Headlines Dataset
Papers and Code
Acting Flatterers via LLMs Sycophancy: Combating Clickbait with LLMs Opposing-Stance Reasoning
Jan 17, 2026The widespread proliferation of online content has intensified concerns about clickbait, deceptive or exaggerated headlines designed to attract attention. While Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising avenue for addressing this issue, their effectiveness is often hindered by Sycophancy, a tendency to produce reasoning that matches users' beliefs over truthful ones, which deviates from instruction-following principles. Rather than treating sycophancy as a flaw to be eliminated, this work proposes a novel approach that initially harnesses this behavior to generate contrastive reasoning from opposing perspectives. Specifically, we design a Self-renewal Opposing-stance Reasoning Generation (SORG) framework that prompts LLMs to produce high-quality agree and disagree reasoning pairs for a given news title without requiring ground-truth labels. To utilize the generated reasoning, we develop a local Opposing Reasoning-based Clickbait Detection (ORCD) model that integrates three BERT encoders to represent the title and its associated reasoning. The model leverages contrastive learning, guided by soft labels derived from LLM-generated credibility scores, to enhance detection robustness. Experimental evaluations on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms LLM prompting, fine-tuned smaller language models, and state-of-the-art clickbait detection baselines.
PartisanLens: A Multilingual Dataset of Hyperpartisan and Conspiratorial Immigration Narratives in European Media
Jan 07, 2026Detecting hyperpartisan narratives and Population Replacement Conspiracy Theories (PRCT) is essential to addressing the spread of misinformation. These complex narratives pose a significant threat, as hyperpartisanship drives political polarisation and institutional distrust, while PRCTs directly motivate real-world extremist violence, making their identification critical for social cohesion and public safety. However, existing resources are scarce, predominantly English-centric, and often analyse hyperpartisanship, stance, and rhetorical bias in isolation rather than as interrelated aspects of political discourse. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textsc{PartisanLens}, the first multilingual dataset of \num{1617} hyperpartisan news headlines in Spanish, Italian, and Portuguese, annotated in multiple political discourse aspects. We first evaluate the classification performance of widely used Large Language Models (LLMs) on this dataset, establishing robust baselines for the classification of hyperpartisan and PRCT narratives. In addition, we assess the viability of using LLMs as automatic annotators for this task, analysing their ability to approximate human annotation. Results highlight both their potential and current limitations. Next, moving beyond standard judgments, we explore whether LLMs can emulate human annotation patterns by conditioning them on socio-economic and ideological profiles that simulate annotator perspectives. At last, we provide our resources and evaluation, \textsc{PartisanLens} supports future research on detecting partisan and conspiratorial narratives in European contexts.
When a Nation Speaks: Machine Learning and NLP in People's Sentiment Analysis During Bangladesh's 2024 Mass Uprising
Dec 17, 2025Sentiment analysis, an emerging research area within natural language processing (NLP), has primarily been explored in contexts like elections and social media trends, but there remains a significant gap in understanding emotional dynamics during civil unrest, particularly in the Bangla language. Our study pioneers sentiment analysis in Bangla during a national crisis by examining public emotions amid Bangladesh's 2024 mass uprising. We curated a unique dataset of 2,028 annotated news headlines from major Facebook news portals, classifying them into Outrage, Hope, and Despair. Through Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), we identified prevalent themes like political corruption and public protests, and analyzed how events such as internet blackouts shaped sentiment patterns. It outperformed multilingual transformers (mBERT: 67%, XLM-RoBERTa: 71%) and traditional machine learning methods (SVM and Logistic Regression: both 70%). These results highlight the effectiveness of language-specific models and offer valuable insights into public sentiment during political turmoil.
Cardiac mortality prediction in patients undergoing PCI based on real and synthetic data
Dec 24, 2025Patient status, angiographic and procedural characteristics encode crucial signals for predicting long-term outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The aim of the study was to develop a predictive model for assessing the risk of cardiac death based on the real and synthetic data of patients undergoing PCI and to identify the factors that have the greatest impact on mortality. We analyzed 2,044 patients, who underwent a PCI for bifurcation lesions. The primary outcome was cardiac death at 3-year follow-up. Several machine learning models were applied to predict three-year mortality after PCI. To address class imbalance and improve the representation of the minority class, an additional 500 synthetic samples were generated and added to the training set. To evaluate the contribution of individual features to model performance, we applied permutation feature importance. An additional experiment was conducted to evaluate how the model's predictions would change after removing non-informative features from the training and test datasets. Without oversampling, all models achieve high overall accuracy (0.92-0.93), yet they almost completely ignore the minority class. Across models, augmentation consistently increases minority-class recall with minimal loss of AUROC, improves probability quality, and yields more clinically reasonable risk estimates on the constructed severe profiles. According to feature importance analysis, four features emerged as the most influential: Age, Ejection Fraction, Peripheral Artery Disease, and Cerebrovascular Disease. These results show that straightforward augmentation with realistic and extreme cases can expose, quantify, and reduce brittleness in imbalanced clinical prediction using only tabular records, and motivate routine reporting of probability quality and stress tests alongside headline metrics.
Adaptive Financial Sentiment Analysis for NIFTY 50 via Instruction-Tuned LLMs , RAG and Reinforcement Learning Approaches
Dec 24, 2025Financial sentiment analysis plays a crucial role in informing investment decisions, assessing market risk, and predicting stock price trends. Existing works in financial sentiment analysis have not considered the impact of stock prices or market feedback on sentiment analysis. In this paper, we propose an adaptive framework that integrates large language models (LLMs) with real-world stock market feedback to improve sentiment classification in the context of the Indian stock market. The proposed methodology fine-tunes the LLaMA 3.2 3B model using instruction-based learning on the SentiFin dataset. To enhance sentiment predictions, a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipeline is employed that dynamically selects multi-source contextual information based on the cosine similarity of the sentence embeddings. Furthermore, a feedback-driven module is introduced that adjusts the reliability of the source by comparing predicted sentiment with actual next-day stock returns, allowing the system to iteratively adapt to market behavior. To generalize this adaptive mechanism across temporal data, a reinforcement learning agent trained using proximal policy optimization (PPO) is incorporated. The PPO agent learns to optimize source weighting policies based on cumulative reward signals from sentiment-return alignment. Experimental results on NIFTY 50 news headlines collected from 2024 to 2025 demonstrate that the proposed system significantly improves classification accuracy, F1-score, and market alignment over baseline models and static retrieval methods. The results validate the potential of combining instruction-tuned LLMs with dynamic feedback and reinforcement learning for robust, market-aware financial sentiment modeling.
Comparative Evaluation of Embedding Representations for Financial News Sentiment Analysis
Dec 15, 2025Financial sentiment analysis enhances market understanding; however, standard natural language processing approaches encounter significant challenges when applied to small datasets. This study provides a comparative evaluation of embedding-based methods for financial news sentiment classification in resource-constrained environments. Word2Vec, GloVe, and sentence transformer representations are evaluated in combination with gradient boosting on manually labeled headlines. Experimental results identify a substantial gap between validation and test performance, with models performing worse than trivial baselines despite strong validation metrics. The analysis demonstrates that pretrained embeddings yield diminishing returns below a critical data sufficiency threshold, and that small validation sets contribute to overfitting during model selection. Practical application is illustrated through weekly sentiment aggregation and narrative summarization for market monitoring workflows. The findings offer empirical evidence that embedding quality alone cannot address fundamental data scarcity in sentiment classification. For practitioners operating with limited resources, the results indicate the need to consider alternative approaches such as few-shot learning, data augmentation, or lexicon-enhanced hybrid methods when labeled samples are scarce.
A Hybrid Model for Stock Market Forecasting: Integrating News Sentiment and Time Series Data with Graph Neural Networks
Dec 09, 2025Stock market prediction is a long-standing challenge in finance, as accurate forecasts support informed investment decisions. Traditional models rely mainly on historical prices, but recent work shows that financial news can provide useful external signals. This paper investigates a multimodal approach that integrates companies' news articles with their historical stock data to improve prediction performance. We compare a Graph Neural Network (GNN) model with a baseline LSTM model. Historical data for each company is encoded using an LSTM, while news titles are embedded with a language model. These embeddings form nodes in a heterogeneous graph, and GraphSAGE is used to capture interactions between articles, companies, and industries. We evaluate two targets: a binary direction-of-change label and a significance-based label. Experiments on the US equities and Bloomberg datasets show that the GNN outperforms the LSTM baseline, achieving 53% accuracy on the first target and a 4% precision gain on the second. Results also indicate that companies with more associated news yield higher prediction accuracy. Moreover, headlines contain stronger predictive signals than full articles, suggesting that concise news summaries play an important role in short-term market reactions.
* 11 pages, 6 figures. Published in the Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Research (ICAIR 2025). Published version available at: https://papers.academic-conferences.org/index.php/icair/article/view/4294
Efficient Zero-Shot Long Document Classification by Reducing Context Through Sentence Ranking
Aug 24, 2025Transformer-based models like BERT excel at short text classification but struggle with long document classification (LDC) due to input length limitations and computational inefficiencies. In this work, we propose an efficient, zero-shot approach to LDC that leverages sentence ranking to reduce input context without altering the model architecture. Our method enables the adaptation of models trained on short texts, such as headlines, to long-form documents by selecting the most informative sentences using a TF-IDF-based ranking strategy. Using the MahaNews dataset of long Marathi news articles, we evaluate three context reduction strategies that prioritize essential content while preserving classification accuracy. Our results show that retaining only the top 50\% ranked sentences maintains performance comparable to full-document inference while reducing inference time by up to 35\%. This demonstrates that sentence ranking is a simple yet effective technique for scalable and efficient zero-shot LDC.
Beyond Quality: Unlocking Diversity in Ad Headline Generation with Large Language Models
Aug 26, 2025
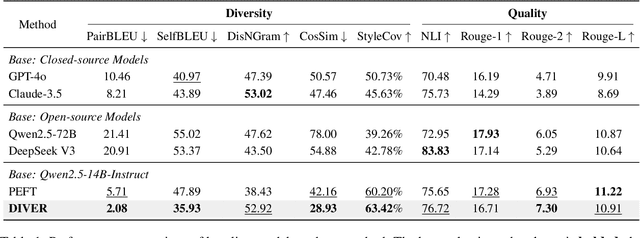
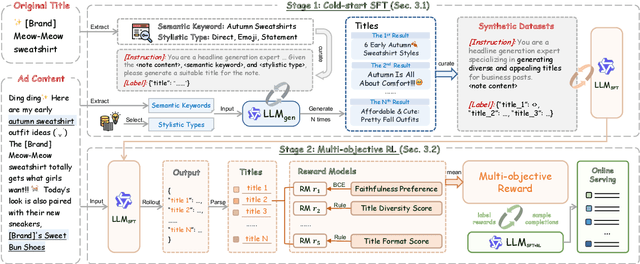
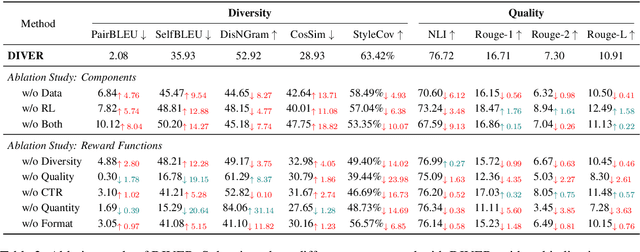
The generation of ad headlines plays a vital role in modern advertising, where both quality and diversity are essential to engage a broad range of audience segments. Current approaches primarily optimize language models for headline quality or click-through rates (CTR), often overlooking the need for diversity and resulting in homogeneous outputs. To address this limitation, we propose DIVER, a novel framework based on large language models (LLMs) that are jointly optimized for both diversity and quality. We first design a semantic- and stylistic-aware data generation pipeline that automatically produces high-quality training pairs with ad content and multiple diverse headlines. To achieve the goal of generating high-quality and diversified ad headlines within a single forward pass, we propose a multi-stage multi-objective optimization framework with supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL). Experiments on real-world industrial datasets demonstrate that DIVER effectively balances quality and diversity. Deployed on a large-scale content-sharing platform serving hundreds of millions of users, our framework improves advertiser value (ADVV) and CTR by 4.0% and 1.4%.
Improved Personalized Headline Generation via Denoising Fake Interests from Implicit Feedback
Aug 10, 2025Accurate personalized headline generation hinges on precisely capturing user interests from historical behaviors. However, existing methods neglect personalized-irrelevant click noise in entire historical clickstreams, which may lead to hallucinated headlines that deviate from genuine user preferences. In this paper, we reveal the detrimental impact of click noise on personalized generation quality through rigorous analysis in both user and news dimensions. Based on these insights, we propose a novel Personalized Headline Generation framework via Denoising Fake Interests from Implicit Feedback (PHG-DIF). PHG-DIF first employs dual-stage filtering to effectively remove clickstream noise, identified by short dwell times and abnormal click bursts, and then leverages multi-level temporal fusion to dynamically model users' evolving and multi-faceted interests for precise profiling. Moreover, we release DT-PENS, a new benchmark dataset comprising the click behavior of 1,000 carefully curated users and nearly 10,000 annotated personalized headlines with historical dwell time annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PHG-DIF substantially mitigates the adverse effects of click noise and significantly improves headline quality, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on DT-PENS. Our framework implementation and dataset are available at https://github.com/liukejin-up/PHG-DIF.
* Accepted by the 34th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM '25), Full Research Papers track
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge