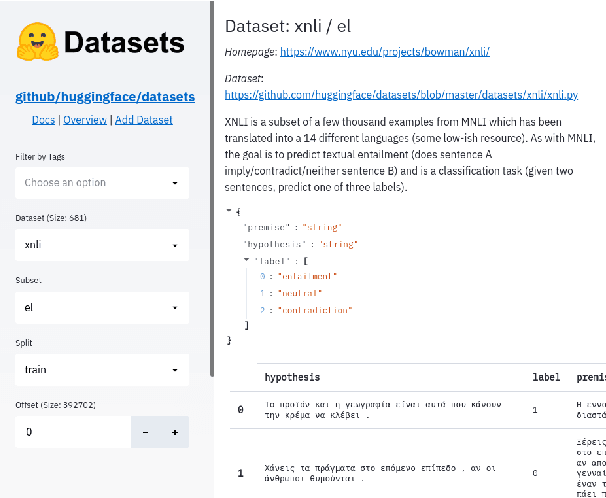
Abstract:The scale, variety, and quantity of publicly-available NLP datasets has grown rapidly as researchers propose new tasks, larger models, and novel benchmarks. Datasets is a community library for contemporary NLP designed to support this ecosystem. Datasets aims to standardize end-user interfaces, versioning, and documentation, while providing a lightweight front-end that behaves similarly for small datasets as for internet-scale corpora. The design of the library incorporates a distributed, community-driven approach to adding datasets and documenting usage. After a year of development, the library now includes more than 650 unique datasets, has more than 250 contributors, and has helped support a variety of novel cross-dataset research projects and shared tasks. The library is available at https://github.com/huggingface/datasets.
NeBula: Quest for Robotic Autonomy in Challenging Environments; TEAM CoSTAR at the DARPA Subterranean Challenge
Mar 28, 2021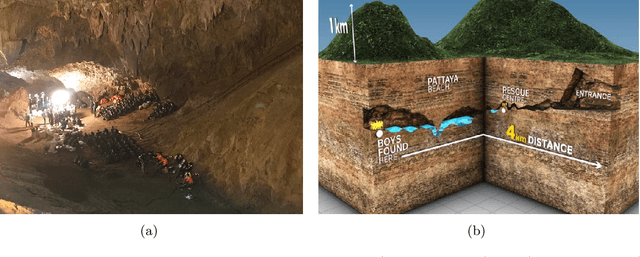
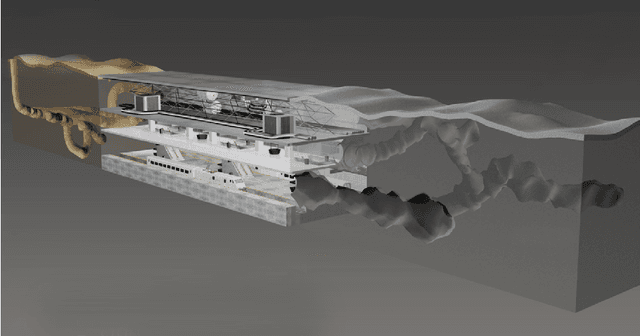
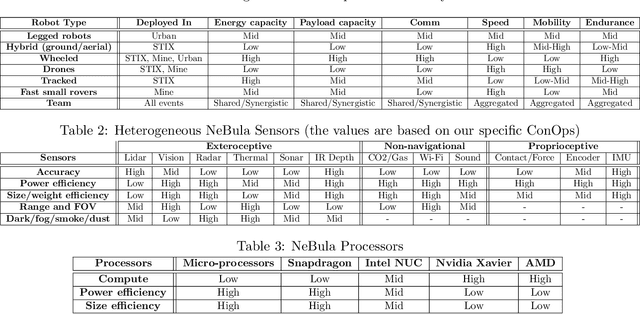
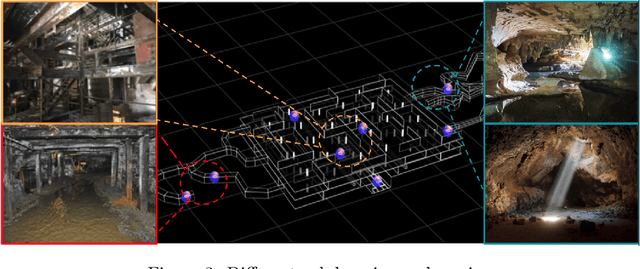
Abstract:This paper presents and discusses algorithms, hardware, and software architecture developed by the TEAM CoSTAR (Collaborative SubTerranean Autonomous Robots), competing in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge. Specifically, it presents the techniques utilized within the Tunnel (2019) and Urban (2020) competitions, where CoSTAR achieved 2nd and 1st place, respectively. We also discuss CoSTAR's demonstrations in Martian-analog surface and subsurface (lava tubes) exploration. The paper introduces our autonomy solution, referred to as NeBula (Networked Belief-aware Perceptual Autonomy). NeBula is an uncertainty-aware framework that aims at enabling resilient and modular autonomy solutions by performing reasoning and decision making in the belief space (space of probability distributions over the robot and world states). We discuss various components of the NeBula framework, including: (i) geometric and semantic environment mapping; (ii) a multi-modal positioning system; (iii) traversability analysis and local planning; (iv) global motion planning and exploration behavior; (i) risk-aware mission planning; (vi) networking and decentralized reasoning; and (vii) learning-enabled adaptation. We discuss the performance of NeBula on several robot types (e.g. wheeled, legged, flying), in various environments. We discuss the specific results and lessons learned from fielding this solution in the challenging courses of the DARPA Subterranean Challenge competition.
LAMP: Large-Scale Autonomous Mapping and Positioning for Exploration of Perceptually-Degraded Subterranean Environments
Mar 05, 2020
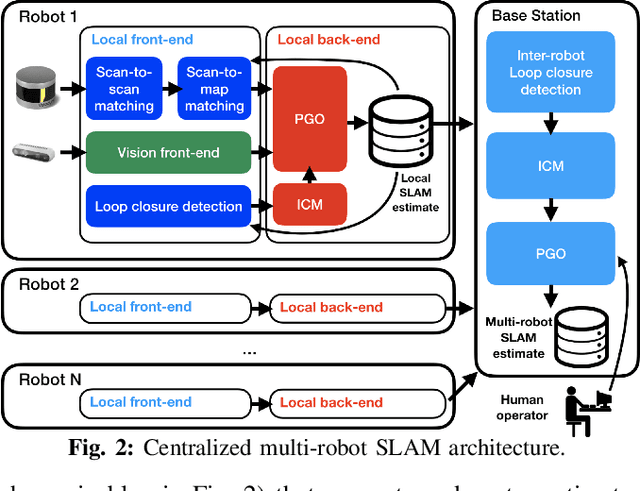
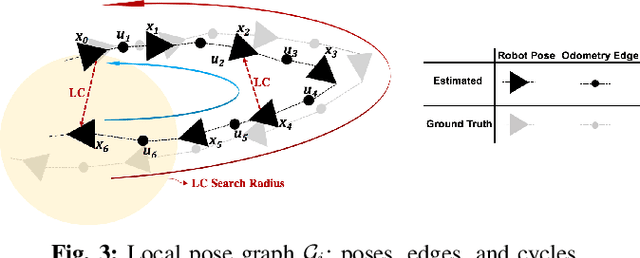

Abstract:Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) in large-scale, unknown, and complex subterranean environments is a challenging problem. Sensors must operate in off-nominal conditions; uneven and slippery terrains make wheel odometry inaccurate, while long corridors without salient features make exteroceptive sensing ambiguous and prone to drift; finally, spurious loop closures that are frequent in environments with repetitive appearance, such as tunnels and mines, could result in a significant distortion of the entire map. These challenges are in stark contrast with the need to build highly-accurate 3D maps to support a wide variety of applications, ranging from disaster response to the exploration of underground extraterrestrial worlds. This paper reports on the implementation and testing of a lidar-based multi-robot SLAM system developed in the context of the DARPA Subterranean Challenge. We present a system architecture to enhance subterranean operation, including an accurate lidar-based front-end, and a flexible and robust back-end that automatically rejects outlying loop closures. We present an extensive evaluation in large-scale, challenging subterranean environments, including the results obtained in the Tunnel Circuit of the DARPA Subterranean Challenge. Finally, we discuss potential improvements, limitations of the state of the art, and future research directions.
AutoCompete: A Framework for Machine Learning Competition
Jul 08, 2015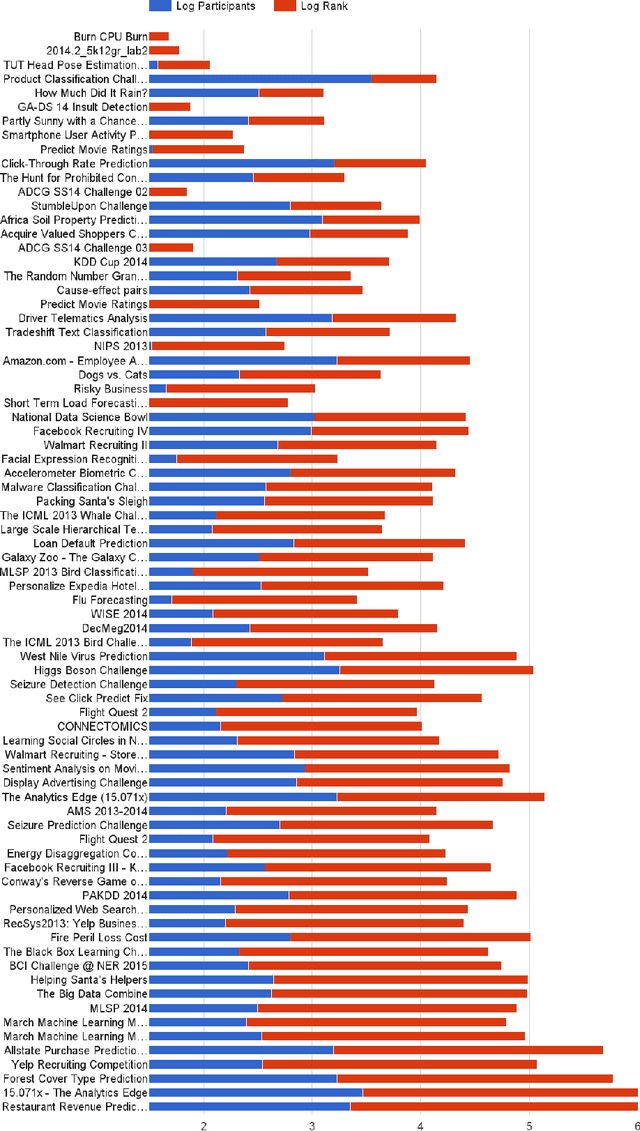
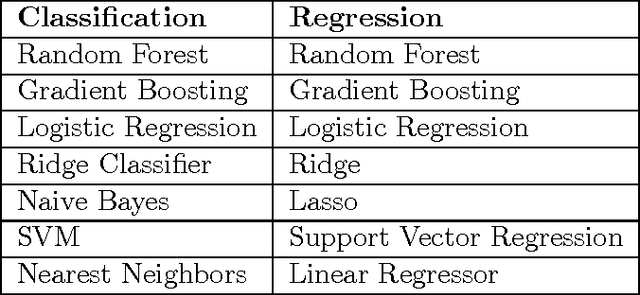
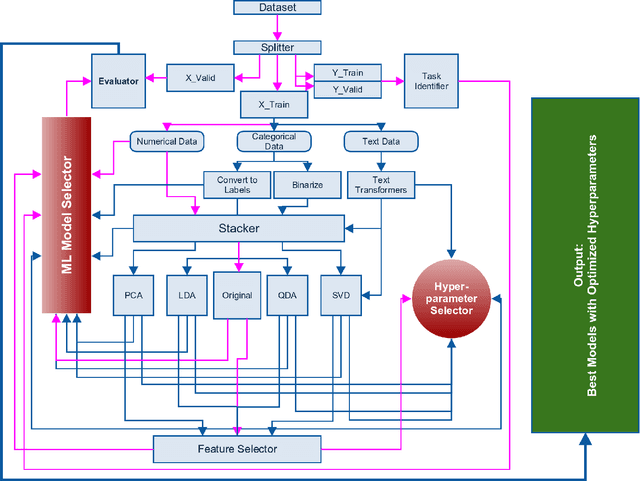
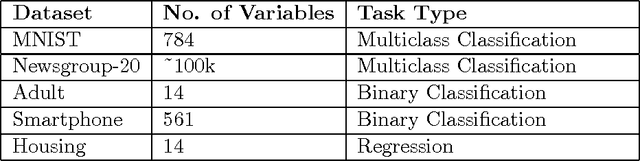
Abstract:In this paper, we propose AutoCompete, a highly automated machine learning framework for tackling machine learning competitions. This framework has been learned by us, validated and improved over a period of more than two years by participating in online machine learning competitions. It aims at minimizing human interference required to build a first useful predictive model and to assess the practical difficulty of a given machine learning challenge. The proposed system helps in identifying data types, choosing a machine learn- ing model, tuning hyper-parameters, avoiding over-fitting and optimization for a provided evaluation metric. We also observe that the proposed system produces better (or comparable) results with less runtime as compared to other approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge