Wenpei Luo
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
Improving Cross-lingual Representation for Semantic Retrieval with Code-switching
Mar 03, 2024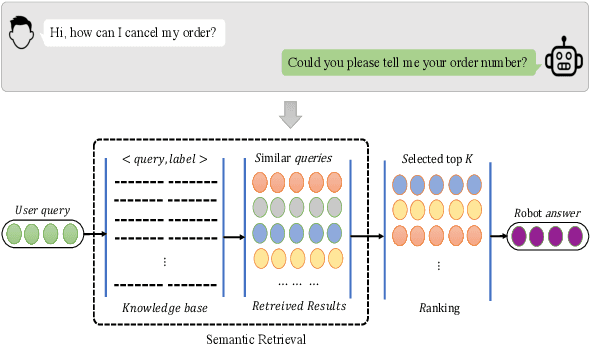



Abstract:Semantic Retrieval (SR) has become an indispensable part of the FAQ system in the task-oriented question-answering (QA) dialogue scenario. The demands for a cross-lingual smart-customer-service system for an e-commerce platform or some particular business conditions have been increasing recently. Most previous studies exploit cross-lingual pre-trained models (PTMs) for multi-lingual knowledge retrieval directly, while some others also leverage the continual pre-training before fine-tuning PTMs on the downstream tasks. However, no matter which schema is used, the previous work ignores to inform PTMs of some features of the downstream task, i.e. train their PTMs without providing any signals related to SR. To this end, in this work, we propose an Alternative Cross-lingual PTM for SR via code-switching. We are the first to utilize the code-switching approach for cross-lingual SR. Besides, we introduce the novel code-switched continual pre-training instead of directly using the PTMs on the SR tasks. The experimental results show that our proposed approach consistently outperforms the previous SOTA methods on SR and semantic textual similarity (STS) tasks with three business corpora and four open datasets in 20+ languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge