Music Genre Classification
Papers and Code
Bangla Music Genre Classification Using Bidirectional LSTMS
Jan 21, 2026Bangla music is enrich in its own music cultures. Now a days music genre classification is very significant because of the exponential increase in available music, both in digital and physical formats. It is necessary to index them accordingly to facilitate improved retrieval. Automatically classifying Bangla music by genre is essential for efficiently locating specific pieces within a vast and diverse music library. Prevailing methods for genre classification predominantly employ conventional machine learning or deep learning approaches. This work introduces a novel music dataset comprising ten distinct genres of Bangla music. For the task of audio classification, we utilize a recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture. Specifically, a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network is implemented to train the model and perform the classification. Feature extraction represents a foundational stage in audio data processing. This study utilizes Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) to transform raw audio waveforms into a compact and representative set of features. The proposed framework facilitates music genre classification by leveraging these extracted features. Experimental results demonstrate a classification accuracy of 78%, indicating the system's strong potential to enhance and streamline the organization of Bangla music genres.
Beyond Mapping : Domain-Invariant Representations via Spectral Embedding of Optimal Transport Plans
Jan 19, 2026Distributional shifts between training and inference time data remain a central challenge in machine learning, often leading to poor performance. It motivated the study of principled approaches for domain alignment, such as optimal transport based unsupervised domain adaptation, that relies on approximating Monge map using transport plans, which is sensitive to the transport problem regularization strategy and hyperparameters, and might yield biased domains alignment. In this work, we propose to interpret smoothed transport plans as adjacency matrices of bipartite graphs connecting source to target domain and derive domain-invariant samples' representations through spectral embedding. We evaluate our approach on acoustic adaptation benchmarks for music genre recognition, music-speech discrimination, as well as electrical cable defect detection and classification tasks using time domain reflection in different diagnosis settings, achieving overall strong performances.
Parallel Algorithms for Combined Regularized Support Vector Machines: Application in Music Genre Classification
Dec 08, 2025In the era of rapid development of artificial intelligence, its applications span across diverse fields, relying heavily on effective data processing and model optimization. Combined Regularized Support Vector Machines (CR-SVMs) can effectively handle the structural information among data features, but there is a lack of efficient algorithms in distributed-stored big data. To address this issue, we propose a unified optimization framework based on consensus structure. This framework is not only applicable to various loss functions and combined regularization terms but can also be effectively extended to non-convex regularization terms, showing strong scalability. Based on this framework, we develop a distributed parallel alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm to efficiently compute CR-SVMs when data is stored in a distributed manner. To ensure the convergence of the algorithm, we also introduce the Gaussian back-substitution method. Meanwhile, for the integrity of the paper, we introduce a new model, the sparse group lasso support vector machine (SGL-SVM), and apply it to music information retrieval. Theoretical analysis confirms that the computational complexity of the proposed algorithm is not affected by different regularization terms and loss functions, highlighting the universality of the parallel algorithm. Experiments on synthetic and free music archiv datasets demonstrate the reliability, stability, and efficiency of the algorithm.
Music4All A+A: A Multimodal Dataset for Music Information Retrieval Tasks
Sep 18, 2025Music is characterized by aspects related to different modalities, such as the audio signal, the lyrics, or the music video clips. This has motivated the development of multimodal datasets and methods for Music Information Retrieval (MIR) tasks such as genre classification or autotagging. Music can be described at different levels of granularity, for instance defining genres at the level of artists or music albums. However, most datasets for multimodal MIR neglect this aspect and provide data at the level of individual music tracks. We aim to fill this gap by providing Music4All Artist and Album (Music4All A+A), a dataset for multimodal MIR tasks based on music artists and albums. Music4All A+A is built on top of the Music4All-Onion dataset, an existing track-level dataset for MIR tasks. Music4All A+A provides metadata, genre labels, image representations, and textual descriptors for 6,741 artists and 19,511 albums. Furthermore, since Music4All A+A is built on top of Music4All-Onion, it allows access to other multimodal data at the track level, including user--item interaction data. This renders Music4All A+A suitable for a broad range of MIR tasks, including multimodal music recommendation, at several levels of granularity. To showcase the use of Music4All A+A, we carry out experiments on multimodal genre classification of artists and albums, including an analysis in missing-modality scenarios, and a quantitative comparison with genre classification in the movie domain. Our experiments show that images are more informative for classifying the genres of artists and albums, and that several multimodal models for genre classification struggle in generalizing across domains. We provide the code to reproduce our experiments at https://github.com/hcai-mms/Music4All-A-A, the dataset is linked in the repository and provided open-source under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
Training a Perceptual Model for Evaluating Auditory Similarity in Music Adversarial Attack
Sep 05, 2025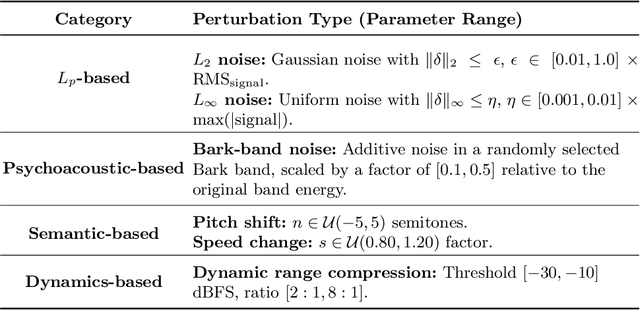
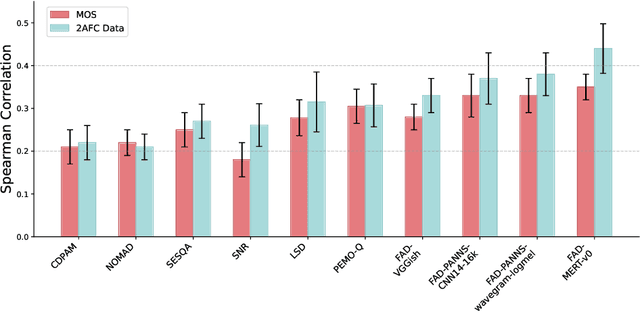
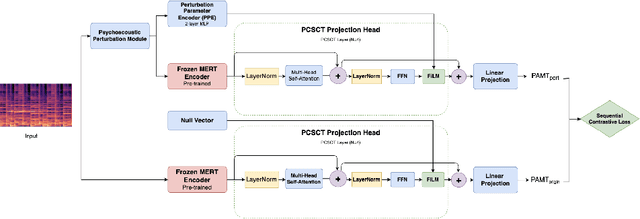
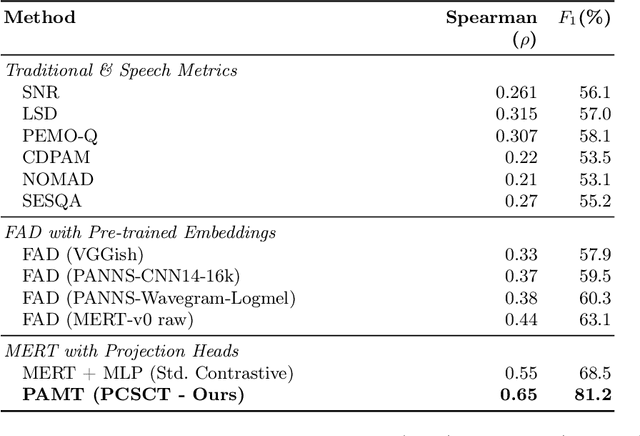
Music Information Retrieval (MIR) systems are highly vulnerable to adversarial attacks that are often imperceptible to humans, primarily due to a misalignment between model feature spaces and human auditory perception. Existing defenses and perceptual metrics frequently fail to adequately capture these auditory nuances, a limitation supported by our initial listening tests showing low correlation between common metrics and human judgments. To bridge this gap, we introduce Perceptually-Aligned MERT Transformer (PAMT), a novel framework for learning robust, perceptually-aligned music representations. Our core innovation lies in the psychoacoustically-conditioned sequential contrastive transformer, a lightweight projection head built atop a frozen MERT encoder. PAMT achieves a Spearman correlation coefficient of 0.65 with subjective scores, outperforming existing perceptual metrics. Our approach also achieves an average of 9.15\% improvement in robust accuracy on challenging MIR tasks, including Cover Song Identification and Music Genre Classification, under diverse perceptual adversarial attacks. This work pioneers architecturally-integrated psychoacoustic conditioning, yielding representations significantly more aligned with human perception and robust against music adversarial attacks.
X-ARES: A Comprehensive Framework for Assessing Audio Encoder Performance
May 22, 2025We introduces X-ARES (eXtensive Audio Representation and Evaluation Suite), a novel open-source benchmark designed to systematically assess audio encoder performance across diverse domains. By encompassing tasks spanning speech, environmental sounds, and music, X-ARES provides two evaluation approaches for evaluating audio representations: linear fine-tuning and unparameterized evaluation. The framework includes 22 distinct tasks that cover essential aspects of audio processing, from speech recognition and emotion detection to sound event classification and music genre identification. Our extensive evaluation of state-of-the-art audio encoders reveals significant performance variations across different tasks and domains, highlighting the complexity of general audio representation learning.
CMI-Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Music Instruction Following
Jun 14, 2025Recent advances in audio-text large language models (LLMs) have opened new possibilities for music understanding and generation. However, existing benchmarks are limited in scope, often relying on simplified tasks or multi-choice evaluations that fail to reflect the complexity of real-world music analysis. We reinterpret a broad range of traditional MIR annotations as instruction-following formats and introduce CMI-Bench, a comprehensive music instruction following benchmark designed to evaluate audio-text LLMs on a diverse set of music information retrieval (MIR) tasks. These include genre classification, emotion regression, emotion tagging, instrument classification, pitch estimation, key detection, lyrics transcription, melody extraction, vocal technique recognition, instrument performance technique detection, music tagging, music captioning, and (down)beat tracking: reflecting core challenges in MIR research. Unlike previous benchmarks, CMI-Bench adopts standardized evaluation metrics consistent with previous state-of-the-art MIR models, ensuring direct comparability with supervised approaches. We provide an evaluation toolkit supporting all open-source audio-textual LLMs, including LTU, Qwen-audio, SALMONN, MusiLingo, etc. Experiment results reveal significant performance gaps between LLMs and supervised models, along with their culture, chronological and gender bias, highlighting the potential and limitations of current models in addressing MIR tasks. CMI-Bench establishes a unified foundation for evaluating music instruction following, driving progress in music-aware LLMs.
Recognizing Ornaments in Vocal Indian Art Music with Active Annotation
May 07, 2025Ornamentations, embellishments, or microtonal inflections are essential to melodic expression across many musical traditions, adding depth, nuance, and emotional impact to performances. Recognizing ornamentations in singing voices is key to MIR, with potential applications in music pedagogy, singer identification, genre classification, and controlled singing voice generation. However, the lack of annotated datasets and specialized modeling approaches remains a major obstacle for progress in this research area. In this work, we introduce R\=aga Ornamentation Detection (ROD), a novel dataset comprising Indian classical music recordings curated by expert musicians. The dataset is annotated using a custom Human-in-the-Loop tool for six vocal ornaments marked as event-based labels. Using this dataset, we develop an ornamentation detection model based on deep time-series analysis, preserving ornament boundaries during the chunking of long audio recordings. We conduct experiments using different train-test configurations within the ROD dataset and also evaluate our approach on a separate, manually annotated dataset of Indian classical concert recordings. Our experimental results support the superior performance of our proposed approach over the baseline CRNN.
Progressive Rock Music Classification
Apr 15, 2025This study investigates the classification of progressive rock music, a genre characterized by complex compositions and diverse instrumentation, distinct from other musical styles. Addressing this Music Information Retrieval (MIR) task, we extracted comprehensive audio features, including spectrograms, Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs), chromagrams, and beat positions from song snippets using the Librosa library. A winner-take-all voting strategy was employed to aggregate snippet-level predictions into final song classifications. We conducted a comparative analysis of various machine learning techniques. Ensemble methods, encompassing Bagging (Random Forest, ExtraTrees, Bagging Classifier) and Boosting (XGBoost, Gradient Boosting), were explored, utilizing Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for dimensionality reduction to manage computational constraints with high-dimensional feature sets. Additionally, deep learning approaches were investigated, including the development of custom 1D Convolutional Neural Network (1D CNN) architectures (named "Zuck" and "Satya") featuring specific layer configurations, normalization, and activation functions. Furthermore, we fine-tuned a state-of-the-art Audio Spectrogram Transformer (AST) model, leveraging its attention-based mechanisms for audio classification. Performance evaluation on validation and test sets revealed varying effectiveness across models, with ensemble methods like Extra Trees achieving test accuracies up to 76.38%. This research provides insights into the application and relative performance of diverse machine learning paradigms for the nuanced task of progressive rock genre classification.
BAN: Neuroanatomical Aligning in Auditory Recognition between Artificial Neural Network and Human Cortex
Feb 21, 2025



Drawing inspiration from neurosciences, artificial neural networks (ANNs) have evolved from shallow architectures to highly complex, deep structures, yielding exceptional performance in auditory recognition tasks. However, traditional ANNs often struggle to align with brain regions due to their excessive depth and lack of biologically realistic features, like recurrent connection. To address this, a brain-like auditory network (BAN) is introduced, which incorporates four neuroanatomically mapped areas and recurrent connection, guided by a novel metric called the brain-like auditory score (BAS). BAS serves as a benchmark for evaluating the similarity between BAN and human auditory recognition pathway. We further propose that specific areas in the cerebral cortex, mainly the middle and medial superior temporal (T2/T3) areas, correspond to the designed network structure, drawing parallels with the brain's auditory perception pathway. Our findings suggest that the neuroanatomical similarity in the cortex and auditory classification abilities of the ANN are well-aligned. In addition to delivering excellent performance on a music genre classification task, the BAN demonstrates a high BAS score. In conclusion, this study presents BAN as a recurrent, brain-inspired ANN, representing the first model that mirrors the cortical pathway of auditory recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge