Yuanhang Zheng
Beyond Quality: Unlocking Diversity in Ad Headline Generation with Large Language Models
Aug 26, 2025
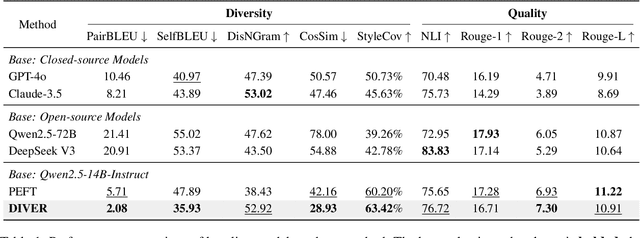
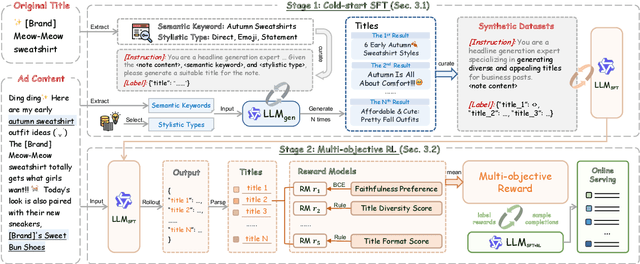
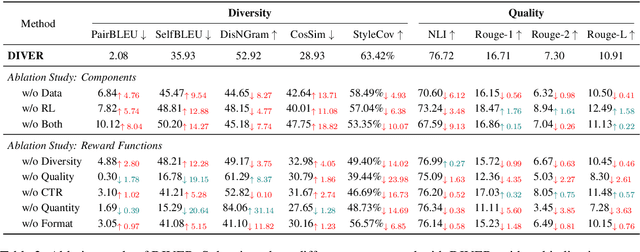
Abstract:The generation of ad headlines plays a vital role in modern advertising, where both quality and diversity are essential to engage a broad range of audience segments. Current approaches primarily optimize language models for headline quality or click-through rates (CTR), often overlooking the need for diversity and resulting in homogeneous outputs. To address this limitation, we propose DIVER, a novel framework based on large language models (LLMs) that are jointly optimized for both diversity and quality. We first design a semantic- and stylistic-aware data generation pipeline that automatically produces high-quality training pairs with ad content and multiple diverse headlines. To achieve the goal of generating high-quality and diversified ad headlines within a single forward pass, we propose a multi-stage multi-objective optimization framework with supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL). Experiments on real-world industrial datasets demonstrate that DIVER effectively balances quality and diversity. Deployed on a large-scale content-sharing platform serving hundreds of millions of users, our framework improves advertiser value (ADVV) and CTR by 4.0% and 1.4%.
How Good are LLMs at Relation Extraction under Low-Resource Scenario? Comprehensive Evaluation
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Relation Extraction (RE) serves as a crucial technology for transforming unstructured text into structured information, especially within the framework of Knowledge Graph development. Its importance is emphasized by its essential role in various downstream tasks. Besides the conventional RE methods which are based on neural networks and pre-trained language models, large language models (LLMs) are also utilized in the research field of RE. However, on low-resource languages (LRLs), both conventional RE methods and LLM-based methods perform poorly on RE due to the data scarcity issues. To this end, this paper constructs low-resource relation extraction datasets in 10 LRLs in three regions (Central Asia, Southeast Asia and Middle East). The corpora are constructed by translating the original publicly available English RE datasets (NYT10, FewRel and CrossRE) using an effective multilingual machine translation. Then, we use the language perplexity (PPL) to filter out the low-quality data from the translated datasets. Finally, we conduct an empirical study and validate the performance of several open-source LLMs on these generated LRL RE datasets.
ToolRerank: Adaptive and Hierarchy-Aware Reranking for Tool Retrieval
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Tool learning aims to extend the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) with external tools. A major challenge in tool learning is how to support a large number of tools, including unseen tools. To address this challenge, previous studies have proposed retrieving suitable tools for the LLM based on the user query. However, previously proposed methods do not consider the differences between seen and unseen tools, nor do they take the hierarchy of the tool library into account, which may lead to suboptimal performance for tool retrieval. Therefore, to address the aforementioned issues, we propose ToolRerank, an adaptive and hierarchy-aware reranking method for tool retrieval to further refine the retrieval results. Specifically, our proposed ToolRerank includes Adaptive Truncation, which truncates the retrieval results related to seen and unseen tools at different positions, and Hierarchy-Aware Reranking, which makes retrieval results more concentrated for single-tool queries and more diverse for multi-tool queries. Experimental results show that ToolRerank can improve the quality of the retrieval results, leading to better execution results generated by the LLM.
Improving Cross-lingual Representation for Semantic Retrieval with Code-switching
Mar 03, 2024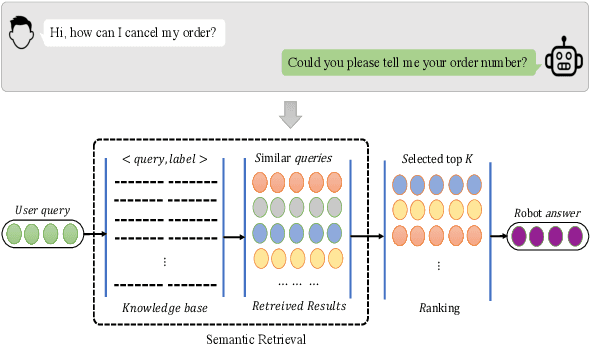



Abstract:Semantic Retrieval (SR) has become an indispensable part of the FAQ system in the task-oriented question-answering (QA) dialogue scenario. The demands for a cross-lingual smart-customer-service system for an e-commerce platform or some particular business conditions have been increasing recently. Most previous studies exploit cross-lingual pre-trained models (PTMs) for multi-lingual knowledge retrieval directly, while some others also leverage the continual pre-training before fine-tuning PTMs on the downstream tasks. However, no matter which schema is used, the previous work ignores to inform PTMs of some features of the downstream task, i.e. train their PTMs without providing any signals related to SR. To this end, in this work, we propose an Alternative Cross-lingual PTM for SR via code-switching. We are the first to utilize the code-switching approach for cross-lingual SR. Besides, we introduce the novel code-switched continual pre-training instead of directly using the PTMs on the SR tasks. The experimental results show that our proposed approach consistently outperforms the previous SOTA methods on SR and semantic textual similarity (STS) tasks with three business corpora and four open datasets in 20+ languages.
Budget-Constrained Tool Learning with Planning
Feb 25, 2024Abstract:Despite intensive efforts devoted to tool learning, the problem of budget-constrained tool learning, which focuses on resolving user queries within a specific budget constraint, has been widely overlooked. This paper proposes a novel method for budget-constrained tool learning. Our approach involves creating a preferable plan under the budget constraint before utilizing the tools. This plan outlines the feasible tools and the maximum number of times they can be employed, offering a comprehensive overview of the tool learning process for large language models. This allows them to allocate the budget from a broader perspective. To devise the plan without incurring significant extra costs, we suggest initially estimating the usefulness of the candidate tools based on past experience. Subsequently, we employ dynamic programming to formulate the plan. Experimental results demonstrate that our method can be integrated with various tool learning methods, significantly enhancing their effectiveness under strict budget constraints.
Black-box Prompt Tuning with Subspace Learning
May 04, 2023Abstract:Black-box prompt tuning uses derivative-free optimization algorithms to learn prompts in low-dimensional subspaces instead of back-propagating through the network of Large Language Models (LLMs). Recent studies have found that black-box prompt tuning lacks versatility across tasks and LLMs, which we believe is related to the inappropriate choice of subspaces. In this paper, we propose Black-box prompt tuning with Subspace Learning (BSL) to improve the versatility of black-box prompt tuning. Based on the assumption that nearly optimal prompts for similar tasks exist in a common subspace, we propose identifying such subspaces by meta-learning on a set of similar source tasks. Therefore, for a target task that shares similarities with source tasks, we guarantee that optimizing in the subspace can find a prompt that performs well on the target task. Experiments confirm that our BSL framework consistently achieves competitive performance regardless of downstream tasks and LLMs.
MHITNet: a minimize network with a hierarchical context-attentional filter for segmenting medical ct images
Nov 01, 2022



Abstract:In the field of medical CT image processing, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been the dominant technique.Encoder-decoder CNNs utilise locality for efficiency, but they cannot simulate distant pixel interactions properly.Recent research indicates that self-attention or transformer layers can be stacked to efficiently learn long-range dependencies.By constructing and processing picture patches as embeddings, transformers have been applied to computer vision applications. However, transformer-based architectures lack global semantic information interaction and require a large-scale training dataset, making it challenging to train with small data samples. In order to solve these challenges, we present a hierarchical contextattention transformer network (MHITNet) that combines the multi-scale, transformer, and hierarchical context extraction modules in skip-connections. The multi-scale module captures deeper CT semantic information, enabling transformers to encode feature maps of tokenized picture patches from various CNN stages as input attention sequences more effectively. The hierarchical context attention module augments global data and reweights pixels to capture semantic context.Extensive trials on three datasets show that the proposed MHITNet beats current best practises
MGIMN: Multi-Grained Interactive Matching Network for Few-shot Text Classification
Apr 18, 2022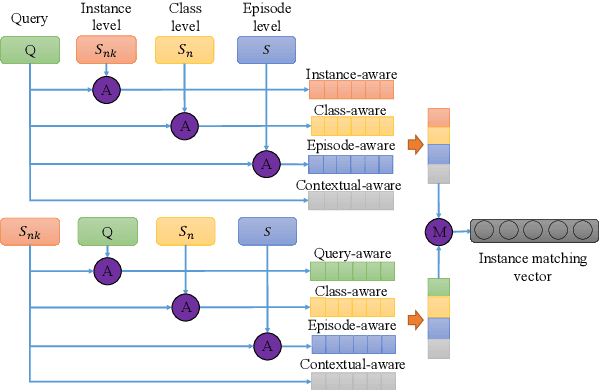
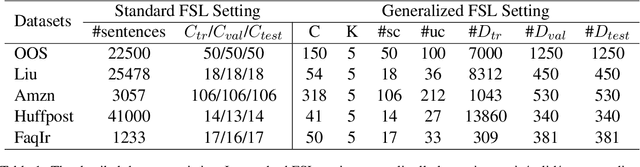
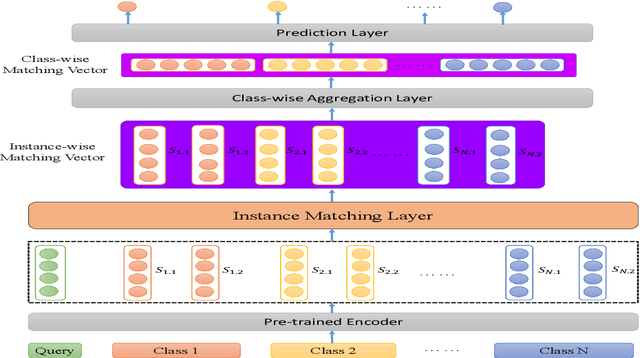
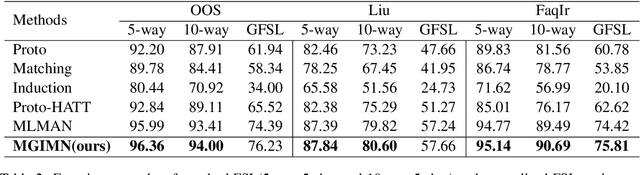
Abstract:Text classification struggles to generalize to unseen classes with very few labeled text instances per class. In such a few-shot learning (FSL) setting, metric-based meta-learning approaches have shown promising results. Previous studies mainly aim to derive a prototype representation for each class. However, they neglect that it is challenging-yet-unnecessary to construct a compact representation which expresses the entire meaning for each class. They also ignore the importance to capture the inter-dependency between query and the support set for few-shot text classification. To deal with these issues, we propose a meta-learning based method MGIMN which performs instance-wise comparison followed by aggregation to generate class-wise matching vectors instead of prototype learning. The key of instance-wise comparison is the interactive matching within the class-specific context and episode-specific context. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms the existing state-of-the-art approaches, under both the standard FSL and generalized FSL settings.
Auto-MLM: Improved Contrastive Learning for Self-supervised Multi-lingual Knowledge Retrieval
Mar 30, 2022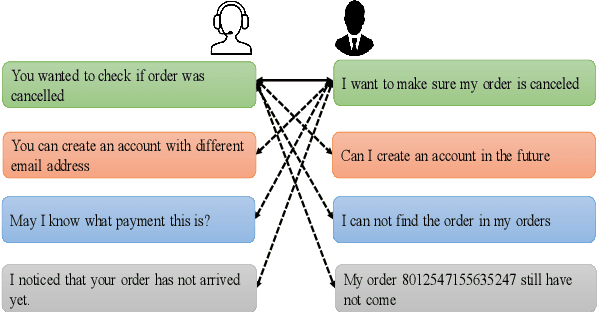
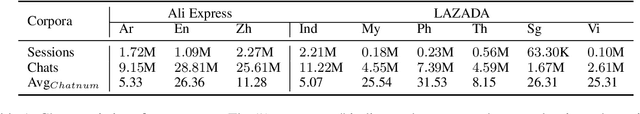
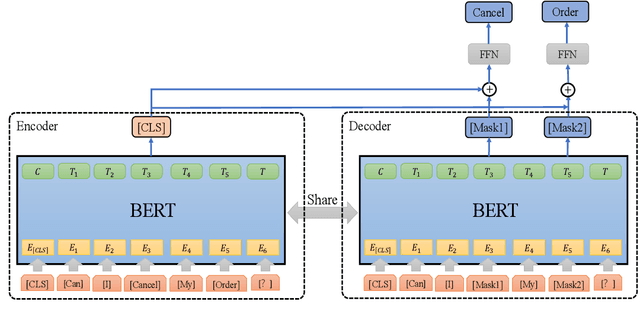
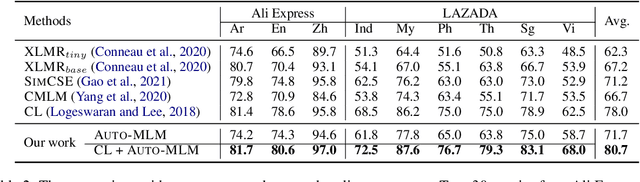
Abstract:Contrastive learning (CL) has become a ubiquitous approach for several natural language processing (NLP) downstream tasks, especially for question answering (QA). However, the major challenge, how to efficiently train the knowledge retrieval model in an unsupervised manner, is still unresolved. Recently the commonly used methods are composed of CL and masked language model (MLM). Unexpectedly, MLM ignores the sentence-level training, and CL also neglects extraction of the internal info from the query. To optimize the CL hardly obtain internal information from the original query, we introduce a joint training method by combining CL and Auto-MLM for self-supervised multi-lingual knowledge retrieval. First, we acquire the fixed dimensional sentence vector. Then, mask some words among the original sentences with random strategy. Finally, we generate a new token representation for predicting the masked tokens. Experimental results show that our proposed approach consistently outperforms all the previous SOTA methods on both AliExpress $\&$ LAZADA service corpus and openly available corpora in 8 languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge