Abhishek Goswami
Phi-4-Mini Technical Report: Compact yet Powerful Multimodal Language Models via Mixture-of-LoRAs
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Phi-4-Mini and Phi-4-Multimodal, compact yet highly capable language and multimodal models. Phi-4-Mini is a 3.8-billion-parameter language model trained on high-quality web and synthetic data, significantly outperforming recent open-source models of similar size and matching the performance of models twice its size on math and coding tasks requiring complex reasoning. This achievement is driven by a carefully curated synthetic data recipe emphasizing high-quality math and coding datasets. Compared to its predecessor, Phi-3.5-Mini, Phi-4-Mini features an expanded vocabulary size of 200K tokens to better support multilingual applications, as well as group query attention for more efficient long-sequence generation. Phi-4-Multimodal is a multimodal model that integrates text, vision, and speech/audio input modalities into a single model. Its novel modality extension approach leverages LoRA adapters and modality-specific routers to allow multiple inference modes combining various modalities without interference. For example, it now ranks first in the OpenASR leaderboard to date, although the LoRA component of the speech/audio modality has just 460 million parameters. Phi-4-Multimodal supports scenarios involving (vision + language), (vision + speech), and (speech/audio) inputs, outperforming larger vision-language and speech-language models on a wide range of tasks. Additionally, we experiment to further train Phi-4-Mini to enhance its reasoning capabilities. Despite its compact 3.8-billion-parameter size, this experimental version achieves reasoning performance on par with or surpassing significantly larger models, including DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B.
CapHDR2IR: Caption-Driven Transfer from Visible Light to Infrared Domain
Nov 25, 2024
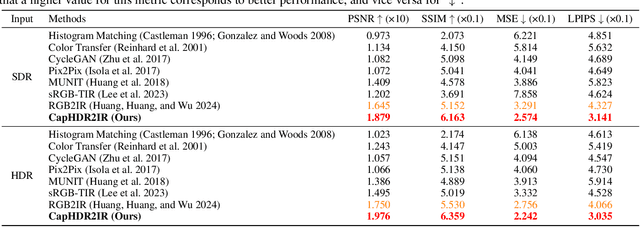

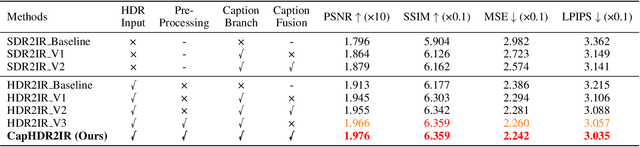
Abstract:Infrared (IR) imaging offers advantages in several fields due to its unique ability of capturing content in extreme light conditions. However, the demanding hardware requirements of high-resolution IR sensors limit its widespread application. As an alternative, visible light can be used to synthesize IR images but this causes a loss of fidelity in image details and introduces inconsistencies due to lack of contextual awareness of the scene. This stems from a combination of using visible light with a standard dynamic range, especially under extreme lighting, and a lack of contextual awareness can result in pseudo-thermal-crossover artifacts. This occurs when multiple objects with similar temperatures appear indistinguishable in the training data, further exacerbating the loss of fidelity. To solve this challenge, this paper proposes CapHDR2IR, a novel framework incorporating vision-language models using high dynamic range (HDR) images as inputs to generate IR images. HDR images capture a wider range of luminance variations, ensuring reliable IR image generation in different light conditions. Additionally, a dense caption branch integrates semantic understanding, resulting in more meaningful and discernible IR outputs. Extensive experiments on the HDRT dataset show that the proposed CapHDR2IR achieves state-of-the-art performance compared with existing general domain transfer methods and those tailored for visible-to-infrared image translation.
Semantic Aware Diffusion Inverse Tone Mapping
May 24, 2024



Abstract:The range of real-world scene luminance is larger than the capture capability of many digital camera sensors which leads to details being lost in captured images, most typically in bright regions. Inverse tone mapping attempts to boost these captured Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) images back to High Dynamic Range (HDR) by creating a mapping that linearizes the well exposed values from the SDR image, and provides a luminance boost to the clipped content. However, in most cases, the details in the clipped regions cannot be recovered or estimated. In this paper, we present a novel inverse tone mapping approach for mapping SDR images to HDR that generates lost details in clipped regions through a semantic-aware diffusion based inpainting approach. Our method proposes two major contributions - first, we propose to use a semantic graph to guide SDR diffusion based inpainting in masked regions in a saturated image. Second, drawing inspiration from traditional HDR imaging and bracketing methods, we propose a principled formulation to lift the SDR inpainted regions to HDR that is compatible with generative inpainting methods. Results show that our method demonstrates superior performance across different datasets on objective metrics, and subjective experiments show that the proposed method matches (and in most cases outperforms) state-of-art inverse tone mapping operators in terms of objective metrics and outperforms them for visual fidelity.
Phi-3 Technical Report: A Highly Capable Language Model Locally on Your Phone
Apr 23, 2024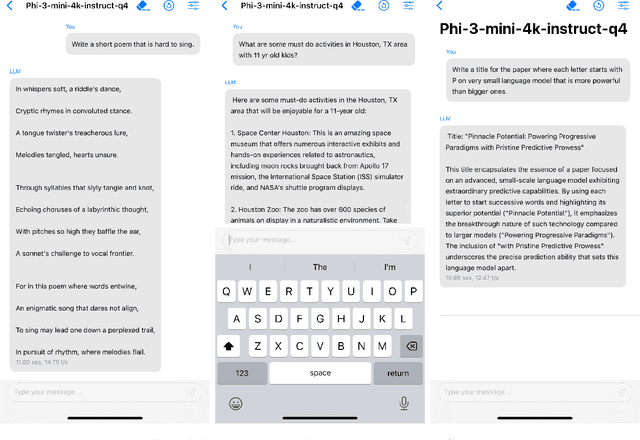
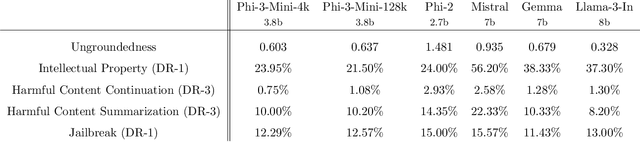
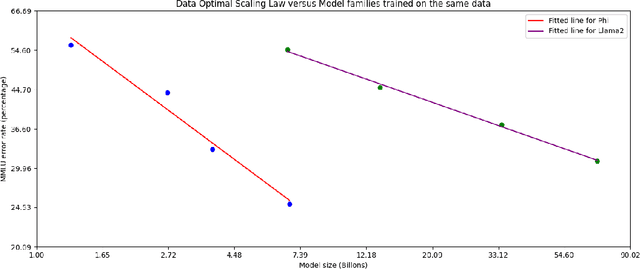
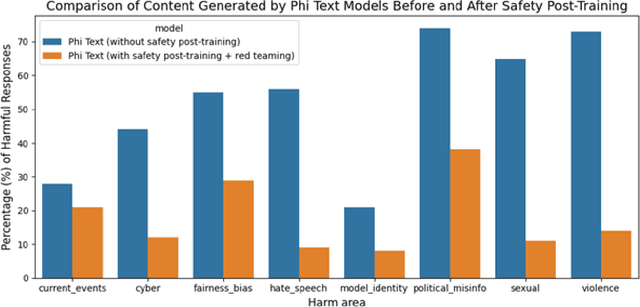
Abstract:We introduce phi-3-mini, a 3.8 billion parameter language model trained on 3.3 trillion tokens, whose overall performance, as measured by both academic benchmarks and internal testing, rivals that of models such as Mixtral 8x7B and GPT-3.5 (e.g., phi-3-mini achieves 69% on MMLU and 8.38 on MT-bench), despite being small enough to be deployed on a phone. The innovation lies entirely in our dataset for training, a scaled-up version of the one used for phi-2, composed of heavily filtered web data and synthetic data. The model is also further aligned for robustness, safety, and chat format. We also provide some initial parameter-scaling results with a 7B and 14B models trained for 4.8T tokens, called phi-3-small and phi-3-medium, both significantly more capable than phi-3-mini (e.g., respectively 75% and 78% on MMLU, and 8.7 and 8.9 on MT-bench).
G-SemTMO: Tone Mapping with a Trainable Semantic Graph
Aug 30, 2022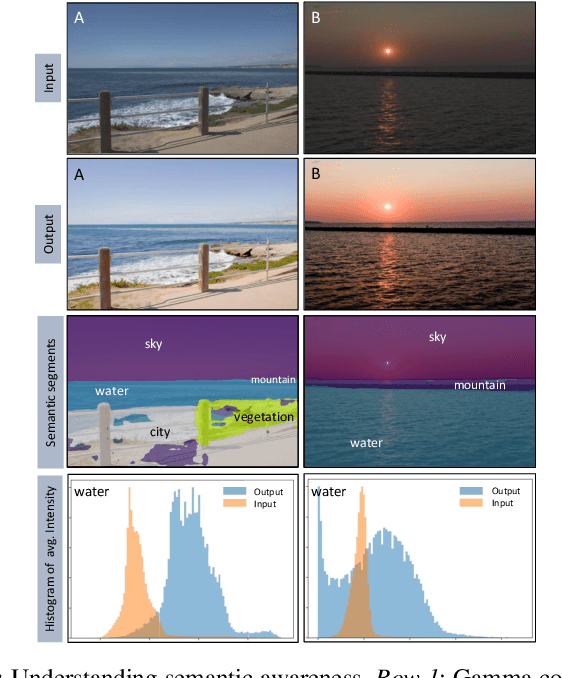
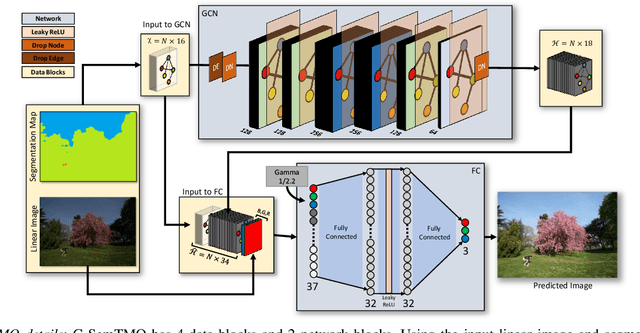
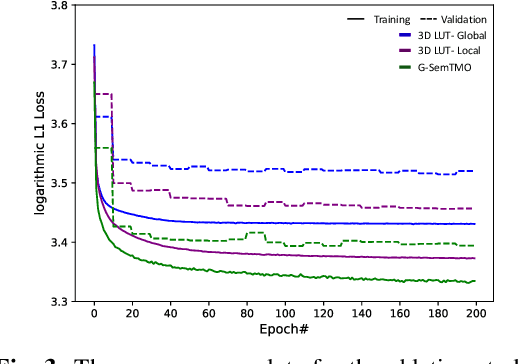

Abstract:A Tone Mapping Operator (TMO) is required to render images with a High Dynamic Range (HDR) on media with limited dynamic capabilities. TMOs compress the dynamic range with the aim of preserving the visually perceptual cues of the scene. Previous literature has established the benefits of TMOs being semantic aware, understanding the content in the scene to preserve the cues better. Expert photographers analyze the semantic and the contextual information of a scene and decide tonal transformations or local luminance adjustments. This process can be considered a manual analogy to tone mapping. In this work, we draw inspiration from an expert photographer's approach and present a Graph-based Semantic-aware Tone Mapping Operator, G-SemTMO. We leverage semantic information as well as the contextual information of the scene in the form of a graph capturing the spatial arrangements of its semantic segments. Using Graph Convolutional Network (GCN), we predict intermediate parameters called Semantic Hints and use these parameters to apply tonal adjustments locally to different semantic segments in the image. In addition, we also introduce LocHDR, a dataset of 781 HDR images tone mapped manually by an expert photo-retoucher with local tonal enhancements. We conduct ablation studies to show that our approach, G-SemTMO\footnote{Code and dataset to be published with the final version of the manuscript}, can learn both global and local tonal transformations from a pair of input linear and manually retouched images by leveraging the semantic graphs and produce better results than both classical and learning based TMOs. We also conduct ablation experiments to validate the advantage of using GCN.
Example-Based Named Entity Recognition
Aug 24, 2020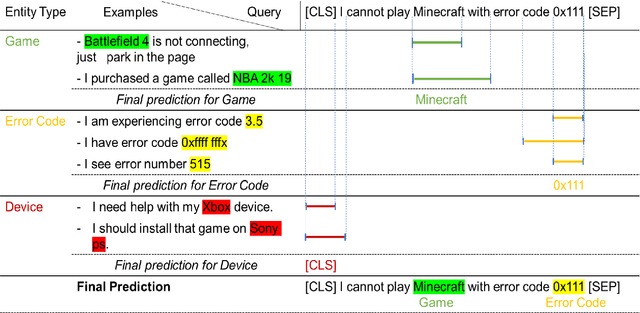
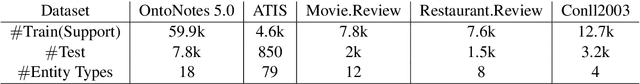
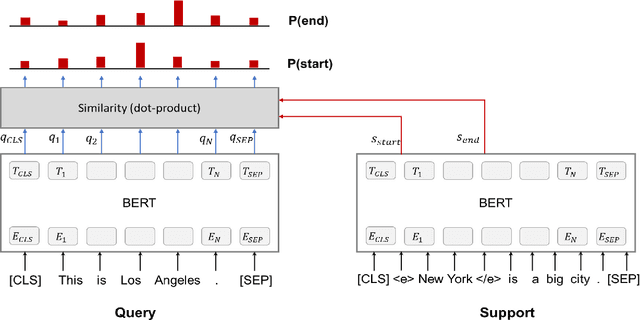
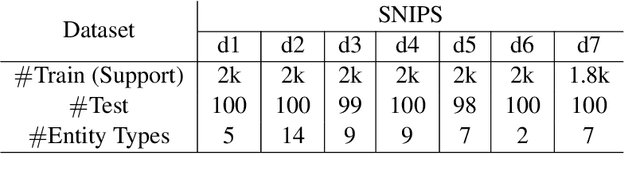
Abstract:We present a novel approach to named entity recognition (NER) in the presence of scarce data that we call example-based NER. Our train-free few-shot learning approach takes inspiration from question-answering to identify entity spans in a new and unseen domain. In comparison with the current state-of-the-art, the proposed method performs significantly better, especially when using a low number of support examples.
Machine Learning at Microsoft with ML .NET
May 15, 2019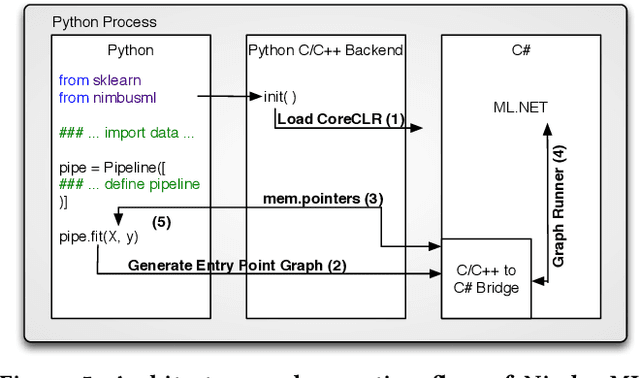
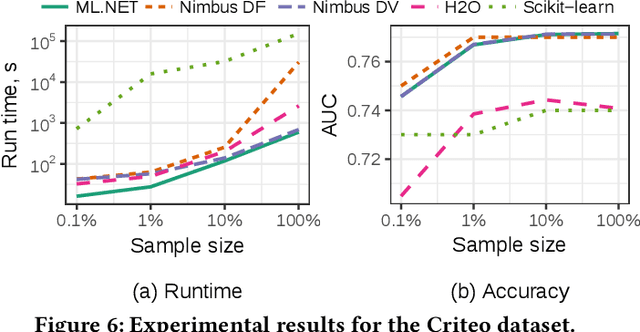
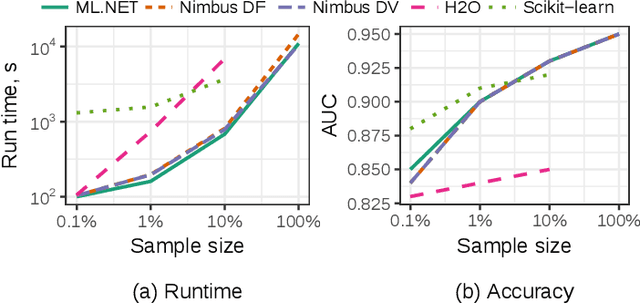
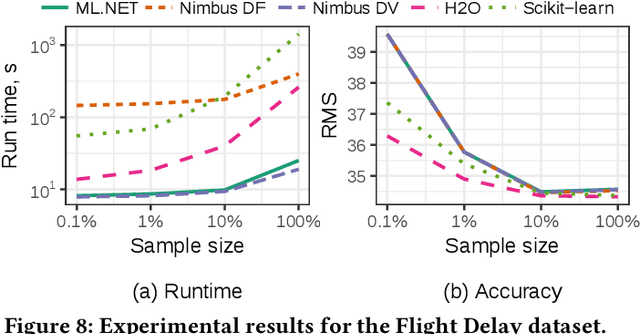
Abstract:Machine Learning is transitioning from an art and science into a technology available to every developer. In the near future, every application on every platform will incorporate trained models to encode data-based decisions that would be impossible for developers to author. This presents a significant engineering challenge, since currently data science and modeling are largely decoupled from standard software development processes. This separation makes incorporating machine learning capabilities inside applications unnecessarily costly and difficult, and furthermore discourage developers from embracing ML in first place. In this paper we present ML .NET, a framework developed at Microsoft over the last decade in response to the challenge of making it easy to ship machine learning models in large software applications. We present its architecture, and illuminate the application demands that shaped it. Specifically, we introduce DataView, the core data abstraction of ML .NET which allows it to capture full predictive pipelines efficiently and consistently across training and inference lifecycles. We close the paper with a surprisingly favorable performance study of ML .NET compared to more recent entrants, and a discussion of some lessons learned.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge