Jianhai Zhang
Robust Diffusion Models for Adversarial Purification
Mar 24, 2024Abstract:Diffusion models (DMs) based adversarial purification (AP) has shown to be the most powerful alternative to adversarial training (AT). However, these methods neglect the fact that pre-trained diffusion models themselves are not robust to adversarial attacks as well. Additionally, the diffusion process can easily destroy semantic information and generate a high quality image but totally different from the original input image after the reverse process, leading to degraded standard accuracy. To overcome these issues, a natural idea is to harness adversarial training strategy to retrain or fine-tune the pre-trained diffusion model, which is computationally prohibitive. We propose a novel robust reverse process with adversarial guidance, which is independent of given pre-trained DMs and avoids retraining or fine-tuning the DMs. This robust guidance can not only ensure to generate purified examples retaining more semantic content but also mitigate the accuracy-robustness trade-off of DMs for the first time, which also provides DM-based AP an efficient adaptive ability to new attacks. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate that our method achieves the state-of-the-art results and exhibits generalization against different attacks.
Adversarial Training on Purification (AToP): Advancing Both Robustness and Generalization
Jan 29, 2024

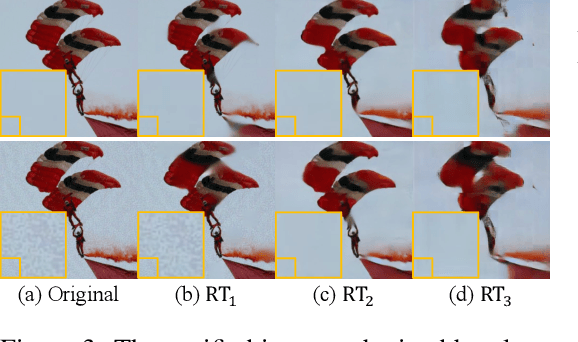

Abstract:The deep neural networks are known to be vulnerable to well-designed adversarial attacks. The most successful defense technique based on adversarial training (AT) can achieve optimal robustness against particular attacks but cannot generalize well to unseen attacks. Another effective defense technique based on adversarial purification (AP) can enhance generalization but cannot achieve optimal robustness. Meanwhile, both methods share one common limitation on the degraded standard accuracy. To mitigate these issues, we propose a novel framework called Adversarial Training on Purification (AToP), which comprises two components: perturbation destruction by random transforms (RT) and purifier model fine-tuned (FT) by adversarial loss. RT is essential to avoid overlearning to known attacks resulting in the robustness generalization to unseen attacks and FT is essential for the improvement of robustness. To evaluate our method in an efficient and scalable way, we conduct extensive experiments on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and ImageNette to demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art results and exhibits generalization ability against unseen attacks.
Multi-Subdomain Adversarial Network for Cross-Subject EEG-based Emotion Recognition
Aug 27, 2023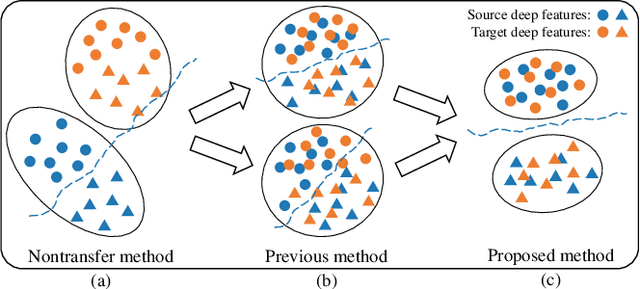
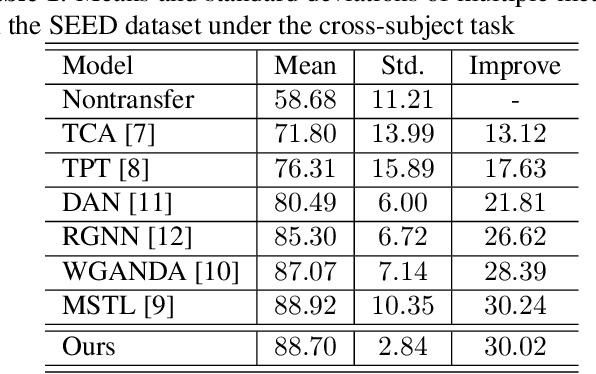
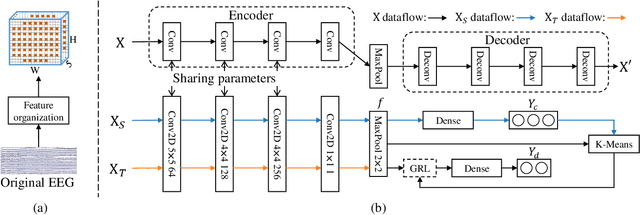
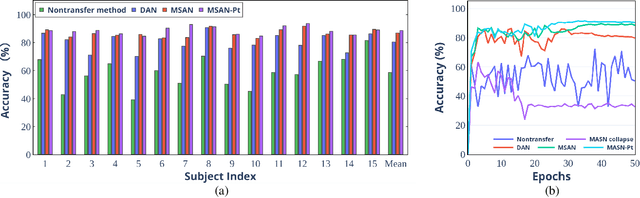
Abstract:The individual difference between subjects is significant in EEG-based emotion recognition, resulting in the difficulty of sharing the model across subjects. Previous studies use domain adaptation algorithms to minimize the global domain discrepancy while ignoring the class information, which may cause misalignment of subdomains and reduce model performance. This paper proposes a multi-subdomain adversarial network (MSAN) for cross-subject EEG-based emotion recognition. MSAN uses adversarial training to model the discrepancy in the global domain and subdomain to reduce the intra-class distance and enlarge the inter-class distance. In addition, MSAN initializes parameters through a pre-trained autoencoder to ensure the stability and convertibility of the model. The experimental results show that the accuracy of MSAN is improved by 30.02\% on the SEED dataset comparing with the nontransfer method.
Synchronous Image-Label Diffusion Probability Model with Application to Stroke Lesion Segmentation on Non-contrast CT
Jul 18, 2023Abstract:Stroke lesion volume is a key radiologic measurement for assessing the prognosis of Acute Ischemic Stroke (AIS) patients, which is challenging to be automatically measured on Non-Contrast CT (NCCT) scans. Recent diffusion probabilistic models have shown potentials of being used for image segmentation. In this paper, a novel Synchronous image-label Diffusion Probability Model (SDPM) is proposed for stroke lesion segmentation on NCCT using Markov diffusion process. The proposed SDPM is fully based on a Latent Variable Model (LVM), offering a complete probabilistic elaboration. An additional net-stream, parallel with a noise prediction stream, is introduced to obtain initial noisy label estimates for efficiently inferring the final labels. By optimizing the specified variational boundaries, the trained model can infer multiple label estimates for reference given the input images with noises. The proposed model was assessed on three stroke lesion datasets including one public and two private datasets. Compared to several U-net and transformer-based segmentation methods, our proposed SDPM model is able to achieve state-of-the-art performance. The code is publicly available.
ChatPLUG: Open-Domain Generative Dialogue System with Internet-Augmented Instruction Tuning for Digital Human
Apr 28, 2023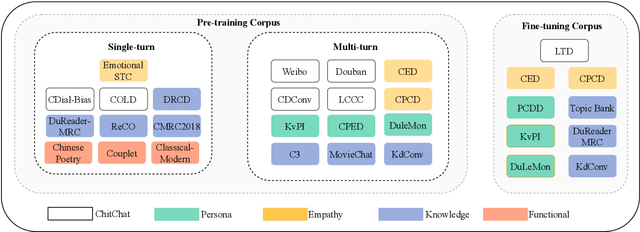

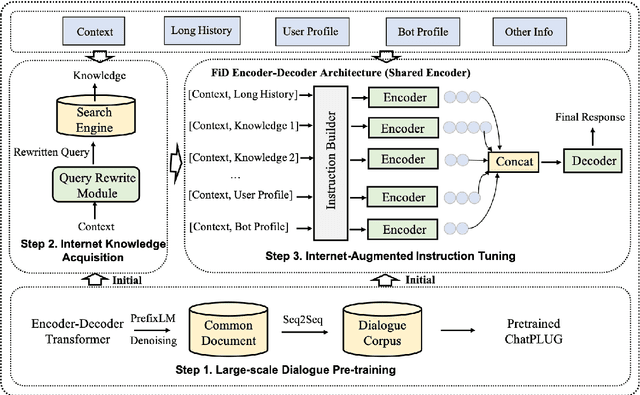
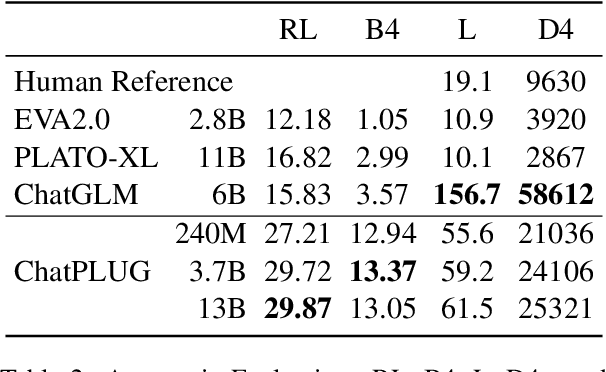
Abstract:In this paper, we present ChatPLUG, a Chinese open-domain dialogue system for digital human applications that instruction finetunes on a wide range of dialogue tasks in a unified internet-augmented format. Different from other open-domain dialogue models that focus on large-scale pre-training and scaling up model size or dialogue corpus, we aim to build a powerful and practical dialogue system for digital human with diverse skills and good multi-task generalization by internet-augmented instruction tuning. To this end, we first conduct large-scale pre-training on both common document corpus and dialogue data with curriculum learning, so as to inject various world knowledge and dialogue abilities into ChatPLUG. Then, we collect a wide range of dialogue tasks spanning diverse features of knowledge, personality, multi-turn memory, and empathy, on which we further instruction tune \modelname via unified natural language instruction templates. External knowledge from an internet search is also used during instruction finetuning for alleviating the problem of knowledge hallucinations. We show that \modelname outperforms state-of-the-art Chinese dialogue systems on both automatic and human evaluation, and demonstrates strong multi-task generalization on a variety of text understanding and generation tasks. In addition, we deploy \modelname to real-world applications such as Smart Speaker and Instant Message applications with fast inference. Our models and code will be made publicly available on ModelScope~\footnote{\small{https://modelscope.cn/models/damo/ChatPLUG-3.7B}} and Github~\footnote{\small{https://github.com/X-PLUG/ChatPLUG}}.
MGIMN: Multi-Grained Interactive Matching Network for Few-shot Text Classification
Apr 18, 2022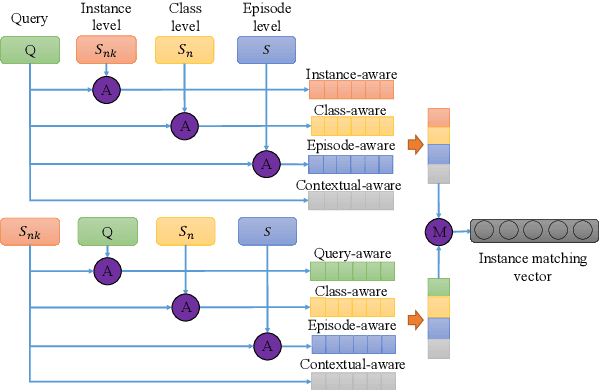
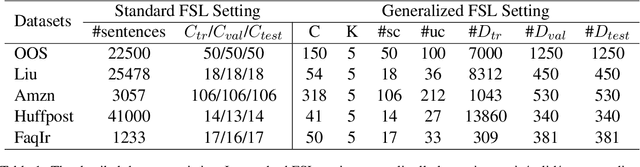
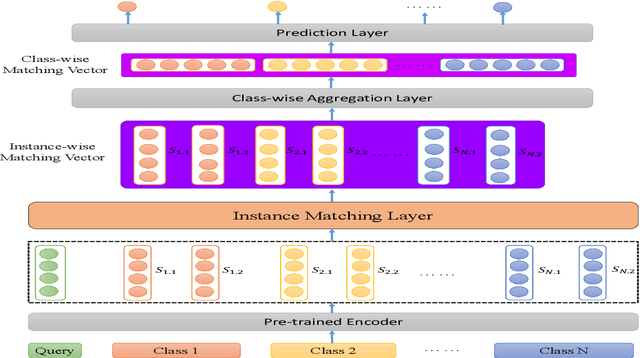
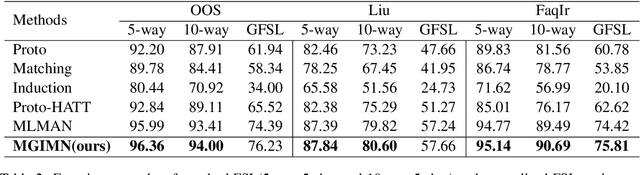
Abstract:Text classification struggles to generalize to unseen classes with very few labeled text instances per class. In such a few-shot learning (FSL) setting, metric-based meta-learning approaches have shown promising results. Previous studies mainly aim to derive a prototype representation for each class. However, they neglect that it is challenging-yet-unnecessary to construct a compact representation which expresses the entire meaning for each class. They also ignore the importance to capture the inter-dependency between query and the support set for few-shot text classification. To deal with these issues, we propose a meta-learning based method MGIMN which performs instance-wise comparison followed by aggregation to generate class-wise matching vectors instead of prototype learning. The key of instance-wise comparison is the interactive matching within the class-specific context and episode-specific context. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms the existing state-of-the-art approaches, under both the standard FSL and generalized FSL settings.
Single Shot Reversible GAN for BCG artifact removal in simultaneous EEG-fMRI
Nov 04, 2020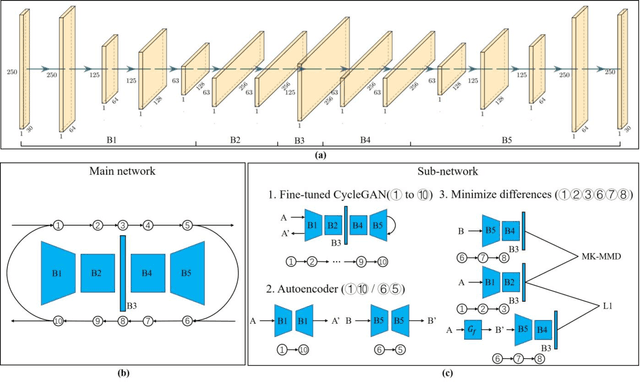
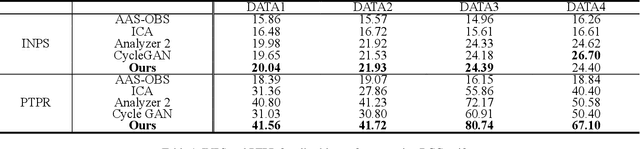


Abstract:Simultaneous EEG-fMRI acquisition and analysis technology has been widely used in various research fields of brain science. However, how to remove the ballistocardiogram (BCG) artifacts in this scenario remains a huge challenge. Because it is impossible to obtain clean and BCG-contaminated EEG signals at the same time, BCG artifact removal is a typical unpaired signal-to-signal problem. To solve this problem, this paper proposed a new GAN training model - Single Shot Reversible GAN (SSRGAN). The model is allowing bidirectional input to better combine the characteristics of the two types of signals, instead of using two independent models for bidirectional conversion as in the past. Furthermore, the model is decomposed into multiple independent convolutional blocks with specific functions. Through additional training of the blocks, the local representation ability of the model is improved, thereby improving the overall model performance. Experimental results show that, compared with existing methods, the method proposed in this paper can remove BCG artifacts more effectively and retain the useful EEG information.
Simple and Effective Text Matching with Richer Alignment Features
Aug 01, 2019
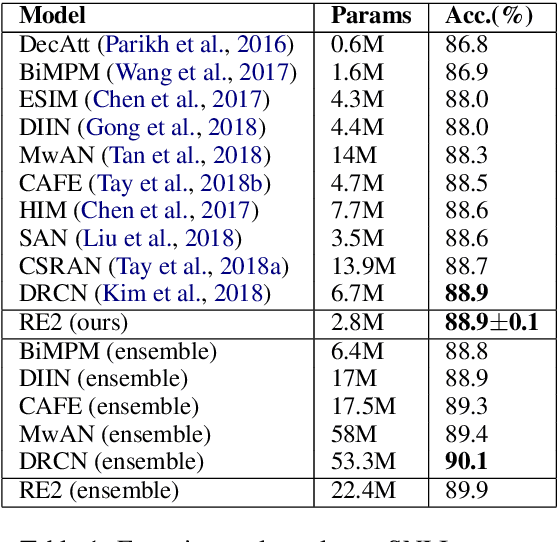
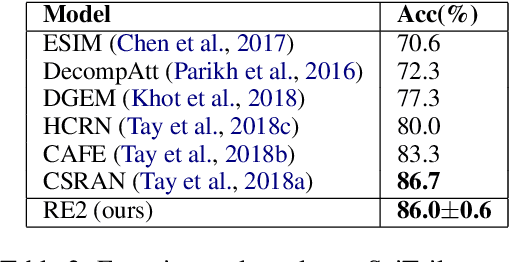

Abstract:In this paper, we present a fast and strong neural approach for general purpose text matching applications. We explore what is sufficient to build a fast and well-performed text matching model and propose to keep three key features available for inter-sequence alignment: original point-wise features, previous aligned features, and contextual features while simplifying all the remaining components. We conduct experiments on four well-studied benchmark datasets across tasks of natural language inference, paraphrase identification and answer selection. The performance of our model is on par with the state-of-the-art on all datasets with much fewer parameters and the inference speed is at least 6 times faster compared with similarly performed ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge