Zonggang Yuan
NeuralKG: An Open Source Library for Diverse Representation Learning of Knowledge Graphs
Feb 25, 2022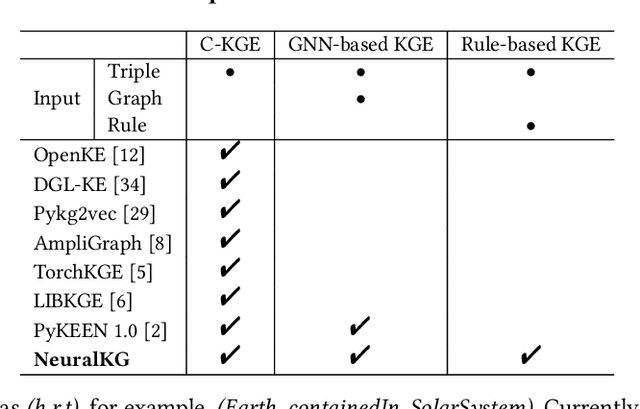
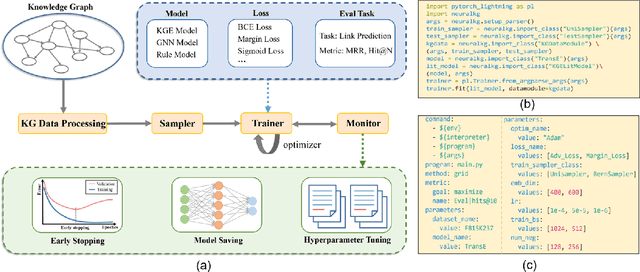
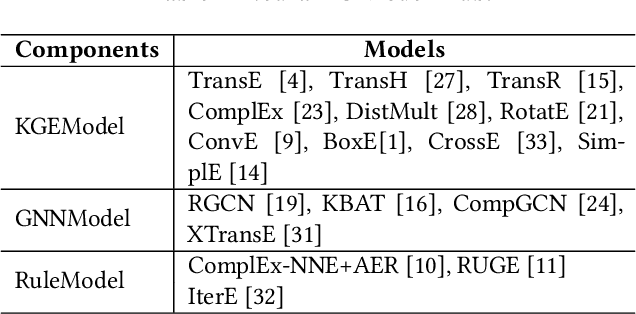
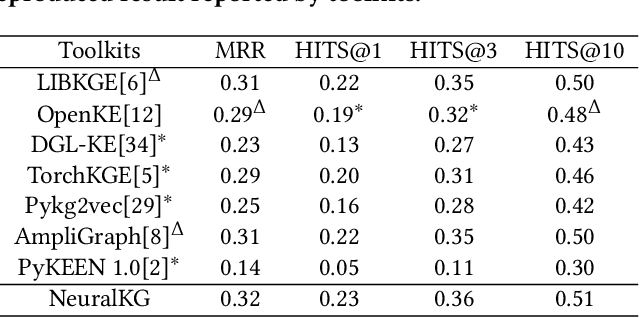
Abstract:NeuralKG is an open-source Python-based library for diverse representation learning of knowledge graphs. It implements three different series of Knowledge Graph Embedding (KGE) methods, including conventional KGEs, GNN-based KGEs, and Rule-based KGEs. With a unified framework, NeuralKG successfully reproduces link prediction results of these methods on benchmarks, freeing users from the laborious task of reimplementing them, especially for some methods originally written in non-python programming languages. Besides, NeuralKG is highly configurable and extensible. It provides various decoupled modules that can be mixed and adapted to each other. Thus with NeuralKG, developers and researchers can quickly implement their own designed models and obtain the optimal training methods to achieve the best performance efficiently. We built an website in http://neuralkg.zjukg.cn to organize an open and shared KG representation learning community. The source code is all publicly released at https://github.com/zjukg/NeuralKG.
Standing on the Shoulders of Predecessors: Meta-Knowledge Transfer for Knowledge Graphs
Oct 27, 2021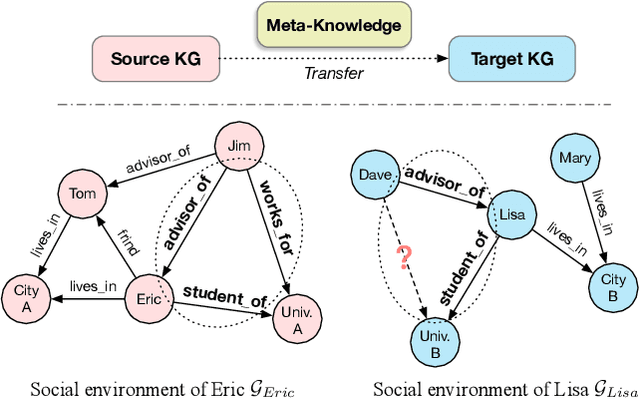
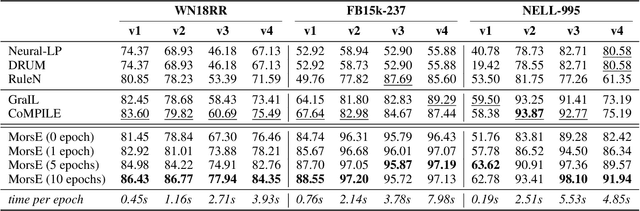
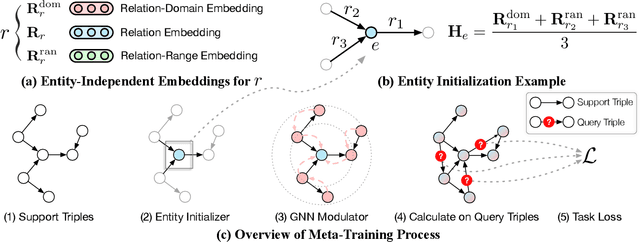
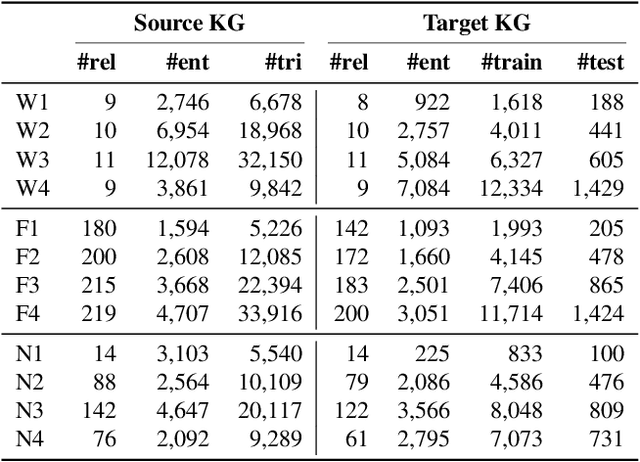
Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) have become widespread, and various knowledge graphs are constructed incessantly to support many in-KG and out-of-KG applications. During the construction of KGs, although new KGs may contain new entities with respect to constructed KGs, some entity-independent knowledge can be transferred from constructed KGs to new KGs. We call such knowledge meta-knowledge, and refer to the problem of transferring meta-knowledge from constructed (source) KGs to new (target) KGs to improve the performance of tasks on target KGs as meta-knowledge transfer for knowledge graphs. However, there is no available general framework that can tackle meta-knowledge transfer for both in-KG and out-of-KG tasks uniformly. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a framework, MorsE, which means conducting Meta-Learning for Meta-Knowledge Transfer via Knowledge Graph Embedding. MorsE represents the meta-knowledge via Knowledge Graph Embedding and learns the meta-knowledge by Meta-Learning. Specifically, MorsE uses an entity initializer and a Graph Neural Network (GNN) modulator to entity-independently obtain entity embeddings given a KG and is trained following the meta-learning setting to gain the ability of effectively obtaining embeddings. Experimental results on meta-knowledge transfer for both in-KG and out-of-KG tasks show that MorsE is able to learn and transfer meta-knowledge between KGs effectively, and outperforms existing state-of-the-art models.
Zero-shot Visual Question Answering using Knowledge Graph
Jul 14, 2021
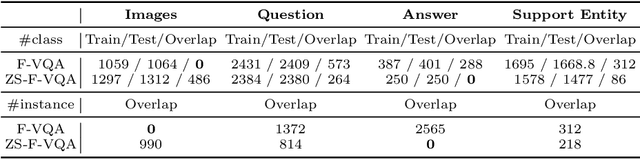

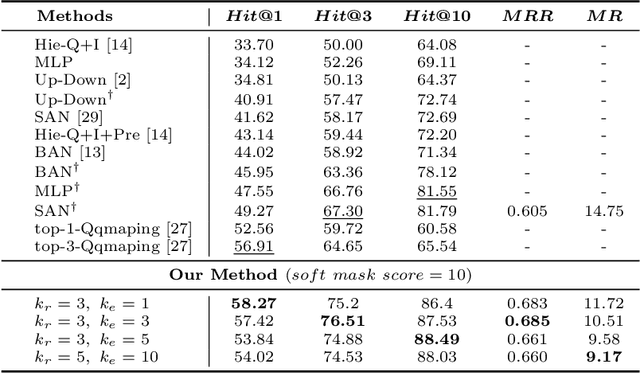
Abstract:Incorporating external knowledge to Visual Question Answering (VQA) has become a vital practical need. Existing methods mostly adopt pipeline approaches with different components for knowledge matching and extraction, feature learning, etc.However, such pipeline approaches suffer when some component does not perform well, which leads to error propagation and poor overall performance. Furthermore, the majority of existing approaches ignore the answer bias issue -- many answers may have never appeared during training (i.e., unseen answers) in real-word application. To bridge these gaps, in this paper, we propose a Zero-shot VQA algorithm using knowledge graphs and a mask-based learning mechanism for better incorporating external knowledge, and present new answer-based Zero-shot VQA splits for the F-VQA dataset. Experiments show that our method can achieve state-of-the-art performance in Zero-shot VQA with unseen answers, meanwhile dramatically augment existing end-to-end models on the normal F-VQA task.
K-ZSL: Resources for Knowledge-driven Zero-shot Learning
Jun 29, 2021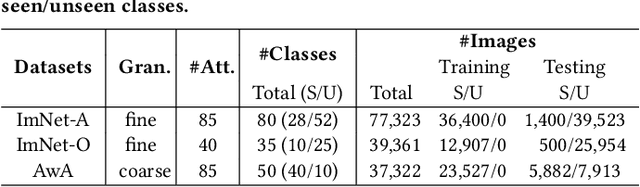
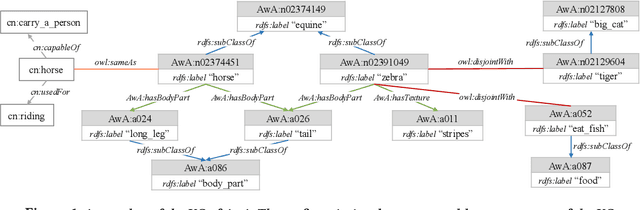
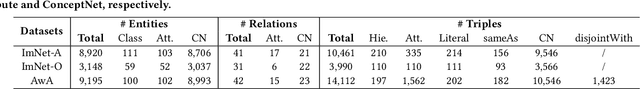
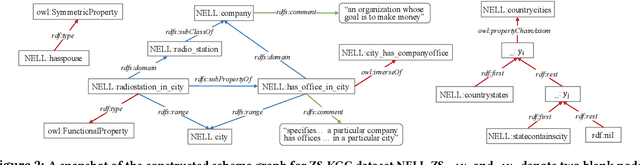
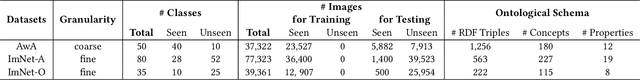
Abstract:External knowledge (a.k.a side information) plays a critical role in zero-shot learning (ZSL) which aims to predict with unseen classes that have never appeared in training data. Several kinds of external knowledge such as text and attribute have been widely investigated, but they alone are limited with incomplete semantics. Therefore, some very recent studies propose to use Knowledge Graph (KG) due to its high expressivity and compatibility for representing kinds of knowledge. However, the ZSL community is still short of standard benchmarks for studying and comparing different KG-based ZSL methods. In this paper, we proposed 5 resources for KG-based research in zero-shot image classification (ZS-IMGC) and zero-shot KG completion (ZS-KGC). For each resource, we contributed a benchmark and its KG with semantics ranging from text to attributes, from relational knowledge to logical expressions. We have clearly presented how the resources are constructed, their statistics and formats, and how they can be utilized with cases in evaluating ZSL methods' performance and explanations. Our resources are available at https://github.com/China-UK-ZSL/Resources_for_KZSL.
OntoZSL: Ontology-enhanced Zero-shot Learning
Feb 15, 2021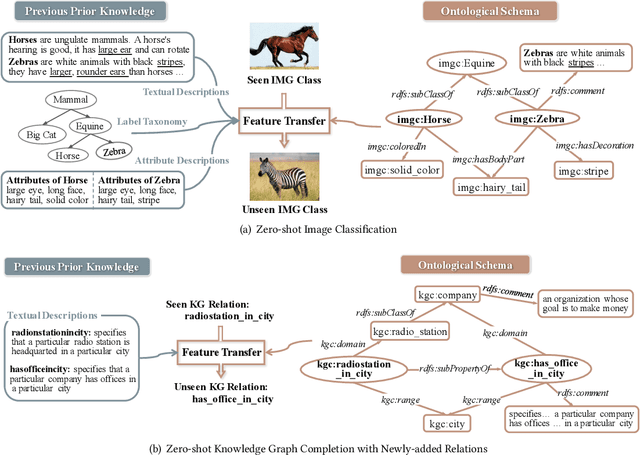
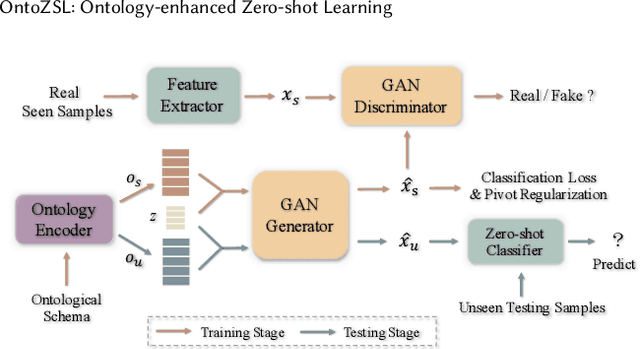
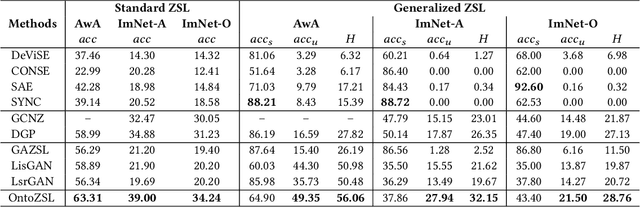
Abstract:Zero-shot Learning (ZSL), which aims to predict for those classes that have never appeared in the training data, has arisen hot research interests. The key of implementing ZSL is to leverage the prior knowledge of classes which builds the semantic relationship between classes and enables the transfer of the learned models (e.g., features) from training classes (i.e., seen classes) to unseen classes. However, the priors adopted by the existing methods are relatively limited with incomplete semantics. In this paper, we explore richer and more competitive prior knowledge to model the inter-class relationship for ZSL via ontology-based knowledge representation and semantic embedding. Meanwhile, to address the data imbalance between seen classes and unseen classes, we developed a generative ZSL framework with Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). Our main findings include: (i) an ontology-enhanced ZSL framework that can be applied to different domains, such as image classification (IMGC) and knowledge graph completion (KGC); (ii) a comprehensive evaluation with multiple zero-shot datasets from different domains, where our method often achieves better performance than the state-of-the-art models. In particular, on four representative ZSL baselines of IMGC, the ontology-based class semantics outperform the previous priors e.g., the word embeddings of classes by an average of 12.4 accuracy points in the standard ZSL across two example datasets (see Figure 4).
FedE: Embedding Knowledge Graphs in Federated Setting
Oct 24, 2020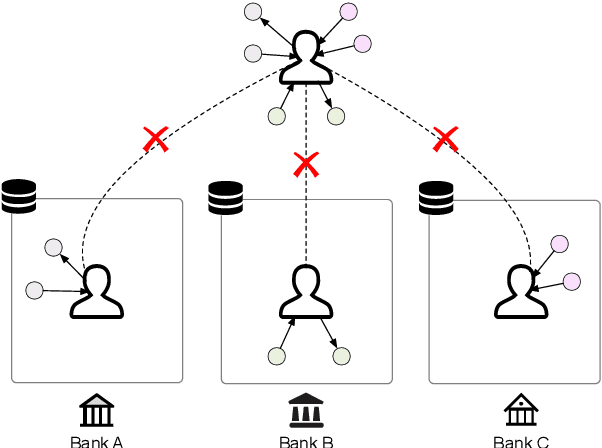


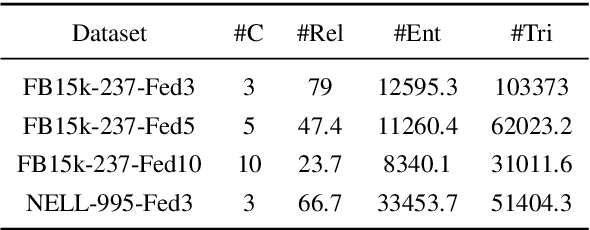
Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) consisting of triples are always incomplete, so it's important to do Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC) by predicting missing triples. Multi-Source KG is a common situation in real KG applications which can be viewed as a set of related individual KGs where different KGs contains relations of different aspects of entities. It's intuitive that, for each individual KG, its completion could be greatly contributed by the triples defined and labeled in other ones. However, because of the data privacy and sensitivity, a set of relevant knowledge graphs cannot complement each other's KGC by just collecting data from different knowledge graphs together. Therefore, in this paper, we introduce federated setting to keep their privacy without triple transferring between KGs and apply it in embedding knowledge graph, a typical method which have proven effective for KGC in the past decade. We propose a Federated Knowledge Graph Embedding framework FedE, focusing on learning knowledge graph embeddings by aggregating locally-computed updates. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on datasets derived from KGE benchmark datasets and results show the effectiveness of our proposed FedE.
The Devil is the Classifier: Investigating Long Tail Relation Classification with Decoupling Analysis
Sep 15, 2020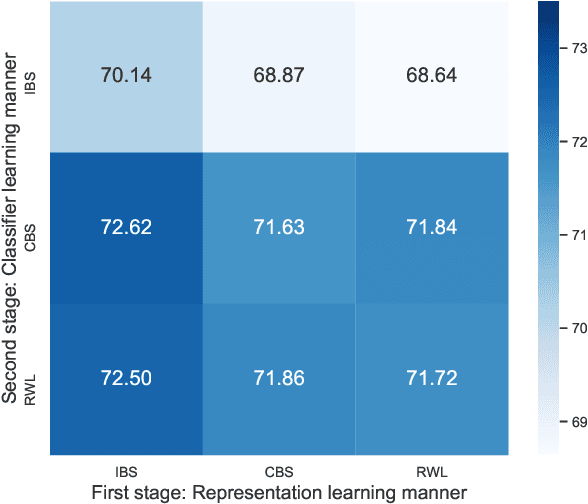
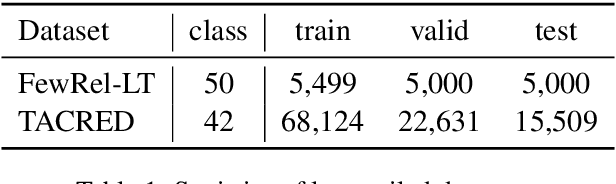
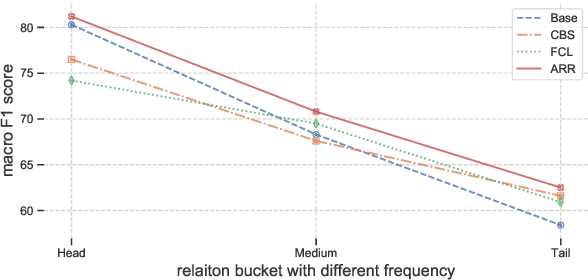
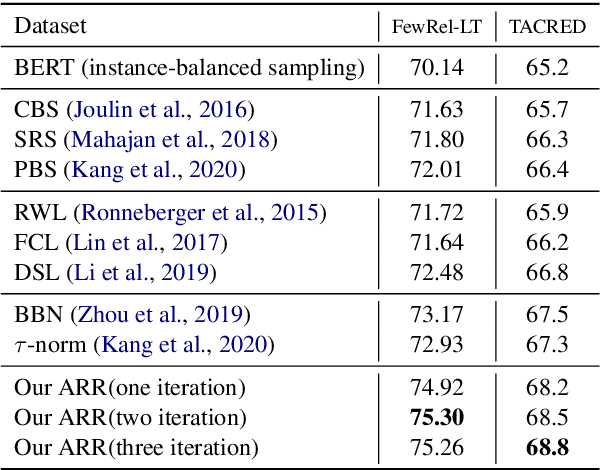
Abstract:Long-tailed relation classification is a challenging problem as the head classes may dominate the training phase, thereby leading to the deterioration of the tail performance. Existing solutions usually address this issue via class-balancing strategies, e.g., data re-sampling and loss re-weighting, but all these methods adhere to the schema of entangling learning of the representation and classifier. In this study, we conduct an in-depth empirical investigation into the long-tailed problem and found that pre-trained models with instance-balanced sampling already capture the well-learned representations for all classes; moreover, it is possible to achieve better long-tailed classification ability at low cost by only adjusting the classifier. Inspired by this observation, we propose a robust classifier with attentive relation routing, which assigns soft weights by automatically aggregating the relations. Extensive experiments on two datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach. Code and datasets are available in https://github.com/zjunlp/deepke.
Generative Adversarial Zero-shot Learning via Knowledge Graphs
Apr 07, 2020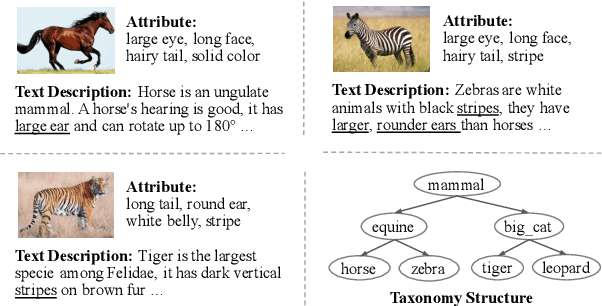
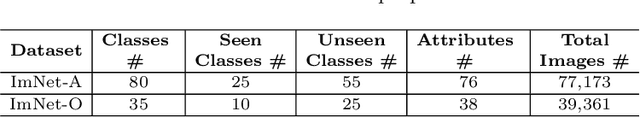
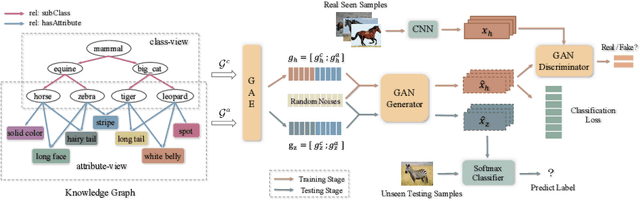
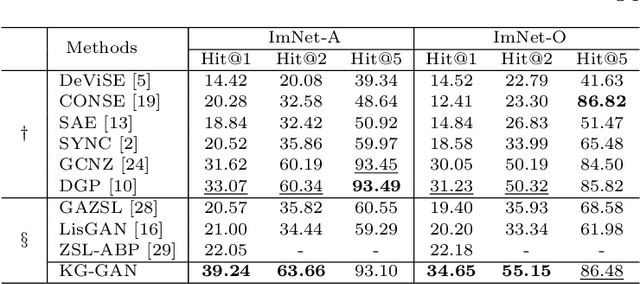
Abstract:Zero-shot learning (ZSL) is to handle the prediction of those unseen classes that have no labeled training data. Recently, generative methods like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are being widely investigated for ZSL due to their high accuracy, generalization capability and so on. However, the side information of classes used now is limited to text descriptions and attribute annotations, which are in short of semantics of the classes. In this paper, we introduce a new generative ZSL method named KG-GAN by incorporating rich semantics in a knowledge graph (KG) into GANs. Specifically, we build upon Graph Neural Networks and encode KG from two views: class view and attribute view considering the different semantics of KG. With well-learned semantic embeddings for each node (representing a visual category), we leverage GANs to synthesize compelling visual features for unseen classes. According to our evaluation with multiple image classification datasets, KG-GAN can achieve better performance than the state-of-the-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge