Artus Krohn-Grimberghe
Multi-Stage Reinforcement Learning For Object Detection
Oct 26, 2018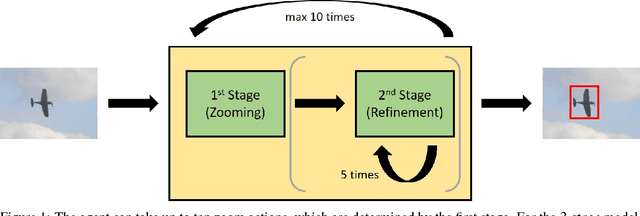
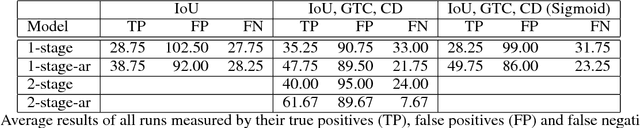
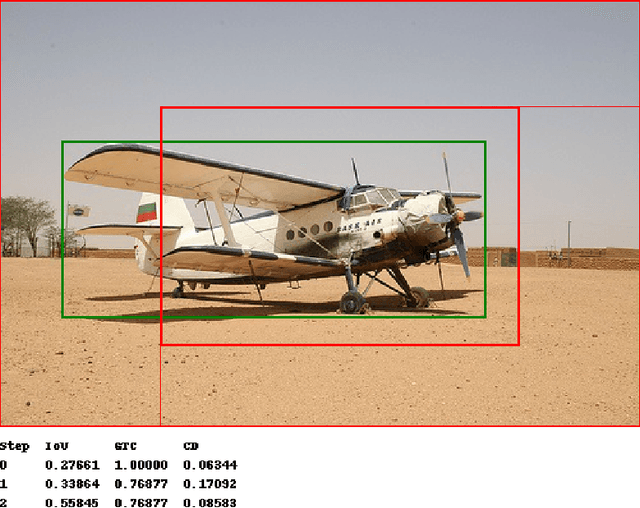
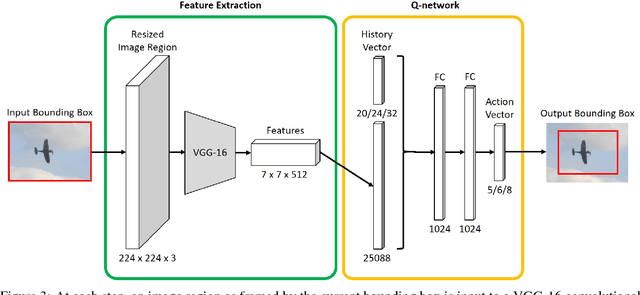
Abstract:We present a reinforcement learning approach for detecting objects within an image. Our approach performs a step-wise deformation of a bounding box with the goal of tightly framing the object. It uses a hierarchical tree-like representation of predefined region candidates, which the agent can zoom in on. This reduces the number of region candidates that must be evaluated so that the agent can afford to compute new feature maps before each step to enhance detection quality. We compare an approach that is based purely on zoom actions with one that is extended by a second refinement stage to fine-tune the bounding box after each zoom step. We also improve the fitting ability by allowing for different aspect ratios of the bounding box. Finally, we propose different reward functions to lead to a better guidance of the agent while following its search trajectories. Experiments indicate that each of these extensions leads to more correct detections. The best performing approach comprises a zoom stage and a refinement stage, uses aspect-ratio modifying actions and is trained using a combination of three different reward metrics.
Facial Key Points Detection using Deep Convolutional Neural Network - NaimishNet
Oct 03, 2017



Abstract:Facial Key Points (FKPs) Detection is an important and challenging problem in the fields of computer vision and machine learning. It involves predicting the co-ordinates of the FKPs, e.g. nose tip, center of eyes, etc, for a given face. In this paper, we propose a LeNet adapted Deep CNN model - NaimishNet, to operate on facial key points data and compare our model's performance against existing state of the art approaches.
AutoCompete: A Framework for Machine Learning Competition
Jul 08, 2015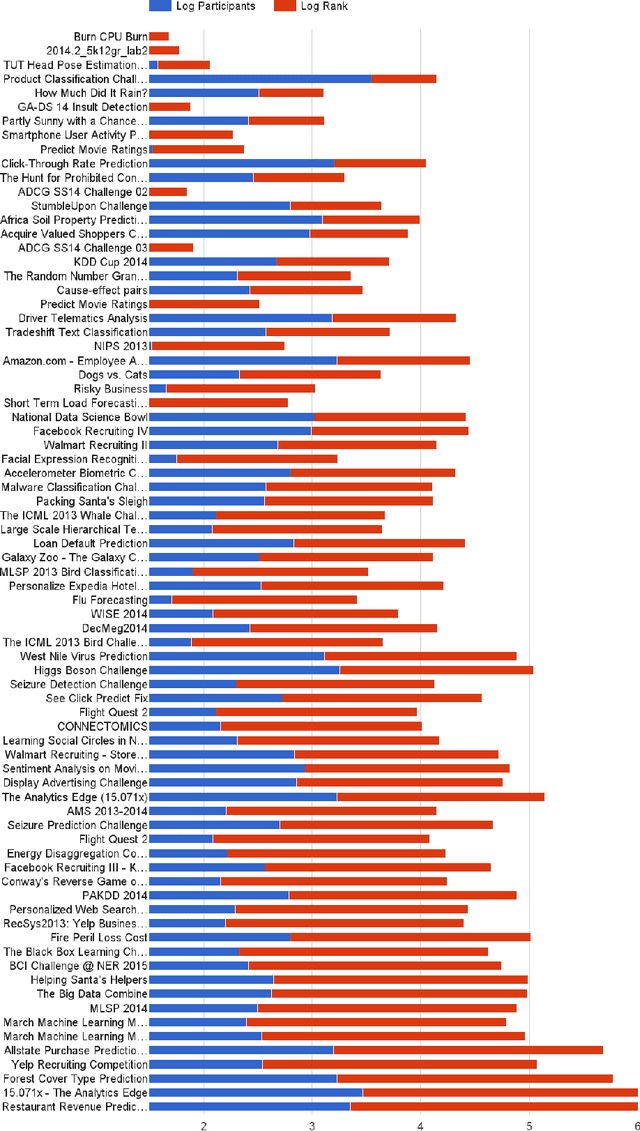
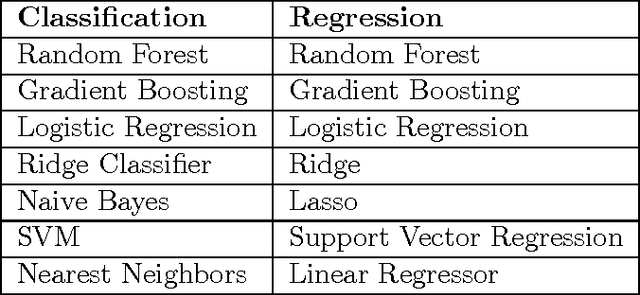
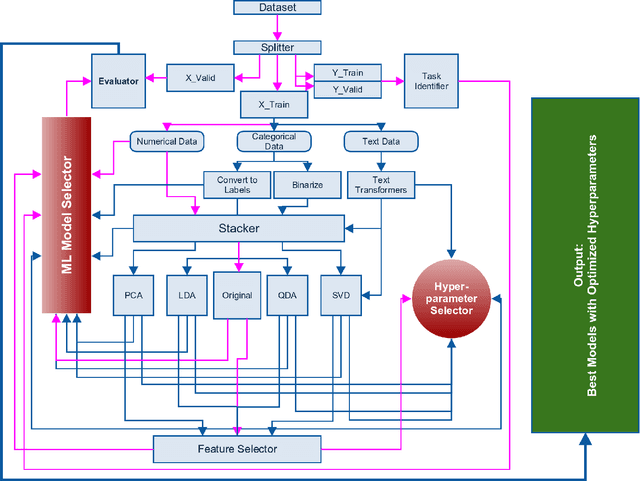
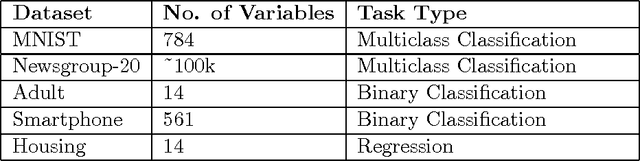
Abstract:In this paper, we propose AutoCompete, a highly automated machine learning framework for tackling machine learning competitions. This framework has been learned by us, validated and improved over a period of more than two years by participating in online machine learning competitions. It aims at minimizing human interference required to build a first useful predictive model and to assess the practical difficulty of a given machine learning challenge. The proposed system helps in identifying data types, choosing a machine learn- ing model, tuning hyper-parameters, avoiding over-fitting and optimization for a provided evaluation metric. We also observe that the proposed system produces better (or comparable) results with less runtime as compared to other approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge