Joint Entity And Relation Extraction
Joint entity-and-relation extraction is the task of extracting entity mentions and semantic relations between entities from unstructured text with a single model.
Papers and Code
An LLM + ASP Workflow for Joint Entity-Relation Extraction
Aug 18, 2025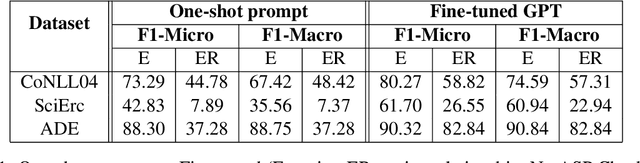
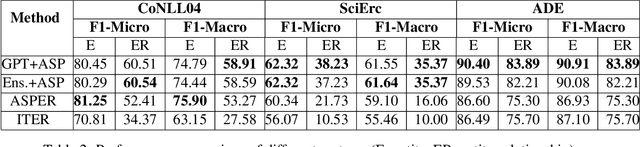
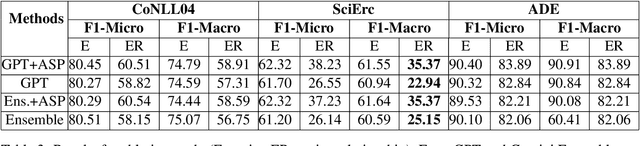
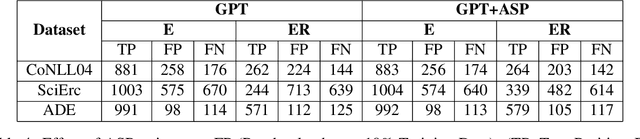
Joint entity-relation extraction (JERE) identifies both entities and their relationships simultaneously. Traditional machine-learning based approaches to performing this task require a large corpus of annotated data and lack the ability to easily incorporate domain specific information in the construction of the model. Therefore, creating a model for JERE is often labor intensive, time consuming, and elaboration intolerant. In this paper, we propose harnessing the capabilities of generative pretrained large language models (LLMs) and the knowledge representation and reasoning capabilities of Answer Set Programming (ASP) to perform JERE. We present a generic workflow for JERE using LLMs and ASP. The workflow is generic in the sense that it can be applied for JERE in any domain. It takes advantage of LLM's capability in natural language understanding in that it works directly with unannotated text. It exploits the elaboration tolerant feature of ASP in that no modification of its core program is required when additional domain specific knowledge, in the form of type specifications, is found and needs to be used. We demonstrate the usefulness of the proposed workflow through experiments with limited training data on three well-known benchmarks for JERE. The results of our experiments show that the LLM + ASP workflow is better than state-of-the-art JERE systems in several categories with only 10\% of training data. It is able to achieve a 2.5 times (35\% over 15\%) improvement in the Relation Extraction task for the SciERC corpus, one of the most difficult benchmarks.
Youtu-GraphRAG: Vertically Unified Agents for Graph Retrieval-Augmented Complex Reasoning
Aug 27, 2025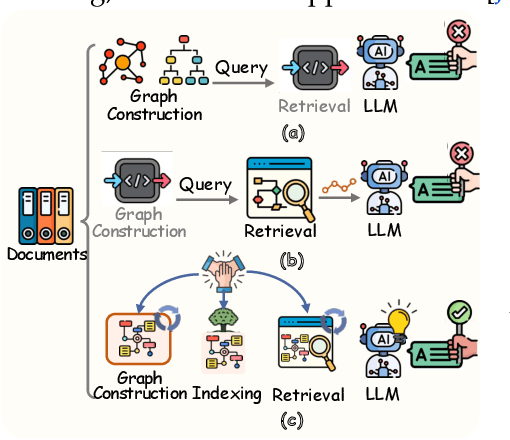
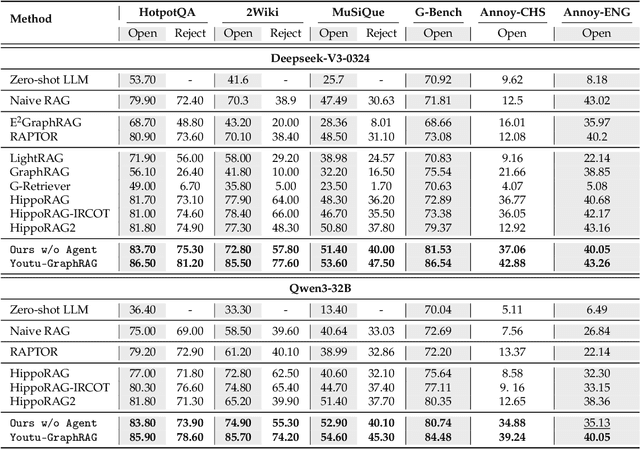
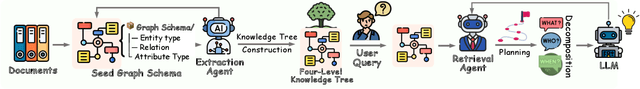
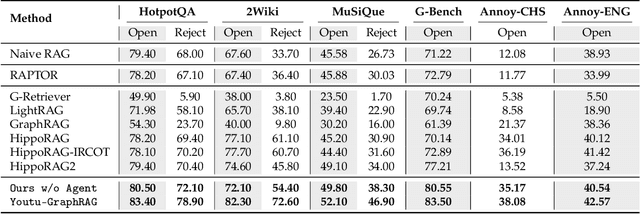
Graph retrieval-augmented generation (GraphRAG) has effectively enhanced large language models in complex reasoning by organizing fragmented knowledge into explicitly structured graphs. Prior efforts have been made to improve either graph construction or graph retrieval in isolation, yielding suboptimal performance, especially when domain shifts occur. In this paper, we propose a vertically unified agentic paradigm, Youtu-GraphRAG, to jointly connect the entire framework as an intricate integration. Specifically, (i) a seed graph schema is introduced to bound the automatic extraction agent with targeted entity types, relations and attribute types, also continuously expanded for scalability over unseen domains; (ii) To obtain higher-level knowledge upon the schema, we develop novel dually-perceived community detection, fusing structural topology with subgraph semantics for comprehensive knowledge organization. This naturally yields a hierarchical knowledge tree that supports both top-down filtering and bottom-up reasoning with community summaries; (iii) An agentic retriever is designed to interpret the same graph schema to transform complex queries into tractable and parallel sub-queries. It iteratively performs reflection for more advanced reasoning; (iv) To alleviate the knowledge leaking problem in pre-trained LLM, we propose a tailored anonymous dataset and a novel 'Anonymity Reversion' task that deeply measures the real performance of the GraphRAG frameworks. Extensive experiments across six challenging benchmarks demonstrate the robustness of Youtu-GraphRAG, remarkably moving the Pareto frontier with up to 90.71% saving of token costs and 16.62% higher accuracy over state-of-the-art baselines. The results indicate our adaptability, allowing seamless domain transfer with minimal intervention on schema.
Knowledge Graph-Infused Fine-Tuning for Structured Reasoning in Large Language Models
Aug 20, 2025This paper addresses the problems of missing reasoning chains and insufficient entity-level semantic understanding in large language models when dealing with tasks that require structured knowledge. It proposes a fine-tuning algorithm framework based on knowledge graph injection. The method builds on pretrained language models and introduces structured graph information for auxiliary learning. A graph neural network is used to encode entities and their relations, constructing a graph-based semantic representation. A fusion mechanism is then designed to jointly model the knowledge graph embeddings with the contextual representations from the language model. To enhance the robustness of knowledge integration, a gating mechanism is introduced to dynamically balance the contributions of linguistic semantics and structural knowledge. This effectively mitigates conflicts between different representational spaces. During training, a joint loss function is constructed to account for both task performance and structural alignment objectives. This helps improve the accuracy of entity prediction and semantic reasoning. The study also includes a series of systematic sensitivity experiments. It evaluates the effects of learning rate, graph coverage, and structural perturbations on model performance. The results further validate the effectiveness and stability of the proposed method across tasks such as entity recognition, question answering, and language generation. Experimental findings show that the proposed structure-aware fine-tuning framework significantly enhances the model's ability to represent complex semantic units. It demonstrates better semantic consistency and contextual logic modeling in scenarios involving structural reasoning and entity extraction.
Interim Report on Human-Guided Adaptive Hyperparameter Optimization with Multi-Fidelity Sprints
May 14, 2025This case study applies a phased hyperparameter optimization process to compare multitask natural language model variants that utilize multiphase learning rate scheduling and optimizer parameter grouping. We employ short, Bayesian optimization sessions that leverage multi-fidelity, hyperparameter space pruning, progressive halving, and a degree of human guidance. We utilize the Optuna TPE sampler and Hyperband pruner, as well as the Scikit-Learn Gaussian process minimization. Initially, we use efficient low-fidelity sprints to prune the hyperparameter space. Subsequent sprints progressively increase their model fidelity and employ hyperband pruning for efficiency. A second aspect of our approach is using a meta-learner to tune threshold values to resolve classification probabilities during inference. We demonstrate our method on a collection of variants of the 2021 Joint Entity and Relation Extraction model proposed by Eberts and Ulges.
Towards a More Generalized Approach in Open Relation Extraction
May 28, 2025Open Relation Extraction (OpenRE) seeks to identify and extract novel relational facts between named entities from unlabeled data without pre-defined relation schemas. Traditional OpenRE methods typically assume that the unlabeled data consists solely of novel relations or is pre-divided into known and novel instances. However, in real-world scenarios, novel relations are arbitrarily distributed. In this paper, we propose a generalized OpenRE setting that considers unlabeled data as a mixture of both known and novel instances. To address this, we propose MixORE, a two-phase framework that integrates relation classification and clustering to jointly learn known and novel relations. Experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that MixORE consistently outperforms competitive baselines in known relation classification and novel relation clustering. Our findings contribute to the advancement of generalized OpenRE research and real-world applications.
The Joint Entity-Relation Extraction Model Based on Span and Interactive Fusion Representation for Chinese Medical Texts with Complex Semantics
Feb 13, 2025Joint entity-relation extraction is a critical task in transforming unstructured or semi-structured text into triplets, facilitating the construction of large-scale knowledge graphs, and supporting various downstream applications. Despite its importance, research on Chinese text, particularly with complex semantics in specialized domains like medicine, remains limited. To address this gap, we introduce the CH-DDI, a Chinese drug-drug interactions dataset designed to capture the intricacies of medical text. Leveraging the strengths of attention mechanisms in capturing long-range dependencies, we propose the SEA module, which enhances the extraction of complex contextual semantic information, thereby improving entity recognition and relation extraction. Additionally, to address the inefficiencies of existing methods in facilitating information exchange between entity recognition and relation extraction, we present an interactive fusion representation module. This module employs Cross Attention for bidirectional information exchange between the tasks and further refines feature extraction through BiLSTM. Experimental results on both our CH-DDI dataset and public CoNLL04 dataset demonstrate that our model exhibits strong generalization capabilities. On the CH-DDI dataset, our model achieves an F1-score of 96.73% for entity recognition and 78.43% for relation extraction. On the CoNLL04 dataset, it attains an entity recognition precision of 89.54% and a relation extraction accuracy of 71.64%.
FinTagging: An LLM-ready Benchmark for Extracting and Structuring Financial Information
May 27, 2025We introduce FinTagging, the first full-scope, table-aware XBRL benchmark designed to evaluate the structured information extraction and semantic alignment capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in the context of XBRL-based financial reporting. Unlike prior benchmarks that oversimplify XBRL tagging as flat multi-class classification and focus solely on narrative text, FinTagging decomposes the XBRL tagging problem into two subtasks: FinNI for financial entity extraction and FinCL for taxonomy-driven concept alignment. It requires models to jointly extract facts and align them with the full 10k+ US-GAAP taxonomy across both unstructured text and structured tables, enabling realistic, fine-grained evaluation. We assess a diverse set of LLMs under zero-shot settings, systematically analyzing their performance on both subtasks and overall tagging accuracy. Our results reveal that, while LLMs demonstrate strong generalization in information extraction, they struggle with fine-grained concept alignment, particularly in disambiguating closely related taxonomy entries. These findings highlight the limitations of existing LLMs in fully automating XBRL tagging and underscore the need for improved semantic reasoning and schema-aware modeling to meet the demands of accurate financial disclosure. Code is available at our GitHub repository and data is at our Hugging Face repository.
Few-Shot Joint Multimodal Entity-Relation Extraction via Knowledge-Enhanced Cross-modal Prompt Model
Oct 18, 2024
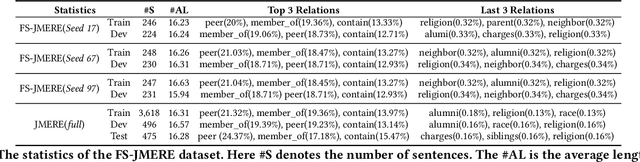

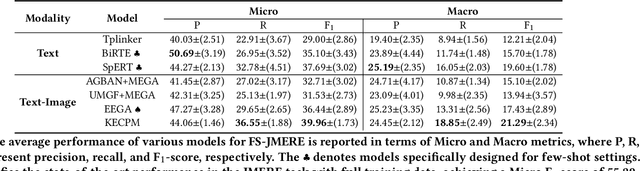
Joint Multimodal Entity-Relation Extraction (JMERE) is a challenging task that aims to extract entities and their relations from text-image pairs in social media posts. Existing methods for JMERE require large amounts of labeled data. However, gathering and annotating fine-grained multimodal data for JMERE poses significant challenges. Initially, we construct diverse and comprehensive multimodal few-shot datasets fitted to the original data distribution. To address the insufficient information in the few-shot setting, we introduce the \textbf{K}nowledge-\textbf{E}nhanced \textbf{C}ross-modal \textbf{P}rompt \textbf{M}odel (KECPM) for JMERE. This method can effectively address the problem of insufficient information in the few-shot setting by guiding a large language model to generate supplementary background knowledge. Our proposed method comprises two stages: (1) a knowledge ingestion stage that dynamically formulates prompts based on semantic similarity guide ChatGPT generating relevant knowledge and employs self-reflection to refine the knowledge; (2) a knowledge-enhanced language model stage that merges the auxiliary knowledge with the original input and utilizes a transformer-based model to align with JMERE's required output format. We extensively evaluate our approach on a few-shot dataset derived from the JMERE dataset, demonstrating its superiority over strong baselines in terms of both micro and macro F$_1$ scores. Additionally, we present qualitative analyses and case studies to elucidate the effectiveness of our model.
Enhancing Biomedical Relation Extraction with Directionality
Jan 23, 2025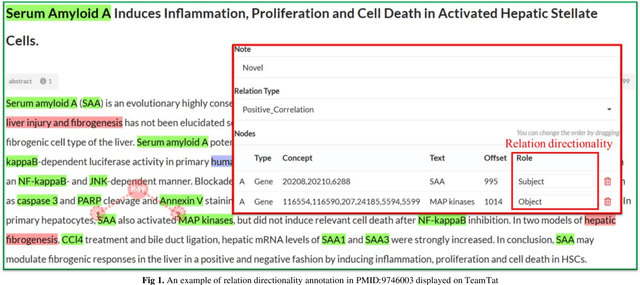
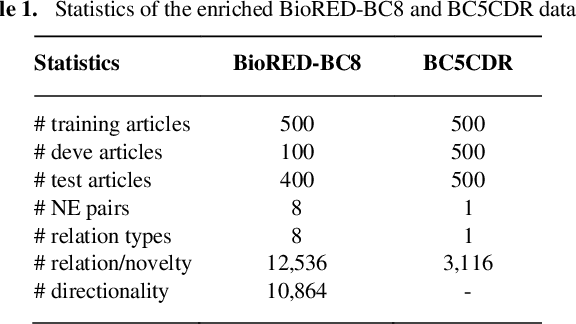
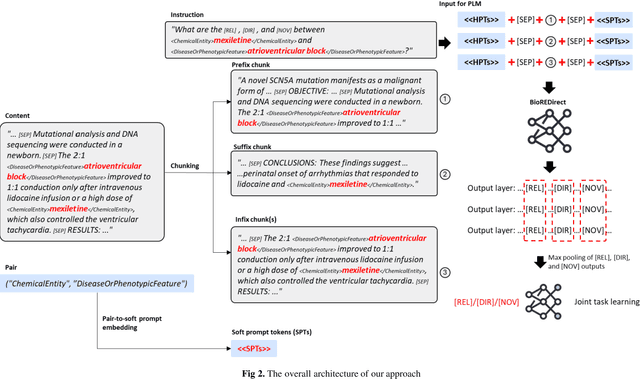
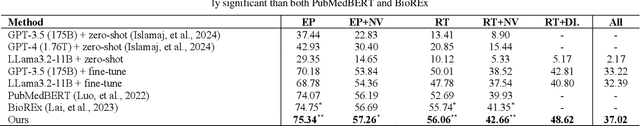
Biological relation networks contain rich information for understanding the biological mechanisms behind the relationship of entities such as genes, proteins, diseases, and chemicals. The vast growth of biomedical literature poses significant challenges updating the network knowledge. The recent Biomedical Relation Extraction Dataset (BioRED) provides valuable manual annotations, facilitating the develop-ment of machine-learning and pre-trained language model approaches for automatically identifying novel document-level (inter-sentence context) relationships. Nonetheless, its annotations lack directionality (subject/object) for the entity roles, essential for studying complex biological networks. Herein we annotate the entity roles of the relationships in the BioRED corpus and subsequently propose a novel multi-task language model with soft-prompt learning to jointly identify the relationship, novel findings, and entity roles. Our results in-clude an enriched BioRED corpus with 10,864 directionality annotations. Moreover, our proposed method outperforms existing large language models such as the state-of-the-art GPT-4 and Llama-3 on two benchmarking tasks. Our source code and dataset are available at https://github.com/ncbi-nlp/BioREDirect.
UniQ: Unified Decoder with Task-specific Queries for Efficient Scene Graph Generation
Jan 10, 2025



Scene Graph Generation(SGG) is a scene understanding task that aims at identifying object entities and reasoning their relationships within a given image. In contrast to prevailing two-stage methods based on a large object detector (e.g., Faster R-CNN), one-stage methods integrate a fixed-size set of learnable queries to jointly reason relational triplets <subject, predicate, object>. This paradigm demonstrates robust performance with significantly reduced parameters and computational overhead. However, the challenge in one-stage methods stems from the issue of weak entanglement, wherein entities involved in relationships require both coupled features shared within triplets and decoupled visual features. Previous methods either adopt a single decoder for coupled triplet feature modeling or multiple decoders for separate visual feature extraction but fail to consider both. In this paper, we introduce UniQ, a Unified decoder with task-specific Queries architecture, where task-specific queries generate decoupled visual features for subjects, objects, and predicates respectively, and unified decoder enables coupled feature modeling within relational triplets. Experimental results on the Visual Genome dataset demonstrate that UniQ has superior performance to both one-stage and two-stage methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge